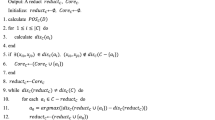Abstract
Attribute reduction plays a vital role in many areas of data mining and knowledge discovery. In the real world, several data sets may vary dynamically and many incremental reduction algorithms have been proposed to update reduct. Further improvement of the performance of the incremental reduction approach is an important task that can help to increase the efficiency of knowledge discovery in dynamic data systems. This paper researches incremental reduction algorithms via an acceleration strategy to compute new reduct based on conflict region. We firstly introduce the concepts and propositions of the conflict region and give a static reduction algorithm based on the conflict region. Consequently, incremental mechanisms based on the conflict region and an acceleration strategy for reduction are discussed. Then, two incremental reduction algorithms for updating new reduct when one single object and multi-objects are added to decision systems are developed. Finally, experiments on different data sets from UCI show the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed algorithms in decision systems with the addition of objects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen HM, Li TR, Qiao SJ, Ruan D (2010) A rough sets based dynamic maintenance approach for approximations in coarsening and refining attribute values. Int J Intell Syst 25(10):1005–1026
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D (2012) Maintenance of approximations in incomplete ordered decision information systems. Knowl Based Syst 31:140–161
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D, Lin JH, Hu CX (2013) A rough set based incremental approach for updating approximations under dynamic maintenance environments. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(2):274–284
Fan YN, Tseng TL, Chern CC, Huang CC (2009) Rule induction based on an incremental rough set. Expert Syst Appl 36(9):11439–11450
Ge H, Li LS, Yang CJ (2012) A efficient attribute reduction algorithm based on conflict region. Chin J Comput 35(2):342–350
Ge H, Li LS, Xu Y, Yang CJ (2015) Bidirectional heuristic attribute reduction based on conflict region. Soft Comput 19(7):1973–1986
Hu XH, Cercone N (1995) Learning in relational databases a rough set approach. Int J Comput Intell 11(2):323–338
Hu F, Wang GY, Huang H, Wu Y (2005) Incremental attribute reduction based on elementary sets. In:10th International conference on rough sets fuzzy sets data mining and granular computing, pp 185–193
Hu QH, Xie ZX, Yu DR (2007) Hybrid attribute reduction based on a novel fuzzy rough model and information granulation. Pattern Recognit 40:3509–3521
Huang CC, Tseng TL, Fan YN, Hsu CH (2013) Alternative rule induction methods based on incremental object using rough set theory. Appl Soft Comput 13(1):372–389
Huang CC, Tseng TL, Tang CY (2016) Feature extraction using rough set theory in service sector application from incremental perspective. Comput Ind Eng 91:30–41
Jing YG, Li TR, Luo C, Horng SJ, Wang GY, Yu Z (2016a) An incremental approach for attribute reduction based on knowledge granularity. Knowl Based Syst 104:24–38
Jing YG, Li TR, Huang JF, Zhang YY (2016b) An incremental attribute reduction approach based on knowledge granularity under the attribute generalization. Int J Approx Reason 76:80–95
Lang GM, Ling QG, Yang T (2014) An incremental approach to attribute reduction of dynamic set-valued information systems. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 5(5):775–788
Li TR, Ruan D, Geert W, Song J, Xu Y (2007) A rough sets based characteristic relation approach for dynamic attribute generalization in data mining. Knowl Based Syst 20:485–494
Li RP, Yao YY (2010) Indiscernibility and similarity in an incomplete information table. In: 5th International conference of rough set and knowledge technology, pp 15–17
Li SY, Li TR, Liu D (2013) Incremental updating approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach under the variation of the attribute set. Knowl Based Syst 40:17–26
Li SY, Li TR (2015) Incremental update of approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach under the variation of attribute values. Inf Sci 294:348–361
Liang JY, Xu ZB (2002) The algorithm on knowledge reduction in incomplete information systems. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness 10(1):95–103
Liang JY, Wang F, Dang CY, Qian YH (2014) A group incremental approach to feature selection applying rough set technique. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(2):294–308
Liu ZT (1999) An incremental arithmetic for the smallest reduction of attributes. Acta Electronica Sinica 27(11):96–98
Liu Y, Xiong R, Chu J (2009) Quick attribute reduction algorithm with hash. Chin J Comput 32(8):1493–1499
Miao DQ, Hu GR (1999) An heuristic algorithm of knowledge reduction. Chin J Comput Res Dev 36(6):681–684
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Qian YH, Liang JY, Wang F (2009) A new method for measuring the uncertainty in incomplete information systems. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness 17(6):855–880
Qian YH, Liang JY, Pedrycz W, Dang CY (2010) Positive approximation: an accelerator for attribute reduction in rough set theory. Artif Intell 174:597–618
Qian J, Miao DQ, Zhang ZH, Li W (2011) Hybrid approaches to attribute reduction based on indiscernibility and discernibility relation. Int J of Approx Reason 52(2):212–230
Shen Q, Jensen R (2004) Selecting informative features with fuzzy-rough sets and its application for complex systems monitoring. Pattern Recognit 37(7):1351–1363
Shu WH, Shen H (2014a) Updating attribute reduction in incomplete decision systems with the variation of attribute set. Int J Approx Reason 55:867–884
Shu WH, Shen H (2014b) Incremental feature selection based on rough set in dynamic incomplete data. Pattern Recognit 47:3890–3906
Skowron A, Rauszer C (1992) The discernibility matrices and functions in information systems. Intell Decis Support 11:331–362
Susmaga R, Słowiński R (2015) Generation of rough sets reducts and constructs based on inter-class and intra-class information. Fuzzy Set Syst 274:124–142
Teng SH, Zan DC, Sun JX (2010) Attribute reduction algorithm based on common discernibility degree. Chin J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 23(1):630–638
Wang F, Liang JY, Qian YH (2013a) Attribute reduction: a dimension incremental strategy. Knowl Based Syst 39:95–108
Wang F, Liang JY, Dang CY (2013b) Attribute reduction for dynamic data sets. Appl Soft Comput 13:676–689
Wei W, Liang JY, Wang JH, Qian YH (2013) Decision-relative discernibility matrixes in the sense of entropies. Int J of Gen Syst 42(7):721–738
Xu YT, Wang LS, Zhang RY (2011) A dynamic attribute reduction algorithm based on 0–1 integer programming. Knowl Based Syst 24(8):1341–1347
Xu ZY, Liu ZP, Yang BY, Song W (2006) A quick attribute reduction algorithm with complexity of max\((O({\vert }C{\vert }{\vert }U{\vert }) O({\vert }C{\vert }^{2}{\vert }U/C{\vert }))\). Chin J Comput 29(3):611–615
Yang M (2007) An incremental updating algorithm for attributes reduction based on the improved discernibility matrix. Chin J Comput 30(5):815–822
Yao YY, Zhao Y (2009) Discernibility matrix simplification for constructing attribute reducts. Inf Sci 179(7):867–882
Zeng AP, Li TR, Liu D, Chen HM (2015) A fuzzy rough set approach for incremental feature selection on hybrid information systems. Fuzzy Set Syst 258(1):39–60
Zhang WX, Mi JS, Wu WZ (2003) Approaches to knowledge reductions in inconsistent systems. Int J Intell Syst 18(9):989–1000
Zhang JB, Li TR, Ruan D, Liu D (2012) Rough sets based matrix approaches with dynamic attribute variation in set valued information systems. Int J Approx Reason 53(4):620–635
Zhao Y, Yao YY, Luo F (2007) Data analysis based on discernibility and indiscernibility. Inf Sci 177(22):4959–4976
Zhou JW, Feng BQ, Liu Y (2007) New algorithm for quick computing core. Chin J Xi’an Jiaotong Univ 41(6):688–691
Acknowledgements
Research on this work is partially supported by the grants from the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51307011, 61402005), by the funds from Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 1508085MF126, 1508085MF127), by the fund from Anhui Education Natural Science Foundation (No. KJ2013A015), by the fund from Outstanding young talent foundation of Chuzhou University (No. 2013RC03), and by the fund from Initial Scientific Research of Chuzhou University (No. 2016qd07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, G., Longshu, L., Chuanjian, Y. et al. Incremental reduction algorithm with acceleration strategy based on conflict region. Artif Intell Rev 51, 507–536 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9570-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9570-6