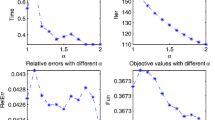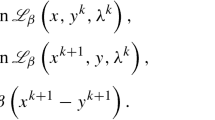Abstract
In this paper, we consider the minimization of a class of nonconvex composite functions with difference of convex structure under linear constraints. While this kind of problems in theory can be solved by the celebrated alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM), a direct application of ADMM often leads to difficult nonconvex subproblems. To address this issue, we propose to convexify the subproblems through a linearization technique as done in the difference of convex functions algorithm (DCA). By assuming the Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz property, we prove that the resulting algorithm sequentially converges to a critical point. It turns out that in the applications of signal and image processing such as compressed sensing and image denoising, the proposed algorithm usually enjoys closed-form solutions of the subproblems and thus can be very efficient. We provide numerical experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boley, D.: Local linear convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers on quadratic or linear programs. SIAM J. Optim. 23(4), 2183–2207 (2013)
Bolte, J., Daniilidis, A., Lewis, A.: The łojasiewicz inequality for nonsmooth subanalytic functions with applications to subgradient dynamical systems. SIAM J. Optim. 17(4), 1205–1223 (2007)
Bolte, J., Sabach, S., Teboulle, M.: Proximal alternating linearized minimization for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems. Math. Programm. 146(1-2), 459–494 (2014)
Bregma, L.M.: The relaxation method of finding the common point of convex sets and its application to the solution of problems in convex programming. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 7(3), 200–217 (1967)
Chen, G., Teboulle, M.: A proximal-based decomposition method for convex minimization problems. Math. Programm. 64(1), 81–101 (1994)
Deng, W., Lai, M.-J., Peng, Z., Yin, W.: Parallel multi-block admm with o (1/k) convergence. Journal of Scientific Computing (2014)
Deng, W., Yin, W.: On the global and linear convergence of the generalized alternating direction method of multipliers. Journal of Scientific Computing, pp. 1–28 (2016)
Eckstein, J., Yao, W.: Understanding the convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers Theoretical and computational perspectives. Pacific Journal of Optimization (2015)
Gabay, D., Mercier, B.: A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite element approximation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2(1), 17–40 (1976)
Gasso, G., Rakotomamonjy, A., Canu, S.: Recovering sparse signals with a certain family of nonconvex penalties and dc programming. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(12), 4686–4698 (2009)
Glowinski, R., Marroco, A.: Sur l’approximation, par éléments finis d’ordre un, et la résolution, par pénalisation-dualité d’une classe de problèmes de dirichlet non linéaires. Rev. Fr. d’automatique, Inf., Rech. Opérationnelle Anal. Numérique 9(R2), 41–76 (1975)
Goldstein, T., Osher, S.: The split bregman method for l1-regularized problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2(2), 323–343 (2009)
He, B., Yuan, X.: On non-ergodic convergence rate of douglas–rachford alternating direction method of multipliers. Numer. Math. 130(3), 567–577 (2012)
He, B., Yuan, X.: On the o(1/n) convergence rate of the douglas-rachford alternating direction method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(2), 700–709 (2012)
Hong, M., Luo, Z.-Q.: On the linear convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1208.3922 (2012)
Kurdykam, K.: On gradients of functions definable in o-minimal structures. In: Annales de l’institut Fourier, vol. 48, pp. 769–784. L’Institut, 1950-, Chartres (1998)
Li, G., Pong, T.K.: Splitting methods for nonconvex composite optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1407.0753 (2014)
Lin, Z., Liu, R., Su, Z.: Linearized alternating direction method with adaptive penalty for low-rank representation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 612–620 (2011)
Łojasiewicz, S.: Sur la géométrie semi-et sous-analytique. Ann. Inst. Fourier 43(5), 1575–1595 (1993)
Lou, Y., Yin, P., He, Q., Xin, J.: Computing sparse representation in a highly coherent dictionary based on difference of l 1 and l 2. J. Sci. Comput. 64(1), 178–196 (2015)
Lou, Y., Yin, P., Xin, J.: Point source super-resolution via non-convex l 1 based methods. J. Sci. Comput. 68(3), 1082–1100 (2016)
Lou, Y., Zeng, T., Osher, S., Xin, J.: A weighted difference of anisotropic and isotropic total variation model for image processing. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 8(3), 1798–1823 (2015)
Mordukhovich, Boris S: Variational analysis and generalized differentiation I: Basic theory, vol. 330. Springer Science & Business Media (2006)
Ng, M.K., Weiss, P., Yuan, X.: Solving constrained total-variation image restoration and reconstruction problems via alternating direction methods. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 32(5), 2710–2736 (2010)
Osher, S., Burger, M., Goldfarb, D., Xu, J., Yin, W.: An iterative regularization method for total variation-based image restoration. Multiscale Model. Simul. 4(2), 460–489 (2005)
Parikh, N., Boyd, S.: Proximal algorithms. Found. Trends Optim. 1(3), 123–231 (2013)
Tyrrell Rockafellar, R., Wets, R.J.-B.: Variational Analysis, vol. 317. Springer Science & Business Media (2009)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Convex Analysis. Princeton University Press, USA (2015)
Rudin, L.I., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenom. 60(1), 259–268 (1992)
Wang, F., Xu, Z., Xu, H.-K.: Convergence of alternating direction method with multipliers for non-convex composite problems. arXiv:1410.8625 (2014)
Wang, H., Banerjee, A.: Bregman alternating direction method of multipliers. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2816–2824 (2014)
Wang, X., Yuan, X.: The linearized alternating direction method of multipliers for dantzig selector. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 34(5), A2792–A2811 (2012)
Wang, Y., Yang, J., Yin, W., Zhang, Y.: A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 1(3), 248–272 (2008)
Yu, W., Yin, W., Zeng, J.: Global convergence of admm in nonconvex nonsmooth optimization. arXiv:1511.06324 (2015)
Wen, Z., Goldfarb, D., Yin, W.: Alternating direction augmented lagrangian methods for semidefinite programming. Math. Programm. Comput. 2(3-4), 203–230 (2010)
Xu, Y., Yin, W., Wen, Z., Zhang, Y.: An alternating direction algorithm for matrix completion with nonnegative factors. Frontiers Math. China 7(2), 365–384 (2012)
Yang, J., Zhang, Y.: Alternating direction algorithms for l1-problems in compressive sensing. Siamj. Sci. Comput. 33, 250278 (2011)
Yang, J., Zhang, Y., Yin, W.: A fast alternating direction method for tvl1-l2 signal reconstruction from partial fourier data. IEEE J. Select. Top. Signal Process. 4(2), 288–297 (2010)
Yin, P., Lou, Y.i, He, Q., Xin, J.: Minimization of 1-2 for compressed sensing. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 37(1), A536–A563 (2015)
Yin, P., Xin, J.: Iterative l 1 minimization for non-convex compressed sensing. Journal of Computational Mathematics, to appear
Yin, W.: Analysis and generalizations of the linearized bregman method. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 3(4), 856–877 (2010)
Yin, W., Osher, S., Goldfarb, D., Darbon, J.: Bregman iterative algorithms for ℓ 1-minimization with applications to compressed sensing. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 1(1), 143–168 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the editors and anonymous referees for their useful suggestions. T. Sun, L. Chen, and H. Jiang are grateful for the support from the National Science Foundation of China (No.61402495).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Stephen Wright
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, T., Yin, P., Cheng, L. et al. Alternating direction method of multipliers with difference of convex functions. Adv Comput Math 44, 723–744 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-017-9559-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-017-9559-3
Keywords
- Nonconvex
- Alternating direction method of multipliers
- Difference of convex functions
- Kurdyka-Łojasiewicz property