Abstract
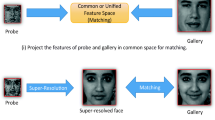
Edges and related features play significant role in discriminating face images. But those features are not enough informative when the face images are captured from a distance (e.g., video surveillance). Traditionally, those features are enhanced by super-resolving low-resolution grayscale face images. In this paper, we demonstrate a superior performance by directly considering such features (continuous gradient value, also known as edginess) in the super-resolution process. Edginess features are extracted using 1-D processing of image. This process is carried out along different directions to obtain partial evidences, which are combined to detect the person’s identity. Here, super-resolution of the face image and its recognition has been performed in sparse domain framework. The explicit usage of edginess feature in the proposed approach shows considerable improvement in both recognition performance as well as computational time, as only the patches related to strong edges are considered for super-resolution. In addition to that, the edginess feature gives improved recognition rate when it is preserved implicitly during super-resolution in grayscale domain.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here, feature means edginess feature for edginess domain and grayscale values for grayscale domain.
Here, we have considered all the angles with respect to x-axis in clockwise direction.
Here, \(\bf {x}\) is representation of face image and it could be gray-level values or partial edge evidences.
The edginess values are normalized to the range 0–255.
Computational time is measured under same system condition for both types of SR.
References
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A (2006) K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(11):4311–4322. doi:10.1109/TSP.2006.881199
Ahonen T, Hadid A, Pietikainen M (2006) Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(12):2037–2041. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2006.244
Belhumeur P, Hespanha J, Kriegman D (1997) Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(7):711–720. doi:10.1109/34.598228
Biswas S, Aggarwal G, Flynn P, Bowyer K (2013) Pose-robust recognition of low-resolution face images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(12):3037–3049. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2013.68
Biswas S, Bowyer KW, Flynn PJ (2012) Multidimensional scaling for matching low-resolution face images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(10):2019–2030. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2011.278
Black JA Jr, Gargesha M, Kahol K, Kuchi P, Panchanathan S (2002) A framework for performance evaluation of face recognition algorithms. In: ITCOM, internet multimedia systems II,pp 163–174. doi:10.1117/12.473032
Chen SS, Donoho DL, Saunders MA (2001) Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Rev 43(1):129–159. doi:10.1137/S003614450037906X
Daubechies I, Defrise M, De Mol C (2004) An iterative thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems with a sparsity constraint. Commun Pure Appl Math 57(11):1413–1457. doi:10.1002/cpa.20042
Dong W, Zhang L, Shi G, Wu X (2011) Image deblurring and super-resolution by adaptive sparse domain selection and adaptive regularization. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(7):1838–1857. doi:10.1109/TIP.2011.2108306
Donoho DL (2006) For most large underdetermined systems of equations, the minimal \(l_1\)-norm near-solution approximates the sparsest near-solution. Commun Pure Appl Math 59(7):907–934. doi:10.1002/cpa.20131
Elad M (2010) Sparse and redundant representations: from theory to applications in signal and image processing. Springer, New York. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-7011-4
Emil Bilgazyev Boris Efraty SS, Kakadiaris I (2011) Sparse representation-based super resolution for face recognition at a distance. In: Proceedings of the British machine vision conference. BMVA Press, pp 52.1–52.11. doi:10.5244/C.25.52
Engan K, Aase S, Hakon Husoy J (1999) Method of optimal directions for frame design. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, vol 5, pp 2443–2446. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.1999.760624
Freeman W, Jones T, Pasztor E (2002) Example-based super-resolution. IEEE Comput Graphics Appl 22(2):56–65. doi:10.1109/38.988747
Georghiades A, Belhumeur P, Kriegman D (2001) From few to many: illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(6):643–660
Grgic M, Delac K, Grgic S (2011) Scface surveillance cameras face database. Multimedia Tools Appl 51(3):863–879. doi:10.1007/s11042-009-0417-2
Hou H, Andrews H (1978) Cubic splines for image interpolation and digital filtering. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 26(6):508–517. doi:10.1109/TASSP.1978.1163154
Irani M, Peleg S (1991) Improving resolution by image registration. CVGIP Graph Models Image Process 53(3):231–239. doi:10.1016/1049-9652(91)90045-L
Kan M, Shan S, Chang H, Chen X (2014) Stacked progressive auto-encoders (spae) for face recognition across poses. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1883–1890. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2014.243
Kanemura A, Ichi Maeda S, Ishii S (2009) Superresolution with compound markov random fields via the variational EM algorithm. Neural Netw 22(7):1025–1034
Keys R (1981) Cubic convolution interpolation for digital image processing. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 29(6):1153–1160. doi:10.1109/TASSP.1981.1163711
Lee K, Ho J, Kriegman D (2005) Acquiring linear subspaces for face recognition under variable lighting. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(5):684–698
Little D, Krishna S, Black J, Panchanathan S (2005) A methodology for evaluating robustness of face recognition algorithms with respect to variations in pose angle and illumination angle. IEEE Intl Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process 2:89–92. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2005.1415348
Liu C, Wechsler H (2002) Gabor feature based classification using the enhanced fisher linear discriminant model for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 11(4):467–476. doi:10.1109/TIP.2002.999679
Lui YM, Bolme D, Draper B, Beveridge J, Givens G, Phillips P (2009) A meta-analysis of face recognition covariates. In: IEEE 3rd international conference on biometrics: theory, applications, and systems, BTAS ’09, pp 1–8 (2009). doi:10.1109/BTAS.2009.5339025
Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, Sapiro G, Zisserman A (2009) Non-local sparse models for image restoration. In: IEEE 12th international conference on computer Vision, pp 2272–2279. doi:10.1109/ICCV.2009.5459452
Mairal J, Elad M, Sapiro G (2008) Sparse representation for color image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(1):53–69. doi:10.1109/TIP.2007.911828
Mallat S, Zhang Z (1993) Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans Signal Process 41(12):3397–3415. doi:10.1109/78.258082
Mandal S, Sao A (2013) Edge preserving single image super resolution in sparse environment. In: 20th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp 967–971. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2013.6738200
Marquina A, Osher S (2008) Image super-resolution by TV-regularization and bregman iteration. J Sci Comput 37(3):367–382. doi:10.1007/s10915-008-9214-8
Mu Y, Lo H, Ding W, Tao D (2014) Face recognition from multiple images per subject. In: Proceedings of the ACM international conference on multimedia, MM ’14. ACM, New York, pp 889–892. doi: 10.1145/2647868.2655054
Nguyen H, Caplier A (2015) Local patterns of gradients for face recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 10(8):1739–1751. doi:10.1109/TIFS.2015.2426144
Park JS, Lee SW (2008) An example-based face hallucination method for single-frame, low-resolution facial images. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(10):1806–1816. doi:10.1109/TIP.2008.2001394
Park SC, Park MK, Kang MG (2003) Super-resolution image reconstruction: a technical overview. IEEE Signal Process Mag 20(3):21–36. doi:10.1109/MSP.2003.1203207
Pelletier S, Cooperstock J (2012) Preconditioning for edge-preserving image super resolution. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(1):67–79. doi:10.1109/TIP.2011.2160188
Punnappurath A, Rajagopalan A, Taheri S, Chellappa R, Seetharaman G (2015) Face recognition across non-uniform motion blur, illumination, and pose. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(7):2067–2082. doi:10.1109/TIP.2015.2412379
Ramesh S, Palanivel S, Das S, Yegnanarayana B (2002) Eigenedginess vs. eigenhill, eigenface and eigenedge. In: European Signal Processing Conference. Toulose, France, pp 559–562 (2002)
Rara H, Elhabian S, Ali A, Miller M, Starr T, Farag A (2009) Distant face recognition based on sparse-stereo reconstruction. In: 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp 4141–4144. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2009.5413467
Rubinstein R, Bruckstein A, Elad M (2010) Dictionaries for sparse representation modeling. Proc IEEE 98(6):1045–1057. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2010.2040551
Rudin LI, Osher S, Fatemi E (1992) Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys D 60(1–4):259–268. doi:10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F
Sao A, Yegnanarayana B (2011) Laplacian of smoothed image as representation for face recognition. IEEE Int Workshop Inf Forensics Secur (WIFS) 2011:1–6. doi:10.1109/WIFS.2011.6123140
Sao AK, Yegnanarayana B, Vijaya Kumar B (2007) Significance of image representation for face verification. Signal Image Video Process 1:225–237. doi:10.1007/s11760-007-0016-5
Shejin T, Sao A (2012) Significance of dictionary for sparse coding based face recognition. In: Proceedings of the international conference of the biometrics special interest group (BIOSIG), pp 1–6
Stark H, Oskoui P (1989) High-resolution image recovery from image-plane arrays, using convex projections. J Opt Soc Am A 6(11):1715–1726
Sun G, Shen Z (2010) Single image super-resolution via edge reconstruction and image fusion. In: Kim TH, Pal S, Grosky W, Pissinou N, Shih T, Ålzak D (eds) Signal processing and multimedia, communications in computer and information science, vol 123. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp 16–23. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17641-8_3
Tang S, Xiao L, Liu P, Zhang J, Huang L (2014) Edge and color preserving single image superresolution. J Electron Imaging 23(3):033002. doi:10.1117/1.JEI.23.3.033002
Turk M, Pentland A (1991) Face recognition using eigenfaces. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 586–591. doi:10.1109/CVPR.1991.139758
Vidal R, Ma Y, Sastry S (2003) Generalized principal component analysis (GPCA). In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 1, pp I-621–I-628. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2003.1211411
Vishnukumar S, Nair MS, Wilscy M (2014) Edge preserving single image super-resolution with improved visual quality. Signal Process 105:283–297. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.05.033
Wang N, Tao D, Gao X, Li X, Li J (2013) Transductive face sketch-photo synthesis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(9):1364–1376. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2258174
Wang N, Tao D, Gao X, Li X, Li J (2014) A comprehensive survey to face hallucination. Int J Comput Vis 106(1):9–30. doi:10.1007/s11263-013-0645-9
Wang X, Tang X (2009) Face photo-sketch synthesis and recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(11):1955–1967. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2008.222
Wei CP, Wang YC (2015) Undersampled face recognition via robust auxiliary dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(6):1722–1734. doi:10.1109/TIP.2015.2409738
Yang J, Wright J, Huang T, Ma Y (2008) Image super-resolution as sparse representation of raw image patches. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–8. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587647
Yang J, Wright J, Huang T, Ma Y (2010) Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(11):2861–2873. doi:10.1109/TIP.2010.2050625
Yang M, Huang D, Tsai C, Wang YF (2012) Self-learning of edge-preserving single image super-resolution via contourlet transform. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE international conference on multimedia and Expo, ICME 2012, Melbourne, Australia, July 9–13, 2012, pp 574–579. doi:10.1109/ICME.2012.169
Yuan Q, Zhang L, Shen H (2012) Multiframe super-resolution employing a spatially weighted total variation model. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 22(3):379–392. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2011.2163447
Zeyde R, Elad M, Protter M (2012) On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In: Boissonnat JD, Chenin P, Cohen A, Gout C, Lyche T, Mazure ML, Schumaker L (eds) Curves and surfaces, lecture notes in computer science, vol 6920. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 711–730. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-27413-8_47
Zhang K, Gao X, Tao D, Li X (2012) Single image super-resolution with non-local means and steering kernel regression. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(11):4544–4556. doi:10.1109/TIP.2012.2208977
Zhang L, Zhang H, Shen H, Li P (2010) A super-resolution reconstruction algorithm for surveillance images. Signal Process 90(3):848–859. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.09.002
Zhang X, Lam E, Wu E, Wong K (2008) Application of Tikhonov regularization to super-resolution reconstruction of brain MRI images. In: Gao X, Mller H, Loomes M, Comley R, Luo S (eds) Medical Imaging and Informatics, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4987. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 51–56. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-79490-5_8
Zhao W, Chellappa R, Phillips PJ, Rosenfeld A (2003) Face recognition: a literature survey. ACM Comput Surv 35(4):399–458. doi:10.1145/954339.954342
Zhou Q, Chen S, Liu J, Tang X (2011) Edge-preserving single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM international conference on multimedia, MM ’11. ACM, New York, pp 1037–1040 (2011). doi:10.1145/2072298.2071932
Zou W, Yuen P (2010) Very low resolution face recognition problem. In: Fourth IEEE international conference on biometrics: theory applications and systems (BTAS), pp 1–6. doi:10.1109/BTAS.2010.5634490
Zou W, Yuen P (2012) Very low resolution face recognition problem. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(1):327–340. doi:10.1109/TIP.2011.2162423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, S., Thavalengal, S. & Sao, A.K. Explicit and implicit employment of edge-related information in super-resolving distant faces for recognition. Pattern Anal Applic 19, 867–884 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-015-0512-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-015-0512-0