Abstract
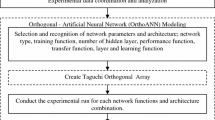
As surveyed, many efforts have been made to model the performances of electrical discharge machining (EDM) using artificial neural network (ANN). However, the selections of the network parameters were mostly prepared in a random manner, resulting to unnecessary trials. Thus, orthogonal array (Taguchi) is employed in the procedure of network function and network architecture assortment to avoid excessive random trial experimentations. This proposed orthogonal based ANN modelling is employed on WEDM of Ti–48Al intermetallic alloys. Meanwhile modified multi objective genetic algorithm (multiGA) is used as the optimization technique. Material removal rate (MRR), surface roughness (Ra), cutting speed (Vc) and width of kerf (Dk) are the machining performances considered in this study. Five machining parameters observed from the previous researches are chosen as significant factors to the machining performances in this study, which are pulse on time, pulse off time, peak current, feed rate and servo voltage. Experimental studies are carried out to verify the machining performances suggested by this approach. Feed forward back propagation neural network (FFNN) is found to be the best network type on the selected dataset. Two hidden layer 5–6–6–4 FFNN showed the most precise and generalized network architecture with very good prediction accuracy. The proposed approach, OrthoANN, reduced ANN experimentation time by a large scale and produced viable results for machining optimization when integrated with multiGA.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhishek K, Kumar VR, Datta S, Mahapatra SS (2015) Parametric appraisal and optimization in machining of CFRP composites by using TLBO (teaching–learning based optimization algorithm). J Intell Manuf 28:1769–1785
Al-Ghamdi K, Taylan O (2015) A comparative study on modelling material removal rate by ANFIS and polynomial methods in electrical discharge machining process. Comput Ind Eng 79:27–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2014.10.023
Ali-Tavoli M, Nariman-Zadeh N, Khakhali A, Mehran M (2006) Multi-objective optimization of abrasive flow machining processes using polynomial neural networks and genetic algorithms. Mach Sci Technol 10:491–510. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910340600996126
Assarzadeh S, Ghoreishi M (2007) Neural-network-based modelling and optimization of the electro-discharge machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39:488–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1235-1
Azad MS, Puri AB (2012) Simultaneous optimisation of multiple performance characteristics in micro-EDM drilling of titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61:1231–1239
Azadi Moghaddam M, Kolahan F (2015) Optimization of EDM process parameters using statistical analysis and simulated annealing algorithm. Int J Eng 28:154–163
Azhiri RB, Teimouri R, Baboly MG, Leseman Z (2014) Application of Taguchi, ANFIS and grey relational analysis for studying, modelling and optimization of wire EDM process while using gaseous media. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71:279–295
Azizul M, Arshad NS, Ghulam AQ (2012) Optimization of EDM process parameters using Taguchi method. In: Proceedings of the international conference on applications and design in mechanical engineering
Baraskar SS, Banwait SS, Laroiya SC (2013) Multiobjective optimization of electrical discharge machining process using a hybrid method. Mater Manuf Process 28:348–354. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2012.700152
Beri N, Maheshwari S, Sharma C, Kumar A (2011) Multi-objective parametric optimisation during electrical discharge machining of Inconel 718 with different electrodes. Int J Mater Eng Innov 2:236–248
Bharti PS, Maheshwari S, Sharma C (2012) Multi-objective optimization of electric-discharge machining process using controlled elitist NSGA-II. J Mech Sci Technol 26:1875–1883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0411-x
Bouacha K, Terrab A (2016) Hard turning behavior improvement using NSGA-II and PSO-NN hybrid model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8479-6
Bouzakis KD, Paraskevopoulou R, Giannopoulos G (2008) Multi-objective optimization of cutting conditions in milling using genetic algorithms. In: Bouzakis KD (ed) Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on manufacturing engineering (ICMEN), Chalkidiki, Greece, 2008. EE\(\Delta \)M and PCCM
Butler NA (2001) Optimal and orthogonal Latin hypercube designs for computer experiments. Biometrika 88:847–857
Choudhuri K, Pratihar DK, Pal DK (2001) Multi-objective optimization in turning—using a genetic algorithm. J Inst Eng (India) Part PR Prod Eng Div 82:37–44
Das R, Pradhan MK (2013) ANN modelling for surface roughness in electrical discharge machining: a comparative study. Int J Serv Comput Orient Manuf 1:124–140
Datta R, Deb K (2009) A classical-cum-evolutionary multi-objective optimization for optimal machining parameters. In: World congress on nature and biologically inspired computing, 2009. NaBIC 2009. IEEE, pp 607–612
Datta R, Majumder A (2010) Optimization of turning process parameters using multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. In: 2010 IEEE congress on in evolutionary computation (CEC). IEEE, pp 1–6
Dave HK, Desai KP, Raval HK (2012) Optimisation of multiple response characteristics in orbital electro discharge machining of Inconel 718 using Taguchi’s loss function. Int J Manuf Technol Manag 25:78–94
Deb K, Datta R (2011) Hybrid evolutionary multi-objective optimization and analysis of machining operations. Eng Optim. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215x.2011.604316
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 6:182–197
Deris AM, Zain AM, Sallehuddin R (2011) Overview of support vector machine in modelling machining performances. Proc Eng 24:308–312
Dhavamani C, Alwarsamy T (2011) Optimization of cutting parameters of composite materials using genetic algorithm. Eur J Sci Res 63:279–285
Dubey AK (2008) A hybrid approach for multi-performance optimization of the electro-chemical honing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1422-8
Durán O, Barrientos R, Consalter LA (2007) Multi objective optimization in machining operations. In: Melin P, Castillo O, Ramírez EG, Kacprzyk J, Pedrycz W (eds) Analysis and design of intelligent systems using soft computing techniques. Springer, Berlin, pp 455–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72432-2_46
El-Hossainy TM, El-Tamimi AM, Abdelmaguid TF (2012) Using NSGA-II to optimise tool life and production time for turning under minimum quantity lubrication. Int J Manuf Res 7:290–310
Fenggou C, Dayong Y (2004) The study of high efficiency and intelligent optimization system in EDM sinking process. J Mater Process Technol 149:83–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2003.10.059
Fonseca CM, Fleming PJ (1993) Multiobjective genetic algorithms. In: IEE colloquium on genetic algorithms for control systems engineering, pp 6/1–6/5
Ganesan H, Mohankumar G (2013) Optimization of machining techniques in CNC turning centre using genetic algorithm. Arab J Sci Eng 38:1529–1538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0539-8
Geem ZW, Kim JH, Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. Simulation 76:60–68
Golshan A, Gohari S, Ayob A (2011a) Comparison of intelligent optimization algorithms for wire electrical discharge machining parameters. In: 2011 third international conference on computational intelligence, modelling and simulation (CIMSiM). IEEE, pp 134–140
Golshan A, Gohari S, Ayob A (2011b) Computational intelligence in optimization of wire electrical discharge machining of cold-work steel 2601. Int J Mech Mechatron Eng 11:14–19
Golshan A, Gohari S, Ayob A (2011c) Modelling and optimization of cylindrical wire electro discharge machining of AISI D3 tool steel using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. In: International conference on graphic and image processing (ICGIP 2011). International Society for Optics and Photonics, vol 8285, p 82853V
Gomes JHDF, De Paiva AP, Ferreira JR, da Costa SC, De Paiva EJ (2011) Modelling and optimization of multiple characteristics in the AISI 52100 hardened steel turning. Adv Mater Res 223:545–553
Gowd GH, Goud MV, Theja KD, Reddy MG (2014) Optimal selection of machining parameters in CNC turning process of EN-31 using intelligent hybrid decision making tools. Proc Eng 97:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.233
Hedayat AS, Sloane NJA, Stufken J (2012) Orthogonal arrays: theory and applications. Springer, Berlin
Ho K, Newman S (2003) State of the art electrical discharge machining (EDM). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:1287–1300
Ho KH, Newman ST, Rahimifard S, Allen RD (2004) State of the art in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44:1247–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.04.017
Huang J-T, Liao Y-S (2003) Optimization of machining parameters of wire-EDM based on grey relational and statistical analyses. Int J Prod Res 41:1707–1720
Hwang Y, Qian PZG, He X (2016) Sliced orthogonal array-based Latin hypercube designs. Technometrics 58:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.2014.993092
Janmanee P, Muttamara A (2011) Optimization of electrical discharge machining of composite 90WC-10Co base on taguchi approach. Eur J Sci Res 64:426–436
Jianling C (2009) Multi-objective optimization of cutting parameters with improved NSGA-II. In: International conference on management and service science, 2009. MASS ’09, pp 1–4
Johari NF, Zain AM, Mustaffa NH, Udin A (2015) Optimization of surface roughness in turning operation using firefly algorithm. Appl Mech Mater 815:268–272
Jones PM, Tiwari A, Roy R, Corbett J (2004) Optimisation of the high efficiency deep grinding process with fuzzy fitness function and constraints. In: Congress on evolutionary computation, 2004. CEC2004, 19–23 June 2004, vol 571, pp 574–581. https://doi.org/10.1109/cec.2004.1330909
Joseph VR, Hung Y (2008) Orthogonal-maximin Latin hypercube designs. Stat Sin 18:171–186
Joshi SN, Pande SS (2011) Intelligent process modelling and optimization of die-sinking electric discharge machining. Appl Soft Comput 11:2743–2755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2010.11.005
Juhr H, Künanz K, Nestler A, Leitte G (2004) Generation of parameter technologies for EDM die sinking with artificial neural networks (ANN) and nonlinear regression functions (NRF). Forschungsergebnis bericht
Kamaruzaman AF, Zain AM, Yusuf SM, Udin A (2013) Levy flight algorithm for optimization problems—a literature review. Appl Mech Mater 421:496–501
Kamsir AS (2006) Wire electrical discharge machining of Ti-48A1 intermetalic alloys using Taguchi approach. Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor Bahru
Kanagarajan D, Karthikeyan R, Palanikumar K, Davim JP (2008) Optimization of electrical discharge machining characteristics of WC/Co composites using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36:1124–1132
Kannan TDB, Kannan GR, Kumar BS, Baskar N (2014) Application of artificial neural network modelling for machining parameters optimization in drilling operation. Proc Mater Sci 5:2242–2249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.433
Kara F, Aslantas K, Çiçek A (2014) ANN and multiple regression method-based modelling of cutting forces in orthogonal machining of AISI 316L stainless steel. Neural Comput Appl 26:237–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1721-y
Karabulut Ş, Karakoç H (2015) Investigation of surface roughness in the milling of Al7075 and open-cell SiC foam composite and optimization of machining parameters. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2058-x
Karagiannis S, Iakovakis V, Kechagias J, Fountas N, Vaxevanidis N (2013) Prediction of surface texture characteristics in turning of FRPs using ANN. In: Iliadis L, Papadopoulos H, Jayne C (eds) Engineering applications of neural networks: 14th international conference, EANN 2013, Halkidiki, Greece, September 13–16, 2013 Proceedings, Part I. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 144–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41013-0_15
Khan MAR, Rahman MM, Kadirgama K (2014) Neural network modelling and analysis for surface characteristics in electrical discharge machining. Proc Eng 90:631–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.783
Kodali SP, Kudikala R, Deb K (2008) Multi-objective optimization of surface grinding process using NSGA II. In: In: First international conference on emerging trends in engineering and technology, 2008. ICETET’08. IEEE, pp 763–767
Kondayya D, Gopala Krishna A (2011) An integrated evolutionary approach for modelling and optimization of wire electrical discharge machining. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 225:549–567
Kumar K, Agarwal S (2011) Multi-objective parametric optimization on machining with wire electric discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62:617–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3833-1
Kuriakose S, Shunmugam MS (2005) Multi-objective optimization of wire-electro discharge machining process by non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. J Mater Process Technol 170:133–141
Latha B, Senthilkumar VS (2009) Simulation optimization of process parameters in composite drilling process using multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. In: International conference on advances in recent technologies in communication and computing, 2009. ARTCom’09. IEEE, pp 154–159
Leary S, Bhaskar A, Keane A (2003) Optimal orthogonal-array-based Latin hypercubes. J Appl Stat 30:585–598
Lin CD, Mukerjee R, Tang B (2009) Construction of orthogonal and nearly orthogonal Latin hypercubes. Biometrika 96:243–247
Lin CD, Bingham D, Sitter RR, Tang B (2010) A new and flexible method for constructing designs for computer experiments. Ann Stat 38:1460–1477
Mahdavinejad R (2010) Optimizing of turning parameters using multi-objective genetic algorithm. Adv Mater Res 118–120:359–363
Mahdavinejad RA (2011) Modelling and optimization of electrical discharge machining of SiC parameters, using neural network and non-dominating sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA II). Mater Sci Appl 2:669
Maity K, Mishra H (2016) ANN modelling and Elitist teaching learning approach for multi-objective optimization of \(\mu \). EDM J Intell Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-016-1193-2
Maji K, Pratihar D (2010) Modelling of electrical discharge machining process using conventional regression analysis and genetic algorithms. J Mater Eng Perform. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9754-6
Mandal D, Pal SK, Saha P (2007) Modelling of electrical discharge machining process using back propagation neural network and multi-objective optimization using non-dominating sorting genetic algorithm-II. J Mater Process Technol 186:154–162
Mandal K (2013) Development of an ANN model to predict surface roughness during cryogenic machining operation. J Adv Mater Manufacturing Char 3:281–284
Markopoulos AP, Manolakos DE, Vaxevanidis NM (2008) Artificial neural network models for the prediction of surface roughness in electrical discharge machining. J Intell Manuf 19:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-008-0081-9
McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ (2000) A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 42:55–61
Mitra K (2009) Multiobjective optimization of an industrial grinding operation under uncertainty. Chem Eng Sci 64:5043–5056
Mitra S, Sarkar S, Paul G, Bhaduri D, Sampad B (2011) Pareto optimization of electro discharge machining of titanium nitride-aluminium oxide composite material using Genetic algorithm. vol 264–265, pp 985–990
Mitra K, Gopinath R (2004) Multiobjective optimization of an industrial grinding operation using elitist nondominated sorting genetic algorithm. Chem Eng Sci 59:385–396
Mohamad A, Zain AM, Bazin NEN, Udin A (2013) A process prediction model based on Cuckoo algorithm for abrasive waterjet machining. J Intell Manuf 26:1247–1252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0853-8
Mohd Adnan MRH, Sarkheyli A, Mohd Zain A, Haron H (2013) Fuzzy logic for modelling machining process: a review. Artif Intell Rev 43:345–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-012-9381-8
Morris MD, Mitchell TJ (1995) Exploratory designs for computational experiments. J Stat Plan Inference 43:381–402
Nidhra S, Dondeti J (2012) Blackbox and whitebox testing techniques—a literature review. Int J Embed Syst Appl (IJESA) 2:29–50
Padhee S, Nayak N, Panda S, Dhal P, Mahapatra S (2012) Multi-objective parametric optimization of powder mixed electro-discharge machining using response surface methodology and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Sadhana 37:223–240
Palanikumar K, Latha B, Senthilkumar VS, Karthikeyan R (2009) Multiple performance optimization in machining of GFRP composites by a PCD tool using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II). Met Mater Int 15:249–258
Panda DK (2010) Modelling and optimization of multiple process attributes of electrodischarge machining process by using a new hybrid approach of neuro-grey modelling. Mater Manuf Process 25:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1080/15394450902996551
Panda DK, Bhoi RK (2005) Artificial neural network prediction of material removal rate in electro discharge machining. Mater Manuf Process 20:645–672. https://doi.org/10.1081/amp-200055033
Park J-S (1994) Optimal Latin-hypercube designs for computer experiments. J Stat Plan Inference 39:95–111
Patowari PK, Saha P, Mishra PK (2010) Artificial neural network model in surface modification by EDM using tungsten-copper powder metallurgy sintered electrodes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2653-z
Pradhan MK, Biswas CK (2010) Neuro-fuzzy and neural network-based prediction of various responses in electrical discharge machining of AISI D2 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50:591–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2531-8
Pradhan MK, Das R (2011) Recurrent neural network estimation of material removal rate in electrical discharge machining of AISI D2 tool steel. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 225:414–421. https://doi.org/10.1177/2041297510394083
Prasad D, Krishna AG (2009) Empirical modeling and optimization of wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 43:914–925
Pressman RS (2005) Software engineering: a practitioner’s approach. Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke
Qian PZ (2012) Sliced Latin hypercube designs. J Am Stat Assoc 107:393–399
Quiza Sardinas R, Albelo Mengana JE, Davim JP (2009) Multi-objective optimisation of multipass turning by using a genetic algorithm. Int J Mater Prod Technol 35:134–144
Rao RV, Kalyankar V (2014) Optimization of modern machining processes using advanced optimization techniques: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73:1159–1188
Rao TB, Krishna AG, Katta RK, Krishna KR (2014) Modelling and multi-response optimization of machining performance while turning hardened steel with self-propelled rotary tool. Adv Manuf 3:84–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-014-0092-z
Saha P, Saha P, Pal S (2011) Parametric optimization in WEDM of WC–Co composite by neuro-genetic technique. In: Proceedings of the world congress on engineering, pp 6–8
Santos MC, Machado AR, Barrozo MAS, Jackson MJ, Ezugwu EO (2014) Multi-objective optimization of cutting conditions when turning aluminum alloys (1350-O and 7075-T6 grades) using genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76:1123–1138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6314-5
Saravanan R, Asokan P, Sachidanandam M (2002) A multi-objective genetic algorithm (GA) approach for optimization of surface grinding operations. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:1327–1334. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0890-6955(02)00074-3
Sardinas RQ, Reis P, Davim JP (2006a) Multi-objective optimization of cutting parameters for drilling laminate composite materials by using genetic algorithms. Compos Sci Technol 66:3083–3088
Sardinas RQ, Santana MR, Brindis EA (2006b) Genetic algorithm-based multi-objective optimization of cutting parameters in turning processes. Eng Appl Artif Intell 19:127–133
Sarkheyli A, Zain AM, Sharif S (2015) Robust optimization of ANFIS based on a new modified GA. Neurocomputing 166:357–366
Satyanarayana B, Yadav GSG, Nitin PR, Reddy MD (2015) Simultaneous optimization of multi performance characteristics in dry turning of Inconel 718 using NSGA-II. Mater Today Proc 2:2423–2432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.182
Schonlau M, Hamada M, Welch WJ (1996) Identifying parametric nonlinear models for computer codes. Technical report RR-96-02, University of Waterloo Institute for Improvement in Quality and Productivity, Waterloo, ON, Canada. http://www.bisrg.uwaterloo.ca/archive/RR-96-02.pdf. Last accessed on 1 Nov 2014
Senthilkumar C, Ganesan G, Karthikeyan R (2010) Bi-performance optimization of electrochemical machining characteristics of Al/20% SiCp composites using NSGA-II. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 224:1399–1407
Senthilkumar C, Ganesan G, Karthikeyan R (2011) Parametric optimization of electrochemical machining of Al/15% SiCp composites using NSGA-II. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China (English Edn) 21:2294–2300
Solimanpur M, Ranjdoostfard F (2009) Optimisation of cutting parameters using a multi-objective genetic algorithm. Int J Prod Res 47:6019–6036
Srinivas N, Deb K (1994) Muiltiobjective optimization using nondominated sorting in genetic algorithms. Evol Comput 2:221–248
Steinberg DM, Lin DK (2006) A construction method for orthogonal Latin hypercube designs. Biometrika 93:279–288
Su CH, Hou TH (2008) Using multi-population intelligent genetic algorithm to find the pareto-optimal parameters for a nano-particle milling process. Expert Syst Appl 34:2502–2510
Sultana I, Dhar NR (2010) GA based multi objective optimization of the predicted models of cutting temperature, chip reduction co-efficient and surface roughness in turning AISI 4320 steel by uncoated carbide insert under HPC condition. In: Proceedings of the 2010 international conference on mechanical, industrial, and manufacturing technologies, MIMT, pp 161–167
Sun F, Tang B (2016) A method of constructing space-filling orthogonal designs. J Am Stat Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.2016.1159211
Sundaram M, Pavalarajan G, Rajurkar K (2008) A study on process parameters of ultrasonic assisted micro EDM based on Taguchi method. J Mater Eng Perform 17:210–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-007-9128-x
Tang B (1993) Orthogonal array-based Latin hypercubes. J Am Stat Assoc 88:1392–1397. https://doi.org/10.2307/2291282
Tang B (1998) Selecting Latin hypercubes using correlation criteria. Stat Sin 8:965–977
Tiwari A, Mandal A, Kumar K (2015) Multi-objective optimization of electro-chemical machining by non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Mater Today Proc 2:2569–2575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.208
Tsai K-M, Wang P-J (2001) Predictions on surface finish in electrical discharge machining based upon neural network models. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41:1385–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(01)00028-1
Ugrasen G, Ravindra HV, Prakash GVN, Keshavamurthy R (2014) Estimation of machining performances using mRA, GMDH and artificial neural network in wire EDM of EN-31. Proc Mater Sci 6:1788–1797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.209
Vates U, Singh N, Singh R (2014) Modelling of process parameters on D2 steel using wire electrical discharge machining with combined approach of RSM and ANN. Int J Sci Eng Res 5:2026
Venkataraman R (2012) Multi objective optimization of electro discharge machining of resin bonded silicon carbide. Appl Mech Mater 110–116:1556–1560
Venkatesan D, Kannan K, Saravanan R (2008) A genetic algorithm-based artificial neural network model for the optimization of machining processes. Neural Comput Appl 18:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-007-0166-y
Wang Z, Wong Y, Rahman M, Sun J (2006) Multi-objective optimization of high-speed milling with parallel genetic simulated annealing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-005-0191-x
Wang Q, Liu F, Wang X (2013) Multi-objective optimization of machining parameters considering energy consumption. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71:1133–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5547-z
Yadav RN, Yadava V (2013) Multiobjective optimization of slotted electrical discharge abrasive grinding of metal matrix composite using artificial neural network and nondominated sorting genetic algorithm. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 227:1442–1452
Yaman S, Lee C-H (2010) A comparison of single-and multi-objective programming approaches to problems with multiple design objectives. J Signal Process Syst 61:39–50
Yang J, Liu M-Q (2012) Construction of orthogonal and nearly orthogonal Latin hypercube designs from orthogonal designs. Stat Sin 22:433–442
Yang S, Natarajan U (2010) Multi-objective optimization of cutting parameters in turning process using differential evolution and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II approaches. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49:773–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2404-1
Ye KQ (1998) Orthogonal column Latin hypercubes and their application in computer experiments. J Am Stat Assoc 93:1430–1439
Yildiz AR, Ozturk F (2006) Hybrid enhanced genetic algorithm to select optimal machining parameters in turning operation. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 220:2041–2053
Yin YH, Lin DKJ, Liu MQ (2014) Sliced Latin hypercube designs via orthogonal arrays. J Stat Plan Inference 149:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspi.2014.02.008
Yusoff Y, Ngadiman MS, Zain AM (2011) Overview of NSGA-II for optimizing machining process parameters. Proc Eng 15:3978–3983
Yusup N, Zain AM, Hashim SZM (2012) Evolutionary techniques in optimizing machining parameters: review and recent applications (2007–2011). Expert Syst Appl 39:9909–9927
Zain AM, Haron H, Sharif S (2009) Review of ANN technique for modelling surface roughness performance measure in machining process. In: Third Asia international conference on modelling and simulation, 2009. AMS’09. IEEE, pp 35–39
Zain AM, Haron H, Sharif S (2012) Integrated ANN-GA for estimating the minimum value for machining performance. Int J Prod Res 50:191–213
Zainal N, Zain AM, Radzi NHM, Othman MR (2014) Glowworm swarm optimization (GSO) for optimization of machining parameters. J Intell Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0914-7
Zhang L, Jia Z, Wang F, Liu W (2010) A hybrid model using supporting vector machine and multi-objective genetic algorithm for processing parameters optimization in micro-EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:575–586
Zhang Q et al (2011) Modelling and optimal design of machining-induced residual stresses in aluminium alloys using a fast hierarchical multiobjective optimization algorithm. Mater Manuf Process 26:508–520
Zitzler E, Thiele L (1998) An evolutionary algorithm for multiobjective optimization: the strength Pareto approach
Acknowledgements
Special appreciations to editor and all reviewers on the useful advices and comments provided. The authors greatly acknowledge the Research Management Centre, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM), Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE) (GUP—vot. No. 16H81, FRGS—vot. No. 4F378) and international grant (ERL—vot. No. 4B310) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yusoff, Y., Zain, A.M., Amrin, A. et al. Orthogonal based ANN and multiGA for optimization on WEDM of Ti–48Al intermetallic alloys. Artif Intell Rev 52, 671–706 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9602-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9602-2