Abstract
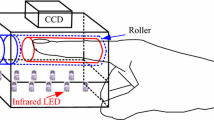
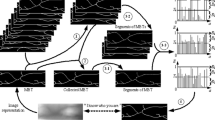
Recently, an emerging biometric recognition based on human finger-vein patterns has received considerable attention. Due to light attenuation in imaging finger tissues, the finger-vein imagery is often seriously degraded. This makes network-based finger-vein feature representation greatly difficult in practice. In order to obtain perfect finger-vein networks, in this paper, we propose a novel scheme for venous region enhancement and finger-vein network segmentation. First, a method aimed at scattering removal, directional filtering and false vein information suppression is put forward to effectively enhance finger-vein images. Then, to achieve the high-fidelity extraction of finger-vein networks in an automated manner, a matting-based segmentation approach is presented considering the variations of veins in intensity and diameter. Extensive experiments are finally conducted to validate the proposed method.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uhl J-F, Gillot C (2007) Embryology and three-dimensional anatomy of the superficial venous system of the lower limbs. Phlebology 22(5):194–206
Zharov V, Ferguson S, Eidt J, Howard P, Fink L, Waner M (2004) Infrared imaging of subcutaneous veins. Lasers Surg Med 34(1):56–61
Guidolin D, Nico B, Mazzocchi G, Vacca A, Nussdorfer GG, Ribatti D (2004) Order and disorder in the vascular network. Leukemia 18:1745–1750
Nguyen T, Unbekandt M, Fleury U (2007) The textural aspects of vessel formation during embryo development and their relation to gastrulation movements. Organogenesis 3(1):49–56
Chang JB (2002) Textbook of angiology. Springer-Verlag Hong Kong Ltd., ISBN 0-3879-8449-6
Truc P, Khan MA, Lee Y, Lee S, Kim T (2009) Vessel enhancement filter using directional filter bank. Comput Vis Image Underst 113(1):101–112
Yang JF, Shi YH, Yang JL (2009a) Finger-vein recognition based on a bank of Gabor filters. In: Proceedings of ACCV, pp 374–383
Yang JF, Yang JL, Shi YH (2009b) Finger-vein segmentation based on multi-channel even-symmetric gabor filters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on intelligent computing and intelligent systems, pp 500–503
Yang JF, Yang JL, Shi YH (2009c) Combination of gabor wavelets and circular gabor filter for finger-vein extraction. In: Proceedings of 5th international conference on intelligent computing, pp 346–354
Lee E, Park K (2009) Restoration method of skin scattering blurred vein image for finger vein recognition. Electron Lett 45(21):1074–1076
Cheng R, Huang B, Wang Y, Zeng H, Xie S (2005) The optical model of human skin. Acta Laser Biol Sin 14:401–404
Xu J, Wei H, Li X, Wu G, Li D (2002) Optical characteristics of human veins tissue in kubelka-munk model at he-ne laser in vitro. J Optoelectron Laser 13(3):401–404
Miura N, Nagasaka A, Miyatake T (2004) Feature extraction of finger-vein patterns based on repeated line tracking and its application to personal identification. Mach Vis Appl 15(4):194–203
Tang D, Huang B, Li R, Li W (2010) A person retrieval solution using finger vein patterns. In: Proceedings of international conference on pattern recognition, pp 1306–1309
Hwan CJ, Wonseok S, Taejeong K, Rae LS, Chan KH (2009) Finger vein extraction using gradient normalization and principal curvature. SPIE 7251:1–9
Da WJ, Huan YS (2009) Driver identification using finger-vein patterns with radon transform and neural network. Expert Syst Appl 36:5793–5799
Zhang Z, Wu D, Ma S, Ma J (2005) Multiscale feature extraction of finger-vein patterns based on wavelet and local interconnection structure neural network. Neural Netw Brain 1:1081–1084
Yang JF, Li X (2010) Efficient finger vein localization and recognition. In: Proceedings of international conference on pattern recognition, pp 1148–1151
Dhawan AP, D’Alessandro B, Fu X (2010) Optical imaging modalities for biomedical applications. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 3:69–92
Delpy DT, Cope M (1997) Quantification in tissue near-infrared spectroscopy. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 352:649–659
Bashkatov AN, Genina EA, Kochubey VI, Tuchin VV (2005) Optical properties of human skin, subcutaneous and mucous tissues in the wavelength rang from 400 to 2000 nm. J Phys D Appl Phys 38(2005):2543–2555
Sassaroli A et al Near-infrared spectroscopy for the study of biological tissue. http://ase.tufts.edu/biomedical/research/fantini/researchAreas/NearInfraredSpectroscopy.pdf
Jean-Philippe T, Nicolas H (2009) Fast visibility restoration from a single color or gray level image. In: Proceedings of ICCV, pp 2201–2208
Narasimhan SG, Nayar SK (2003) Contrast restoration of weather degraded images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(6):713–724
Hautière N, Tarel J-P, Lavenant J, Aubert D (2006) Automatic fog detection and estimation of visibility distance through use of an onboard camera. Mach Vis Appl 17(1):8–20
Daugman JG (1985) Uncertainty relation for resolution in space, spatial frequency, and orientation optimized by 2D visual cortical filters. J Opt Soc Am 2(7):1160–1169
Lee TS (1996) Image representation using 2D Gabor wavelets. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 18(10):959–971
Yang J, Liu L, Jiang T, Fan Y (2003) A modified Gabor filter design method for fingerprint image enhancement. Pattern Recognit Lett 24(12):1805–1817
Zhu Z, Lu H, Zhao Y (2007) Scale multiplication in odd Gabor transform domain for edge detection. J Vis Commun Image Represent 18(1):68–80
Levin A, Lischinski D, Weiss Y (2008) A closed-form solution to natural image matting. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(2):228–242
Levin A, Rav-Acha A, Lischinski D (2008) Spectral matting.IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(10):1–14
Haralick RM, Shapiro LG (2002) Computer and robot vision, vol I. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., Boston, MA
Farid S, Ahmed F (2009) Application of Niblack’s method on images. In: Proceedings of international conference on emerging technologies, pp 280–286
Yu CH, Qing HF, Zhang L (2008) A research on extracting low quality human finger vein pattern characteristics. In: Proceedings of international conference on bioinformatics and biomedical engineering, pp 1876–1879
Kamarainen JK, Kälviäinen H (2006) Invariance properties of Gabor filter-based features-overview and applications. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(5):1088–1099
Movellan RJ (2005) Tutorial on Gabor filters. Technical Report. MPLab Tutorials, Univ. of California, San Diego
Acknowledgments
This research work is jointly supported by NSFC (Grant No. 61073143), TJNSF (Grant No. 07ZCKFGX03700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Let ∆ω denote the frequency bandwidth in octaves, \(\triangle\varphi\) denote the half-magnitude orientation bandwidth, a m and b m respectively represent the short axis and the long axis of a half-magnitude profile of Gabor frequency response in mth scale, as shown in Fig. 18, the following relationships should be determined [27, 35, 36] to make half-magnitude profiles mutually tangent in the spatial frequency domain.
where
Implementing Fourier transformation for G e mk (x, y), the parameter a m can be derived as
Refer to Eq. (16), we can obtain
Based on Eqs. (17, 18), and Fig. 18, we can reduce
Let N be the number of contours with minimum redundancy in a certain scale, \(\triangle\varphi=\pi/N\) is satisfying. Based on Eq. (19), the aspect ratio γ of the elliptical Gaussian envelope is approximately determined by
Therefore, given four parameters ▵ω, σ 1 (the biggest scale), M and N, a bank of even-symmetric Gabor filters with minimum redundancy can be designed accordingly.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Shi, Y. Finger-vein network enhancement and segmentation. Pattern Anal Applic 17, 783–797 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-013-0325-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-013-0325-y