Abstract
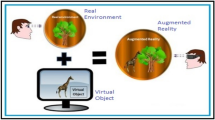
In this paper, we present a vision-based approach for transmitting virtual models for Augmented Reality, which we name In-Place Augmented Reality (IPAR). A two-dimensional representation of the virtual models is embedded in a printed image. We apply computer vision techniques to interpret the printed image and extract the virtual models, which are then overlaid on the printed image. The main advantages of our approach are: (1) the image of the embedded virtual models and their behaviors are understandable to a human without using an AR system and (2) no database or network communication is required to retrieve the models. To demonstrate the technology and test its usability, we implemented several applications and performed a user evaluation. We discuss how the proposed technique can be used for the development of applications in different domains such as education, advertisement, and gaming.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis R (2007) Magic paper: sketch-understanding research. Computer 40:34–41
Design QR-Code (1994). http://www.denso-wave.com/qrcode/
Fiala M (2004) ARTag, an improved marker system based on ARToolkit, NRC institute for information technology
Hagbi N, Bergig O, El-Sana J, Kedem K, Billinghurst M (2008) In-Place Augmented Reality. In: 7th IEEE and ACM international symposium on mixed and augmented reality (ISMAR’08), pp 135–138
Hartley R, Zisserman A (2003) Multiple view geometry in computer vision, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Intel OpenCV (1999). http://opencvlibrary.sourceforge.net/
Kato H and Billinghurst M (1999) Marker tracking and HMD calibration for a video-based augmented reality conferencing system. In: 2nd international workshop on augmented reality, IWAR99, San Francisco, USA
Lam L, Lee SW, Suen CY (1992) Thinning methodologies-A comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 14:879
Landay JA, Myers BA (2001) Sketching interfaces: toward more human interface design. Computer 34:56–64
Langlotz T and Bimber O (2007) Unsynchronized 4D barcodes. International Symposium on Visual Computing, pp. 363–374
LaViola J and Zeleznik R (2004) MathPad2: a system for the creation and exploration of mathematical sketches. ACM Trans Graph (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH04) 23: 432–440
Lepetit V and Fua P (2006) Keypoint recognition using randomized tree, Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28, Nr. 9, pp. 1465–1479
MXRToolKit (2004). http://mxrtoolkit.sourceforge.net/
Nintendo e-Reader (2001). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nintendo_e-Reader
Open Dynamics Engine (2001). http://www.ode.org/
Rekimoto J and Ayatsuka Y (2000) Cybercode: designing augmented reality environments with visual tags. In: Proceedings of DARE 2000 on designing augmented reality environments
Saarelma H (2005) Printed codes—patent survey. Graphic Arts in Finland 34:1–11
Semacode (2004). http://semacode.com/
Semapedia (2005). http://www.semapedia.org/
Shin M, Kim BS, and Park J (2005) AR storyboard: an augmented reality based interactive storyboard authoring tool. In: Fourth IEEE and ACM international symposium on mixed and augmented reality (ISMAR’05), pp 198–199
Studierstube Tracker (2008). http://handheldar.net/stbtracker.php
Telea A (2004) An image inpainting technique based on the fast marching method. J Graph Tools 9:25–36
The Eye of Judgment (2007). http://www.eyeofjudgment.com/
Tsung-Yu L, Tan-Hsu T and Yu-Ling C (2007) 2D barcode and augmented reality supported english learning system. In: Computer and information science Melbourne, Australia, pp 5–10
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments. This work was supported by the Lynn and William Frankel Center for Computer Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergig, O., Hagbi, N., El-Sana, J. et al. In-Place Augmented Reality. Virtual Reality 15, 201–212 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-010-0158-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-010-0158-6