Abstract
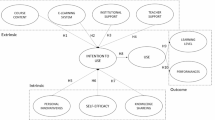
The increasing need for active and accessible learning in the inclusive knowledge society drives the demand for e-learning that engages users much more effectively than ever before. In this context, it is crucial to conduct research that embraces innovation in user sensitive design, or else influential individual user differences may be overlooked. The objective of this paper is to explore the creation of successful e-learning systems that are able to increase users’ learning performance and enhance their personal learning experiences. The paper reports two converging and complimentary approaches, namely case studies and experimentation. First, case studies are used to explore the extent to which effective e-learning systems comply with eight specific factors. Of the eight, accessibility, individual differences and student modeling turn out to be the weakest points in current practice. Second, an empirical study investigates the influences of user individual user differences on users’ learning outcomes in an e-learning environment. The experiment found that individual differences in motivation to learn and expectations about e-learning significantly impacted users’ learning achievements. Third, based on these studies, improvements in research methodology are identified towards greater consideration of user sensitive research issues, thus enabling us to outline improved experimental procedures. Further experiment results should provide us with better insights into the arguments needed to carefully assess benefits of developing and involving a user model in an e-learning application. Consequently, evaluation and justification could now encompass both system performance as well as user performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A KnowledgeNet White Paper (2002) Exploding the e-Learning Myth: Next-Generation, Web-Based Training Is Here Today and It Delivers the “Wow” Experience. [Available On-line] http://www.knowledgenet.com/newsroom/whitepapers/elearningmyth.jsp
Adams, R.: Decision and stress: cognition and e-accessibility in the information workplace. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 5, 363–379 (2007)
Adams, R.: User modeling for intelligent interfaces in e-learning. Lecture Notes in Computer Science: Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction, Application and Services, vol. 4556, pp. 473–480 (2007)
Adams, R.: Universal access through client-centred cognitive assessment and personality profiling. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3196, pp. 3–15 (2004)
Ahmad, A.-R., Basir, O., Hassanein, K.: Adaptive User Interfaces for Intelligent e-Learning: Issues and Trends. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Electronic Business, ICEB2004, 925–934, Beijing, China, December 5–9, 2004 (2004)
Aleven, V., McLaren, B.M., Sewall, J., Koedinger, K.R.: http://www.knowledgenet.com/newsroom/whitepapers/elearningmyth_pf.jsp. The Cognitive tutor authoring tools (CTAT): preliminary evaluation of efficiency gains. In: Ikeda M., Ashley K., Chan T.-W. (eds.) ITS 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4053, pp. 61–70 (2006)
Anderson, J.R.: Rules of the Mind. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ (1993)
Antona, A., Mourouzis, A., Stephanidis, C.: Towards a walkthrough method for universal access evaluation. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4554, pp. 325–334 (2007)
Ayersman, D.J., von Minden, A.: Individual differences, computers, and instruction. Comput. Hum. Behav. 11, 371–390 (1995)
Bell, D.S., Fonarow, G.C., Hays, R.D., Mangione, C.M.: Self-study from web-based and printed guideline materials. A randomized, controlled trial among resident physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 132, 938–946 (2000)
Benyon, D., Murray, D.: Interacting with Computers. Special Issue Intell. Interface Technol. 12, 315–322 (2000)
Benyon, D., Murray, D.: Developing adaptive systems to fit individual aptitudes. In: Gray, W.D., Hefley, W., Murray, D. (eds.) International Workshop on Intelligent User Interfaces; 1993, January 4–7; Orlando, Florida, USA:115–121 (1993)
Benyon, D., Crerar, A., Wilkinson, S.: Individual differences and inclusive design. In: Stephanidis, C. (ed.) User Interfaces for All—Concepts, Methods, and Tools, pp. 21–46. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ (2001)
Berkovsky, S., Kuflik, T., Ricci, F.: Mediation of user models for enhanced personalization in recommender systems”, accepted to User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction (UMUAI). doi:10.1007/s11257-007-9042-9 [available on line] http://www.springerlink.com/content/jt48g17025r8v567/ (2008)
Browne, D., Norman, M., Rithes, D.: Why build adaptive systems? In: Browne, D., Totterdell, P., Norman, M. (eds.) Adaptive User Interfaces, pp. 15–59. Academic Press, London (1990)
Brusilovsky, P.: KnowledgeTree: a distributed architecture for adaptive E-learning. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International World Wide Web Conference (WWW 2004) pp. 104–113. ACM Press, New York (2004)
Brusilovsky, P., Milan, E.: User models for adaptive hypermedia and adaptive educational systems. In: Brusilovsky, P., Kobsa, A. & Nejdl, W. (eds.) The Adaptive Web. Methods and Strategies of Web Personalization. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4321, pp. 3–53. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (2007)
Brusilovsky, P., Kobsa, A., Nejdl, W. (eds.): The Adaptive Web. Methods and Strategies of Web Personalization, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4321 (2007)
Chen, C., Czerwinski, M., Macredie, R.: Individual differences in virtual environments—introduction and overview. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 51, 499–507 (2000)
Chin, D.N.: Empirical evaluation of user models and user-adapted systems. User Model User Adapt Interact. 11, 181–194 (2001)
Christensen, J., Sussman, J., Levy, S., Bennett, W.E., Wolf, T.V., Kellogg, W.A.: Too much information. The future of HCI. ACM Queue 4, 50–57 (2006)
Cronbach, L.J., Snow, R.E.: Aptitudes and Instructional Methods: A Handbook for Research on Interactions. Irvington, New York (1977)
Ćukušić, M., Granić, A., Maršić, I.: Launching an E-learning system in a school. Cross-European e-/m-Learning System UNITE: a Case Study. In: Cordeiro, J., Filipe, J., Hammoudi, S. (eds.) Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies—WEBIST 2008, Vol. 1. e-Learning, Internet Technology, pp. 380–387. INSTICC PRESS, Portugal (2008)
Dewiyanti, S., Brand-Gruwela, S., Jochems, W., Broers, N.J.: Students’ experiences with collaborative learning in asynchronous computer-supported collaborative learning environments. Comput. Hum. Behav. 23, 496–514 (2007)
Dillon, A., Watson, C.: User analysis in HCI—the historical lessons from individual differences research. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 45, 619–637 (1996)
Egan, D.: Individual differences in human-computer interaction. In: Helander, M. (ed.) Handbook of Human-Computer Interaction, pp. 543–568. Elsevier Science B. V. Publishers, North-Holland, Amsterdam (1988)
Fletcher, J.: Evidence for learning from technology—assisted instruction. In: O’Neil, H., Perez, P. (eds.) Technology Applications in Education: A Learning View, pp. 79–99. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New York (2003)
Ford, N., Chen, S.Y.: Individual differences, hypermedia navigation and learning: an empirical study. J. Educ. Multimed. Hypermed. 9, 281–311 (2000)
Granić, A.: Experience with usability evaluation of e-learning systems. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 7, 209–221 (2008)
Granić, A., Nakić, J.: Designing intelligent interfaces for e-learning systems: the role of user individual characteristics. Lecture Notes in Computer Science: Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction, Application and Services, vol. 4556, pp. 627–636 (2007)
Granić, A., Stankov, S., Nakić, J.: Designing intelligent tutors to adapt individual interaction. Lecture Notes in Computer Science: Universal Access in Ambient Intelligence Environments, vol. 4397, pp. 137–153 (2007)
Gregor, P., Newell A.F., Zajicek, M.: Designing for dynamic diversity—interfaces for older people. In: Jacko, J.A. (ed.): ASSETS 2002. The Fifth International ACM Conference on Assistive Technologies, 8–10 July. Edinburgh, Scotland. 151–156 (2002)
Healey, D.: Theory and research: autonomy in language learning. In: Egbert, J., Hanson-Smith, E. (eds.) CALL Environments: Research, Practice, and Critical Issues, pp. 391–402. Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages, Alexandria, VA (1999)
Hook, K.: Steps to take before intelligent user interfaces become real. J. Interact. Comput. 12, 409–426 (2000)
Jennings, F., Benyon, D., Murray, D.: Adapting systems to differences between individuals. Acta Psychol. 78, 243–256 (1991)
Juvina, I., van Oostendorp, H.: Individual differences and behavioral metrics involved in modeling web navigation. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 4, 258–269 (2006)
Karim, S., Tjoa, A.M.: Towards the use of ontologies for improving user interaction for people with special needs. In: Miesenberger, K. et al. (eds.): ICCHP 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4061, pp. 77–84 (2006)
Kerscher, G.: The essential role of libraries serving persons who are blind and print disabled in the information age. In: Miesenberger, K. et al. (eds.): ICCHP 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4061, pp. 100–105 (2006)
Kinshuk, K., Patel, A., Russell, D.: Intelligent and adaptive systems. In: Collis, B., Adelsberger, H., Pawlowski, J. (eds.) Handbook on Information Technologies for Education and Training, pp. 79–92. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Kobsa, A.: Supporting User Interfaces for All through User Modeling. 6th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction HCI International 1995, Yokohama, Japan, 155–157. [Available On-line] http://www.ics.uci.edu/~kobsa/papers/1995-HCI95-kobsa.pdf (1995)
Koedinger, K.R., Aleven, V., Heffernan, N.T.: Toward a rapid development environment for Cognitive Tutors. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, AI-ED 2003 (pp. 455–457). IOS Press, Amsterdam (2003)
Koedinger, K.R., Anderson, J.R., Hadley, W.H., Mark, M.A.: Intelligent tutoring goes to school in the big city. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 8, 30–43 (1997)
Lieberman, H.: Introduction to intelligent interfaces. [Available On-line] http://web.media.mit.edu/~lieber/Teaching/Int-Int/Int-Int-Intro.html (1997)
Liegle, J.O., Janicki, T.N.: The effect of learning styles on the navigation needs of web-based learners. Comput. Hum. Behav. 22, 885–898 (2006)
Magoulas, G.D., Chen, S.Y., Papanikolaou, K.A.: Integrating layered and heuristic evaluation for adaptive learning environments. In: Weibelzahl, S., Paramythis, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Empirical Evaluation of Adaptive Systems, held at the 9th International Conference on User Modeling UM2003, Pittsburgh. pp. 5–14. (2003)
McTear, M.F.: Intelligent interface technology: from theory to reality? Interact. Comput. 12, 323–336 (2000)
Nash, S.S.: Learning objects, learning object repositories and learning theory: preliminary best practices for online courses. Interdiscip. J. Knowl. Learn. Objects 1, 217–228 (2005)
Newell, A., Gregor, P.: User sensitive inclusive design in search of a new paradigm. In: Scholtz, J., Thomas J. (eds.) First ACM Conference on Universal Usability, pp. 39–44 (2000)
Norman, D., Draper, S.W. (eds.): User Centred System Design. New Perspectives on Human-computer Interaction. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ (1986)
Pantazis, C.: Executive summary: A vision of E-learning for America’s workforce. Report of the Commission on Technology and Adult Learning, ASTD. [Available On-line] http://www.learningcircuits.org/2001/aug2001/pantazis.html (2001)
Pullin, G., Newell, A.: Focussing on extra-ordinary users. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4554, pp. 253–262 (2007)
Rich, E.: Users are individuals: individualizing user models. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 51, 323–338 (1999)
Schneider-Hufschmidt, M., Kühme, T., Malinowski, U.: Adaptive User Interfaces: Principles and Practice. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1993)
Schweizer, K.: An overview of research into the cognitive basis of intelligence. J. Individ. Differ. 26, 43–51 (2005)
Shute, V., Towle, B.: Adaptive e-learning. Educ. Psychol. 38, 105–114 (2003)
SIGCHI: Notes from E-learning Special Interest Group (SIG). Discussion at CHI 2001, http://www.elearning.org (2001)
Soloway, E., Guzdial, M., Hay, K.E.: Learner-centred design: the challenge for HCI in the 21st Century. Interactions 1, 36–48 (1994)
Soloway, E., Jackson, S., Klein, J., Quintana, C., Reed, J., Spitulnik, J., Stratford, S., Studer, S., Eng, J., Scala, N.: Learning theory in practice: case studies of learner-centered design. In: Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems: Common Ground. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, pp. 189–196 (1996)
Spector, J.M., Anderson, T.M. (eds.): Integrated and Holistic Perspectives on Learning, Instruction and Technology: Understanding Complexity. Kluwer, Dordrecht (2000)
Squires, D., Preece, J.: Usability and learning: evaluating the potential of educational software. Comput. Educ. 27, 15–22 (1996)
VanLehn, K., Lynch, C., Schulze, K., Shapiro, J.A., Shelby, R.: The Andes physics tutoring system: five years of evaluations. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education. IOS Press, Amsterdam (2005)
Woolf, B.: AI in education. In: Shapiro, I., Stuart, C. (eds.) Artificial Intelligence—Encyclopaedias, pp. 434–444. Wiley, New York (1992)
Woolf, B.P., Cunningham, P.: Building a Community Memory for Intelligent Tutoring Systems, pp. 82–89. AAAI, New York (1987)
Yang, S.C., Chen, Y.: Technology-enhanced language learning: a case study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 23, 860–879 (2007)
Zaharias, P.: E-learning design quality: a holistic conceptual framework. In: Encyclopaedia of Distance Learning, Vol. II. Idea Group Inc (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge support for the work from the project 177-0361994-1998 Usability and Adaptivity of Interfaces for Intelligent Authoring Shells funded by the Ministry of Science, Education and Sports of the Republic of Croatia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granić, A., Adams, R. User sensitive research in e-learning: exploring the role of individual user characteristics. Univ Access Inf Soc 10, 307–318 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-010-0207-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-010-0207-7