Abstract
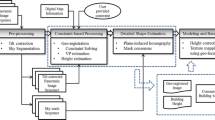
Image-based modeling of urban environments is a key component of enabling outdoor, vision-based augmented reality applications. The images used for modeling may come from off-line efforts, or online user contributions. Panoramas have been used extensively in mapping cities and can be captured quickly by an end-user with a mobile phone. In this paper, we describe and evaluate a reconstruction pipeline for upright panoramas taken in an urban environment. We first describe how panoramas can be aligned to a common vertical orientation using vertical vanishing point detection, which we show to be robust for a range of inputs. The orientation sensors in modern cameras can also be used to correct the vertical orientation. Secondly, we introduce a pose estimation algorithm, which uses knowledge of a common vertical orientation as a simplifying constraint. This procedure is shown to reduce pose estimation error in comparison with the state of the art. Finally, we evaluate our reconstruction pipeline with several real-world examples.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Panoramas available from: http://tracking.mat.ucsb.edu.
From Occipital Inc.: http://www.occipital.com/360.
References
Antone M, Teller S (2002) Scalable extrinsic calibration of omni-directional image networks. Int J Comput Vis 49:143–174
Baatz G, Köser K, Chen D, Grzeszczuk R, Pollefeys M (2010) Handling urban location recognition as a 2d homothetic problem. In: Daniilidis K, Maragos P, Paragios N (eds) Computer vision—ECCV 2010, lecture notes in computer science, Springer, Berlin, pp 266–279
Fraundorfer F, Tanskanen P, Pollefeys M (2010) A minimal case solution to the calibrated relative pose problem for the case of two known orientation angles. In: Proceedings of the 11th European conference on computer vision: part IV, ECCV’10, Springer, Berlin, pp 269–282
Gallagher AC (2005) Using vanishing points to correct camera rotation in images. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Canadian conference on computer and robot vision, CRV ’05, IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 460–467
Haralick RM, Lee CN, Ottenberg K, Nölle M (1994) Review and analysis of solutions of the three point perspective pose estimation problem. Int J Comput Vis 13:331–356
Hartley RI, Zisserman A (2004) Multiple view geometry in computer vision, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, ISBN: 0521540518
Horn BKP, Hilden H, Negahdaripour S (1988) Closed-form solution of absolute orientation using orthonormal matrices. J Opt Soc Am 5(7):1127–1135
Kosecka J, Zhang W (2002) Video compass. In: Proceedings of the 7th European conference on computer vision-part IV, ECCV ’02, Springer, London, pp 476–490
Kukelova Z, Bujnak M, Pajdla T (2011) Closed-form solutions to minimal absolute pose problems with known vertical direction. In: Computer vision—ACCV 2010, lecture notes in computer science, vol 6493, pp 216–229
Lepetit V, Moreno-Noguer F, Fua P (2009) Epnp: An accurate o(n) solution to the pnp problem. Int J Comput Vis 81:155–166
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60:91–110
Micusik B, Kosecka J (2009) Piecewise planar city 3d modeling from street view panoramic sequences. IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Miami, USA, pp 2906–2912
Nistér D (2004) An efficient solution to the five-point relative pose problem. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26:756–777
Pollefeys M, Nistér D, Frahm JM, Akbarzadeh A, Mordohai P, Clipp B, Engels C, Gallup D, Kim SJ, Merrell P, Salmi C, Sinha S, Talton B, Wang L, Yang Q, Stewénius H, Yang R, Welch G, Towles H (2008) Detailed real-time urban 3d reconstruction from video. Int J Comput Vis 78:143–167
Robertson D, Cipolla R (2004) An image-based system for urban navigation. In: British machine vision conference, pp 819–828
Rother C (2002) A new approach to vanishing point detection in architectural environments. Image Vis Comput 20(9-10):647–655
Snavely N, Seitz SM, Szeliski R (2006) Photo tourism: exploring photo collections in 3d. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 papers, SIGGRAPH ’06, ACM, New York, pp 835–846
Tardif JP, Pavlidis Y, Daniilidis K (2008) Monocular visual odometry in urban environments using an omnidirectional camera. In: IROS’08, pp 2531–2538
Torii A, Havlena M, Pajdla T (2009) From google street view to 3d city models. In: Computer vision workshops (ICCV Workshops), 2009 IEEE 12th international conference on 2009
Werner T, Pajdla T (2001) Cheirality in epipolar geometry. Computer vision, IEEE international conference on 1: 548
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Chris Coffin and Sehwan Kim for preparing the tripod panorama datasets, and to Google, Inc. for providing the Street View datasets. This work was partially supported by NSF CAREER grant IIS-0747520.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ventura, J., Höllerer, T. Structure and motion in urban environments using upright panoramas. Virtual Reality 17, 147–156 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-012-0208-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-012-0208-3