Abstract
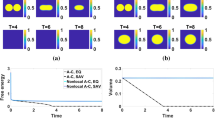
In this paper, we consider numerical approximations for solving the Cahn-Hilliard phase-field model with the Flory-Huggins-de Gennes free energy for homopolymer blends. We develop an efficient, second-order accurate, and unconditionally energy stable scheme that combines the SAV approach with the stabilization technique, in which the H1 norm is split from the total free energy and two extra linear stabilization terms are added to enhance the stability and keeping the required accuracy while using large time steps. The scheme is very easy to implement and non-iterative where one only needs to solve two decoupled fourth-order biharmonic equations with constant coefficients at each time step. We further prove the unconditional energy stability of the scheme rigorously. Through the comparisons with some other prevalent schemes like the non-stabilized-SAV and MSAV schemes for some benchmark numerical examples in 2D and 3D, we demonstrate the stability and the accuracy of the developed scheme numerically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binder, K.: Collective diffusion, nucleation, and spinodal decomposition in polymer mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 79, 6387 (1983)
Chen, C., Yang, X.: Efficient numerical scheme for a dendritic solidification phase field model with melt convection. J Comput. Phys. 388, 41–62 (2019)
Chen, C., Yang, X.: Fast, provably unconditionally energy stable, and second-order accurate algorithms for the anisotropic Cahn-Hilliard model. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg 351, 35–59 (2019)
Chen, F., Shen, J.: Efficient energy stable schemes with spectral discretization in space for anisotropic Cahn-Hilliard systems. Commun Comput. Phys. 05, 1189–1208 (2013)
Chen, L., Zhao, J., Yang, X.: Regularized linear schemes for the molecular beam epitaxy model with slope selection. Appl. Num Math. 128, 139–156 (2018)
Cheng, Q., Shen, J.: Multiple scalar auxiliary variable (MSAV) approach and its application to the phase-field vesicle membrane model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40, A3982–A4006 (2018)
Cheng, Q., Yang, X., Shen, J.: Efficient and accurate numerical schemes for a hydro-dynamically coupled phase field diblock copolymer model. J. Comp. Phys. 341, 44–60 (2017)
Cook, H. E.: Brownian motion in spinodal decomposition mouvement brownien dans la decomposition spinodale brownsche bewegung bei der spinodalen entmischung. Acta Metall 18, 297 (1970)
Copetti, M. I. M., Elliott, C. M.: Numerical analysis of the Cahn-Hilliard equation with a logarithmic free energy. Numer Math. 63(4), 39–65 (1992)
de Gennes, P. G.: Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics. Cornell University Press, Ithaca (1979)
de Gennes, P. G.: Dynamics of fluctuations and spinodal decomposition in polymer blends. J. Chem. Phys. 7, 4756 (1980)
Debussche, A., Dettori, L.: On the Cahn-Hilliard equation with a logarithmic free energy. Nonlinear analysis: Theory. Methods & Applications 24(10), 1491–1514 (1995)
Elliott, C. M., Garcke, H.: On the Cahn-Hilliard equation with degenerate mobility. SIAMJ Math. Anal. 27, 404–423 (1996)
Eyre, D. J.: Unconditionally Gradient Stable Time Marching the Cahn-Hilliard Equation. In: Computational and Mathematical Models of Microstructural Evolution (San Francisco, CA, 1998), volume 529 of Mater. Res. Soc. Sympos. Proc., pp 39–46. MRS, Warrendale (1998)
Feng, X., Prol, A.: Numerical analysis of the Allen-Cahn equation and approximation for mean curvature flows. Numer. Math. 94, 33–65 (2003)
Fialkowski, M., Holyst, R.: Dynamics of phase separation in polymer blends revisited: morphology, spinodal, noise, and nucleation. Macromol. Theory Simul. 17, 263 (2008)
Forster, S., Khandpur, A. K., Zhao, J., Bates, F. S.: Complex phase behavior of polyisoprene-polystyrene diblock copolymers near the order-disorder transition. Macromolecules 27, 6922–6935 (1994)
Gao, Y., He, X., Mei, L., Yang, X.: Decoupled, linear, and energy stable finite element method for Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes-Darcy phase field model. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 40, B110–B137 (2018)
Gomez, H., Calo, V. M., Bazilevs, Y., Hughes, T.J.R.: Isogeometric analystis of the Cahn-Hilliard phase-field model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 197, 4333–4352 (2008)
Gomez, H., Van der, Z., Kristoffer, G.: Computational phase-field modeling. In: Encyclopedia of Computational Mechanics, Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, ISBN 978-1-119-00379-3 (2017)
Gomez, H., Hughes, T.J.R.: Provably unconditionally stable, second-order time-accurate, mixed variational methods for phase-field models. J. Comput. Phys. 230, 5310–5327 (2011)
Han, D., Brylev, A., Yang, X., Tan, Z.: Numerical analysis of second order, fully discrete energy stable schemes for phase field models of two phase incompressible flows. J. Sci Comput. 70, 965–989 (2017)
Han, D., Wang, X.: A second order in time, uniquely solvable, unconditionally stable numerical scheme for Cahn-Hilliard-Navier-Stokes equation. J Comput. Phys. 290, 139–156 (2015)
Huang, Q., Yang, X., He, X.: Numerical approximations for a smectic–a liquid crystal flow model first-order, linear, decoupled and energy stable schemes. Disc. Conti. Dyn. Sys.-B 23, 2177–2192 (2018)
Kim, J., Lowengrub, J.: Phase field modeling and simulation of three-phase flows. Interfaces and Free Boundaries 7, 435–466 (2005)
Lowengrub, J., Truskinovsky, L.: Quasi-incompressible Cahn-Hilliard fluids and topological transitions. R. Soc. Lond. Proc. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454 (1978), 2617–2654 (1998)
Romero, I.: Thermodynamically consistent time stepping algorithms for nonlinear thermomechanical systems. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng. 79, 706–732 (2009)
Schimperna, G., Pawlow, I.: On a class of Cahn-Hilliard models with nonlinear diffusion. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 45(4), 31–63 (2013)
Shen, J., Wang, C., Wang, S., Wang, X.: Second-order convex splitting schemes for gradient flows with Ehrlich-Schwoebel type energy: application to thin film epitaxy. in press, SIAM J. Numer. Anal (2011)
Shen, J., Xu, J.: Convergence and error analysis for the scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) schemes to gradient flows. SIAM J. Numer Anal. 56, 2895–2912 (2019)
Shen, J., Xue, J., Yang, J.: The scalar auxiliary variable (SAV) approach for gradient flows. J. Comput. Phys. 353, 407–416 (2018)
Shen, J., Yang, X.: Numerical approximations of Allen-Cahn and Cahn-Hilliard equations. Disc. Conti. Dyn. Sys.-A 28, 1669–1691 (2010)
Wodo, O., Ganapathysubramanian, B.: Computationally efficient solution to the Cahn-Hilliard equation adaptive implicit time schemes, mesh sensitivity analysis and the 3D isoperimetric problem. J. Comp. Phys. 230(15), 6037–6060 (2011)
Xu, Z., Yang, X., Zhang, H., Xie, Z.: Efficient and linear schemes for anisotropic Cahn-Hilliard model using the stabilized-invariant energy quadratization (s-IEQ) approach. Comput. Phys. Commun. 238, 36–49 (2019)
Yang, X.: Linear, first and second order and unconditionally energy stable numerical schemes for the phase field model of homopolymer blends. J. Comput. Phys. 327, 294–316 (2016)
Yang, X.: Numerical approximations for the Cahn-Hilliard phase field model of the binary fluid-surfactant system. J. Sci. Comput 74, 1533–1553 (2017)
Yang, X.: Efficient Linear, stabilized, second order time marching schemes for an anisotropic phase field dendritic crystal growth model. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 347, 316–339 (2019)
Yang, X., Zhang, G. -D.: Numerical approximations of the Cahn-Hilliard and Allen-Cahn equations with general nonlinear potential using the invariant energy quadratization approach submitted (2018)
Yang, X., Zhao, J., He, X.: Linear, second order and unconditionally energy stable schemes for the viscous Cahn-Hilliard equation with hyperbolic relaxation using the invariant energy quadratization method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 343, 80–97 (2018)
Yang, X., Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Shen, J.: Numerical approximations for a three components Cahn-Hilliard phase-field model based on the invariant energy quadratization method. M3AS: Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences 27, 1993–2030 (2017)
Yuan, C., Zhang, H.: Self-consistent mean field model of hydrogel and its numerical simulation. J. Theor. Comput. Chem. 12, 1350048 (2013)
Zhao, J., Yang, X., Gong, Y., Wang, Q.: A novel linear second order unconditionally energy stable scheme for a hydrodynamic Q-tensor model of liquid crystals. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech Engrg. 318, 803–825 (2017)
Funding
J. Zhang was supported by the Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province (No.[2020]1Y013), and Guizhou Key Laboratory of Big Data Statistics Analysis (No. BDSA20190107) .X. Yang was partially supported by NSF-DMS-1720212 and DMS-1818783.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Long Chen
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Yang, X. Non-iterative, unconditionally energy stable and large time-stepping method for the Cahn-Hilliard phase-field model with Flory-Huggins-de Gennes free energy. Adv Comput Math 46, 47 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-020-09793-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-020-09793-z