Abstract
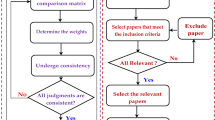
The field of business process modeling has been beset by inter-model consistency problems which are mainly due to the existence of multiple variants of the same business process, for instance when models have been produced by different actors, or through the time by a same (or different) actor(s), as well as the possibility of its modeling from discrete and complementary perspectives (using different lenses). Accordingly, our overall aim in this paper is to provide a thorough overview of consistency requirements in business process modeling, which is strongly needed not only for the sake of a comprehensive investigation of this challenging subject, but also for the sake of empowering significant contributions to it. In order to do so, we opted for a systematic literature review of consistency among business process models as starting point and basis to attain the intended overview and to guide our contributions in this field.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curtis, B., Kellner, M., Over, J.: Process modelling. Commun. ACM 35(9), 75–90 (1992)
Rolland, C.: A primer for method engineering. In: Proceedings of the INFormatique des ORganisations et Systemes d’Information et de Décision, Toulouse, France (1997)
Rolland, C.: A comprehensive view of process engineering. In: Advanced Information Systems Engineering, pp. 1–24, Springer, Berlin (1998)
Feiler, P.H., Humphrey, W.S.: Software process development and enactment: Concepts and definitions. In: Continuous Software Process Improvement, Second International Conference on the Software Process, pp. 28–40, IEEE (1993)
Sandkuhl, K., Stirna, J., Persson, A., Wißotzki, M.: Enterprise Modeling. Tackling Business Challenges with the 4EM Method, vol. 309. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Dumas, M., Van der Aalst, W.M., Ter Hofstede, A.H.: Process-Aware Information Systems: Bridging People and Software Through Process Technology. Wiley, Hoboken (2005)
Hammer, M., Champy, J.: Le Reengineering, vol. 93. Dunod, Paris (1993)
Peterson, R.S., Smith, D.B., Martorana, P.V., Owens, P.D.: The impact of chief executive officer personality on top management team dynamics: one mechanism by which leadership affects organizational performance. J. Appl. Psychol. 88(5), 795 (2003)
Muskens, J., Bril, R.J., Chaudron, M.R.: Generalizing consistency checking between software views . In: 5th Working IEEE/IFIP Conference on Software Architecture, pp. 169–180, IEEE (2005)
Hallerbach, A., Bauer, T., Reichert, M.: Configuration and management of process variants. In: Handbook on Business Process Management 1, pp. 237–255, Springer, Berlin (2010)
Lucas, F.J., Molina, F., Toval, A.: A systematic review of UML model consistency management. Inf. Softw. Technol. 51(12), 1631–1645 (2009)
Spanoudakis, G., Zisman, A.: Inconsistency management in software engineering: Survey and open research issues. In: Handbook of Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering 1, pp. 329–380 (2001)
Nurcan, S.: Ingénierie et Architecture d’Entreprise et des Systèmes d’Information-Concepts, Fondements et Méthodes (Habilitation dissertation, Université Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne) (2012)
Chapurlat, V.: Vérification et validation de modèles de systèmes complexes: application à la Modélisation d’Entreprise (Habilitation dissertation, Université Montpellier II) (2007)
Russell, N., van der Aalst, W.M., Ter Hofstede, A.H., Wohed, P.: On the suitability of UML 2.0 activity diagrams for business process modelling. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Asia-Pacific Conference on Conceptual Modelling. vol. 53, pp. 95–104 (2006)
Mendling, J., Neumann, G., Nüttgens, M.: A comparison of XML interchange formats for business process modelling. Workflow handbook, pp. 185–198 (2005)
Akobeng, A.K.: Understanding systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 90(8), 845–848 (2005)
IEEE standard 42010. IEEE (2011)
Persson, M., Törngren, M., Qamar, A., Westman, J., Biehl, M., Tripakis, S., Denil, J.: A characterization of integrated multi-view modeling in the context of embedded and cyber-physical systems. In: 11th ACM International Conference on Embedded Software, IEEE Press, p. 10 (2013)
Brooks, C., Cheng, C.P., Feng, T.H., Lee, E.A., Von Hanxleden, R.: Model Engineering Using Multimodeling (No. UCB/EECS-2008-39). California University, Berkeley (2008)
Cicchetti, A., Ciccozzi, F., Leveque, T.: A hybrid approach for multi-view modeling. In: Electronic Communications of the European Association for the Study of Science and Technology, 50 (2012)
Broy, M., Feilkas, M., Herrmannsdoerfer, M., Merenda, S., Ratiu, D.: Seamless model-based development: from isolated tools to integrated model engineering environments. Proc. IEEE 98(4), 526–545 (2010)
Engels, G., Küster, J.M., Heckel, R., Groenewegen, L.: A methodology for specifying and analyzing consistency of object-oriented behavioral models. In: ACM SIGSOFT Software Engineering Notes, vol. 26, No. 5, pp. 186–195, ACM (2001)
Kitchenham, B., Brereton, O.P., Budgen, D., Turner, M., Bailey, J., Linkman, S.: Systematic literature reviews in software engineering—a systematic literature review. Inf. Softw. Technol. 51(1), 7–15 (2009)
Kitchenham, B.: Procedures for performing systematic reviews. Keele, UK, Keele University 33(2004), 1–26 (2004)
Keele, S.: Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. In: Technical Report, Ver. 2.3 EBSE Technical Report. EBSE (2007)
Governatori, G., Sadiq, S.: The journey to business process compliance. Handbook of Research on BPM IGI Global, pp. 426–454 (2008)
Bork, D., Karagiannis, D.: Model-driven development of multi-view modeling tools the MuVieMOT approach. In: ICSOFT-PT, 2014, pp. IS-11, IEEE (2014)
Yan, Z., Dijkman, R., Grefen, P.: Business process model repositories—framework and survey. Inf. Softw. Technol. 54(4), 380–395 (2012)
Hallerbach, A., Bauer, T., Reichert, M.: Capturing variability in business process models: the Provop approach. J. Softw. Maint. Evolut. Res. Pract. 22(6–7), 519–546 (2010)
Smirnov, S., Weidlich, M., Mendling, J.: Business process model abstraction based on behavioral profiles. In: Service-Oriented Computing, pp. 1–16, Springer (2010)
Koliadis, G., Vranesevic, A., Bhuiyan, M., Krishna, A., Ghose, A.K.: A combined approach for supporting the business process model lifecycle (2006)
Gerth, C., Luckey, M., Kuster, J.M., Engels, G.: Detection of semantically equivalent fragments for business process model change management. In: IEEE International Conference on Services Computing, pp. 57–64, IEEE (2010)
Zemni, M.A., Mammar, A., Ben Hadj Alouane, N.: A behavior-aware systematic approach for merging business process fragments. In: 19th International Conference on Engineering of Complex Computer Systems, pp. 194–197, IEEE (2014)
Pascalau, E., Awad, A., Sakr, S., Weske, M.: On maintaining consistency of process model variants. In: Business Process Management Workshops, pp. 289–300, Springer (2010)
Weidlich, M., Mendling, J., Weske, M.: Efficient consistency measurement based on behavioral profiles of process models. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 37(3), 410–429 (2011)
Koschmider, A., Blanchard, E.: User assistance for business process model decomposition. In: 1st IEEE International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science, pp. 445–454 (2007)
Koliadis, G., Ghose, A.: Verifying semantic business process models in inter-operation. In: IEEE International Conference on Services Computing, 2007, pp. 731–738 (2007)
Milani, F., Dumas, M., Ahmed, N., Matulevičius, R.: Modelling families of business process variants: a decomposition driven method. arXiv preprint arXiv:1311.1322 (2013)
Dijkman, R., Gfeller, B., Küster, J., Völzer, H.: Identifying refactoring opportunities in process model repositories. Inf. Softw. Technol. 53(9), 937–948 (2011)
Lu, R., Sadiq, S., Governatori, G., Yang, X.: Defining adaptation constraints for business process variants. In: Business Information Systems, pp. 145–156, Springer (2009)
Rastrepkina, M.: Managing variability in process models by structural decomposition. In: Business Process Modeling Notation, pp. 106–113, Springer (2010)
Pascalau, E., Rath, C.: Managing business process variants at eBay. In: Business Process Modeling Notation, pp. 91–105, Springer, Berlin (2010)
Bork, D., Buchmann, R., Karagiannis, D.: Preserving multi-view consistency in diagrammatic knowledge representation. In: Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management, pp. 177–182, Springer International Publishing (2015)
Cheng-Leong, A., Li Pheng, K., Keng Leng, G.R.: IDEF*: a comprehensive modelling methodology for the development of manufacturing enterprise systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 37(17), 3839–3858 (1999)
Chen-Burger, Y.H.: Knowledge sharing and inconsistency checking on multiple enterprise models. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Knowledge Management and Organizational Memories Workshop, Seattle, Washington, USA (2001)
Koehler, J., Tirenni, G., Kumaran, S.: From business process model to consistent implementation: a case for formal verification methods. In: Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Conference. Proceedings. Sixth International, pp. 96–106, IEEE (2002)
Worzberger, R., Kurpick, T., Heer, T.: On correctness, compliance and consistency of process models. In: IEEE 17th Workshop on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises, pp. 251–252, IEEE (2008)
Dijkman, R., Dumas, M., Garcia-Banuelos, L., Käärik, R.: Aligning business process models. In: IEEE International EDOC Conference, pp. 45–53, IEEE (2009)
Lu, R., Sadiq, S.: On the discovery of preferred work practice through business process variants. In: Conceptual Modeling-ER, pp. 165–180, Springer (2007)
Gulden, J., Frank, U.: MEMOCenterNG—a full-featured modeling environment for organization modeling and model-driven software development. In: 22nd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, Hammamet, Tunisia (2010)
Delen, D., Benjamin, P.C.: Towards a truly integrated enterprise modeling and analysis environment. Comput. Ind. 51(3), 257–268 (2003)
Leist, S., Zellner, G.: Evaluation of current architecture frameworks. In: Proceedings of the 2006 ACM Symposium on Applied computing, pp. 1546–1553, ACM (2006)
Shunk, D.L., Kim, J.I., Nam, H.Y.: The application of an integrated enterprise modeling methodology—FIDO—to supply chain integration modeling. Comput. Ind. Eng. 45(1), 167–193 (2003)
Fang, X., Liu, L., Liu, X.: Analyzing the consistency of business process based on behavioral Petri Net. Int. J u- e-Serv. Sci. Technol. 8(2), 25–34 (2015)
Weidlich, M., Dijkman, R., Mendling, J.: The ICoP framework: identification of correspondences between process models. In: 22nd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, Hammamet, Tunisia (2010)
Koubarakis, M., Plexousakis, D.: A formal framework for business process modelling and design. Inf. Syst. 27(5), 299–319 (2002)
Vanderfeesten, I., Reijers, H.A., Mendling, J., van der Aalst, W.M., Cardoso, J.: On a quest for good process models: the cross-connectivity metric. In: CAISE’2008, pp. 480–494, Springer (2008)
Martens, A.: Consistency between executable and abstract processes. In: e-Technology, e-Commerce and e-Service. Proceedings. The 2005 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 60-67, IEEE (2005)
Decker, G., Weske, M.: Behavioral consistency for B2B process integration. In: Advanced Information Systems Engineering, pp. 81–95, Springer (2007)
Fang, X., Wang, M., Yin, Z.: Behavior consistency analysis based on the behavior profile about transition multi-set of Petri Net. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 89(1b), 171–173 (2013)
De Medeiros, A.A., van der Aalst, W.M., Weijters, A.J.M.M.: Quantifying process equivalence based on observed behavior. Data Knowl. Eng. 64(1), 55–74 (2008)
Weidlich, M., Mendling, J.: Perceived consistency between process models. Inf. Syst. 37(2), 80–98 (2012)
Niemann, M., Siebenhaar, M., Schulte, S., Steinmetz, R.: Comparison and retrieval of process models using related cluster pairs. Comput. Ind. 63(2), 168–180 (2012)
Küster, J.M., Gerth, C., Förster, A., Engels, G.: Detecting and resolving process model differences in the absence of a change log. In: Business Process Management, pp. 244–260, Springer (2008)
Dijkman, R., Dumas, M., García-Bañuelos, L.: Graph matching algorithms for business process model similarity search. In: Business Process Management, pp. 48–63, Springer (2009)
Van der Aalst, W.M., De Medeiros, A.A., Weijters, A.J.M.M.: Process equivalence: Comparing two process models based on observed behavior. pp. 129–144, Springer (2006)
Li, C., Reichert, M., Wombacher, A.: Discovering reference process models by mining process variants. In: IEEE International Conference on Web Services, pp. 45–53, IEEE (2008)
Zachman, J.A.: A framework for information systems architecture. IBM Syst. J. 26(3), 276–292 (1987)
Nurcan, S., Rolland, C.: Using EKD-CMM electronic guide book for managing change in organisations. In: Proceedings of the 9th European–Japanese Conference on Information Modeling and Knowledge Bases, Iwate, Japan, pp. 105–123 (1999)
Daoudi, F., Nurcan, S.: A benchmarking framework for methods to design flexible business processes. Special issue of the Software Process: Improvement and Practice. J. Bus. Process Manag. Dev. Support 12(1), 51–63 (2007)
Bhave, A., Krogh, B.H., Garlan, D., Schmerl, B.: View consistency in architectures for cyber-physical systems. In: 2011 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS), pp. 151–160, IEEE (2011)
Qureshi, T.N.: Enhancing model-based development of embedded systems architecture-centric modeling, simulation and model-transformation in an automotive context (2012)
Rosemann, M., Recker, J.C.: Context-aware process design: Exploring the extrinsic drivers for process flexibility. In: The 18th International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering. Proceedings of Workshops and Doctoral Consortium, pp. 149–158, Namur University Press (2006)
Saidani, O., Nurcan, S.: Towards context aware business process modelling. In: 8th Workshop on Business Process Modeling, Development, and Support (BPMDS’07), CAiSE, vol. 7, p. 1 (2007)
Saidani, O., Nurcan, S.: A role-based approach for modeling flexible business processes. BPMDS 6, 111–120 (2006)
Yousfi, A., Dey, A.K., Saidi, R., Hong, J.H.: Introducing decision-aware BPs. Comput. Ind. 70, 13–22 (2015)
Rosemann, M., Recker, J.C., Flender, C., Ansell, P.D.: Understanding context-awareness in business process design (2006)
Awadid, A., Nurcan, S.: A systematic literature review of consistency among business process models. In: International Workshop on Business Process Modeling, Development and Support, pp. 175–195, Springer International Publishing (2016)
Barrios, J., Nurcan, S.: Model driven architectures for enterprise information systems. In: International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, pp. 3–19, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Riga, Lettonie (2004)
Awadid, A., Nurcan, S.: Towards enhancing business process modeling formalisms of EKD with consistency consideration. In: 2016 IEEE Tenth International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science (RCIS), Grenoble, France, pp. 1–12, IEEE(2016)
Branco, M.C., Xiong, Y., Czarnecki, K., Küster, J., Völzer, H.: A case study on consistency management of business and IT process models in banking. Softw. Syst. Model. 13(3), 913–940 (2014)
Küster, J., Völzer, H., Favre, C., Branco, M.C., Czarnecki, K.: Supporting different process views through a shared process model. Softw. Syst. Model. 15(4), 1207–1233 (2016)
Johannsen, F., Leist, S., Braunnagel, D.: Testing the impact of wand and Weber’s decomposition model on process model understandability (2014)
Branco, M.C., Wider, A.: Generating preliminary edit lenses from automatic pattern discovery in business process modeling. In: CAiSE Forum, pp. 65–72 (2013)
Song, W., Zhang, W., Zhang, G., Ding, J., Zhang, X.: Quantifying consistency between conceptual and executable business processes. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on services computing (SCC), pp. 9–16, IEEE (2013)
Xing, J., Zhang, X., Song, W., Yang, Q., Ge, J., Wang, H.: BPEL Similarity—a metric based on activity constraint graphs. In: Asia-Pacific Conference on Business Process Management, pp. 39–55. Springer International Publishing (2013)
ALMEIDA CASTELO BRANCO, M.O.I.S.E.S.: Managing Consistency of Business Process Models across Abstraction Levels (2014)
Letsholo, K.J., Chioasca, E.V., Zhao, L.: An integrative approach to support multi-perspective business process modeling. Int. J. Serv. Comput. 2(1), 11–24 (2014)
Dey, A.K.: Understanding and using context. Int. J. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 5(1), 4–7 (2001)
Zimmermann, A., Lorenz, A., Oppermann, R.: An Operational definition of context. In: International and Indisciplinary Conference on Modeling and Using Context (CONTEXT 07), pp. 558–571, Springer (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Dr. Ilia Bider and Rainer Schmidt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awadid, A., Nurcan, S. Consistency requirements in business process modeling: a thorough overview. Softw Syst Model 18, 1097–1115 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-017-0629-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-017-0629-2