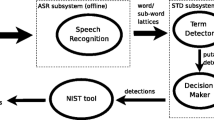
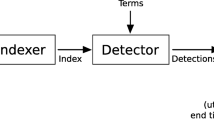
Abstract
Spoken keyword spotting refers to the detection of all occurrences of desired words in continuous speech utterances. This paper includes a comprehensive review on various spoken keyword spotting (especially discriminative spoken keyword spotting) approaches. The most common datasets and evaluation measures for training and evaluating the spoken keyword spotting systems are reviewed in this paper. Moreover, the main framework for structured discriminative spoken keyword spotting (SDKWS) is presented. Different parts of the SDKWS framework such as feature extraction, model training, search algorithm and thresholding are discussed in this paper. Finally, the paper is concluded in the conclusion section and the future works are presented in the last part of that section.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad AR, Viard-Gaudin C, Khalid M (2009) Lexicon-based word recognition using support vector machine and hidden Markov model. In: International conference on document analysis and recognition (ICDAR’09), pp 161–165
Akyol A, Erdogan H (2004) Filler model based confidence measures for spoken dialogue systems: a case study for Turkish. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’04), pp 781–784
Alvarez R, Park H-J (2019) End-to-end streaming keyword spotting. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 6336–6340
Amodei D et al. (2015) Deep speech 2: end-to-end speech recognition in english and mandarin. arXiv preprint arXiv:151202595
Ao C-W, Lee H-Y (2018) Query-by-example spoken term detection using attention-based multi-hop networks. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 6264–6268
Arik SO et al. (2017) Convolutional recurrent neural networks for small-footprint keyword spotting. arXiv preprint arXiv:170305390
Ayed YB, Fohr D, Haton JP, Chollet G (2002) Keyword spotting using support vector machines. In: International conference on text, speech and dialogue, pp 285–292
Bahi H, Benati N (2009) A new keyword spotting approach. In: International conference on multimedia computing and systems (ICMCS’09), pp 77–80
Bahl L, Brown P, De Souza P, Mercer R (1986) Maximum mutual information estimation of hidden Markov model parameters for speech recognition. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’86), pp 49–52
Bai Y, Yi J, Ni H, Wen Z, Liu B, Li Y, Tao J (2016) End-to-end keywords spotting based on connectionist temporal classification for Mandarin. In: International symposium on chinese spoken language processing (ISCSLP), pp 1–5
Bazzi I (2002) Modelling out-of-vocabulary words for robust speech recognition. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
Benayed Y, Fohr D, Haton JP, Chollet G (2003a) Confidence measures for keyword spotting using support vector machines. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’03), pp 588–591
Benayed Y, Fohr D, Haton JP, Chollet G (2003b) Improving the performance of a keyword spotting system by using support vector machines. In: IEEE workshop on automatic speech recognition and understanding (ASRU’03), pp 145–149
Bourlard HA, Morgan N (2012) Connectionist speech recognition: a hybrid approach, vol 247. Springer, Berlin
Bourlard H, D’hoore B, Boite J-M (1994) Optimizing recognition and rejection performance in wordspotting systems. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP-94), pp I/373–I/376
Bridle JS (1973) An efficient elastic-template method for detecting given words in running speech. In: British Acoustical Society meeting, pp 1–4
Burger S, MacLaren V, Yu H (2002) The ISL meeting corpus: the impact of meeting type on speech style. In: International conference on spoken language processing (IICSLP)
Burget L et al. (2008) Combination of strongly and weakly constrained recognizers for reliable detection of OOVs. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’08), pp 4081–4084
Butko T, Camprubí CN, Schulz H (2010) Albayzin-2010 audio segmentation evaluation: evaluation setup and results. In: VI Jornadas en Tecnología del Habla and II Iberian SLTech workshop, pp 305–308
Cernocky J et al. (2007) Search in speech for public security and defense. In: IEEE workshop on signal processing applications for public security and forensics (SAFE), pp 1–7
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 2:27
Chavan M, Chougule S (2012) Speaker features and recognition techniques: a review. Int J Comput Eng Res 2:720–728
Chen CP, Bilmes JA (2007) MVA processing of speech features. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 15:257–270
Chen JC, Chien JT (2009) Bayesian large margin hidden Markov models for speech recognition. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’09), pp 3765–3768
Chen G, Parada C, Heigold G (2014) Small-footprint keyword spotting using deep neural networks. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’14), pp 4087–4091
Chen G, Parada C, Sainath TN (2015) Query-by-example keyword spotting using long short-term memory networks. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 5236–5240
Cieri C, Graff D, Kimball O, Miller D, Walker K (2004) Fisher english training speech part 1 transcripts LDC2004T19 web download. Linguistic Data Consortium, Philadelphia
Cieri C, Graff D, Kimball O, Miller D, Walker K (2005) Fisher english training part 2, transcripts LDC2005T19. Linguistic Data Consortium, Philadelphia
Clemens Vayda WH (2016) Wake-up word detection using LSTM neural networks. Graz University of Technology, Graz
Cortes C, Mohri M (2005) Confidence intervals for the area under the roc curve. In: Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS), Proceedings of the 2004 Conference. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, vol 17, No. 6, pp 305–312
Cristianini N, Shawe Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
De Greve Z (2006) Application in automatic speech recognition: keyword spotting based on online garbage modeling. Faculti Polytechnique de Mons, IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny
Dekel O, Keshet J, Singer Y (2004) An online algorithm for hierarchical phoneme classification. In: International workshop on machine learning for multimodal interaction, pp 146–158
Dymarski P, Wydra S (2008) Large margin hidden Markov models in command recognition and speaker verification problems. In: International conference on systems, signals and image processing (IWSSIP’08), pp 221–224
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett 27:861–874
Fernández S, Graves A, Schmidhuber J (2007) An application of recurrent neural networks to discriminative keyword spotting. In: International conference on artificial neural networks, pp 220–229
Ferrer L, Estienne C (2001) Improving performance of a keyword spotting system by using a new confidence measure. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 2561–2564
Fiscus JG, Ajot J, Garofolo JS, Doddingtion G (2007) Results of the 2006 spoken term detection evaluation. In: Proceedings of SIGIR, pp 51–57
Fisher WM (1986) The DARPA speech recognition research database: specifications and status. In: Fisher WM, Doddington GR, Goudie-Marshall KM (eds) Proceedings of DARPA workshop on speech recognition, pp 93–99
Gales M, Young S (2008) The application of hidden Markov models in speech recognition. Found Trends Signal Process 1:195–304
Gales MJF, Watanabe S, Fosler-Lussier E (2012) Structured discriminative models for speech recognition: an overview. IEEE Signal Process Mag 29:70–81
Gales MJ, Knill KM, Ragni A, Rath SP (2014a) Speech recognition and keyword spotting for low-resource languages: BABEL project research at CUED. In: Spoken language technologies for under-resourced languages, pp 16–23
Gales MJ, Knill KM, Ragni A, Rath SP (2014b) Speech recognition and keyword spotting for low-resource languages: Babel project research at CUED. In: SLTU, pp 16–23
Garofolo J, Graff D, Paul D, Pallett D (1993a) CSR-I (WSJ0) complete LDC93S6A web download. Linguistic Data Consortium, Philadelphia
Garofolo J, Lamel L, Fisher W, Fiscus J, Pallett D, Dahlgren N (1993b) DARPA TIMIT acoustic phonetic continuous speech corpus, vol LDC93S1. Linguistic Data Consortium, Philadelphia
Glass J, Hazen TJ, Hetherington L, Wang C (2004) Analysis and processing of lecture audio data: preliminary investigations. In: Proceedings of the workshop on interdisciplinary approaches to speech indexing and retrieval at HLT-NAACL, pp 9–12
Godfrey EHJ (1993) Switchboard-1 release 2 LDC97S62. Linguistic Data Consortium, Philadelphia
Graves A, Fernández S, Gomez F, Schmidhuber J (2006) Connectionist temporal classification: labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning, ACM, pp 369–376
Guo J, Kumatani K, Sun M, Wu M, Raju A, Ström N, Mandal A (2018) Time-delayed bottleneck highway networks using a DFT feature for keyword spotting. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 5489–5493
He Y, Prabhavalkar R, Rao K, Li W, Bakhtin A, McGraw I (2017) Streaming small-footprint keyword spotting using sequence-to-sequence models. In: Automatic speech recognition and understanding workshop (ASRU), IEEE, pp 474–481
Heracleous P, Shimizu T (2003) An efficient keyword spotting technique using a complementary language for filler models training. In: European conference on speech communication and technology (EuroSpeech), pp 921–924
Hermansky H, Morgan N (1994) RASTA processing of speech. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 2:578–589
Hermansky H, Morgan N, Bayya A, Kohn P (1991) Compensation for the effect of the communication channel in auditory-like analysis of speech (RASTA-PLP). In: European conference on speech communication and technology (EuroSpeech), pp 1367–1370
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9:1735–1780
Huang H, Zhu J (2006) Kernel based non-linear feature extraction methods for speech recognition. In: International conference on intelligent systems design and applications (ISDA’06), pp 749–754
Huang X, Acero A, Hon H-W (2001) Spoken language processing: a guide to theory, algorithm, and system development. Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle River
Hwang K, Lee M, Sung W (2015) Online keyword spotting with a character-level recurrent neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:151208903
Jaimes A, Sebe N (2007) Multimodal human–computer interaction: a survey. Comput Vis Image Underst 108:116–134
Janin A et al. (2003) The ICSI meeting corpus. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’03), IEEE, pp 364–367
Jiang H, Li X, Liu C (2006) Large margin hidden Markov models for speech recognition. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 14:1584–1595
Juang B-H, Katagiri S (1992) Discriminative learning for minimum error classification (pattern recognition). IEEE Trans Signal Process 40:3043–3054
Junkawitsch J, Ruske G, Höge H (1997) Efficient methods for detecting keywords in continuous speech. In: EUROSPEECH, pp 259–262
Kamper H, Shakhnarovich G, Livescu K (2017) Semantic keyword spotting by learning from images and speech. arXiv preprint arXiv:171001949
Këpuska V, Klein T (2009) A novel wake-up-word speech recognition system, wake-up-word recognition task, technology and evaluation. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory Methods Appl 71:e2772–e2789
Keshet J (2007) Theoretical foundations for large-margin kernel-based continuous speech recognition. IDIAP
Keshet J, Bengio S (2009) Automatic speech and speaker recognition: large margin and kernel methods. Wiley, London
Keshet J, Shalev-Shwartz S, Singer Y, Chazan D (2005) Phoneme alignment based on discriminative learning. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 2961–2964
Keshet J, Bengio S, Chazan D, Shalev-Shwartz S, Singer Y (2006) Discriminative kernel-based phoneme sequence recognition. IDIAP
Keshet J, Shalev-Shwartz S, Singer Y, Chazan D (2007) A large margin algorithm for speech-to-phoneme and music-to-score alignment. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 15:2373–2382
Keshet J, Grangier D, Bengio S (2009) Discriminative keyword spotting. Speech Commun 51:317–329
Ketabdar H, Vepa J, Bengio S, Bourlard H (2006) Posterior based keyword spotting with a priori thresholds. In: International conference on spoken language processing (ICSLP), vol LIDIAP-CONF-2006-017, pp 633–636
Knill KM, Gales MJ, Rath SP, Woodland PC, Zhang C, Zhang SX (2013) Investigation of multilingual deep neural networks for spoken term detection. In: IEEE workshop on automatic speech recognition and understanding (ASRU), pp 138–143
Kumatani K, Panchapagesan S, Wu M, Kim M, Strom N, Tiwari G, Mandai A (2017) Direct modeling of raw audio with DNNS for wake word detection. In: IEEE automatic speech recognition and understanding workshop (ASRU), pp 252–257
Kuo J-W, Lo H-Y, Wang H-M (2007) Improved HMM/SVM methods for automatic phoneme segmentation. In: Interspeech, Citeseer, pp 2057–2060
Lafferty J, McCallum A, Pereira F (2001) Conditional random fields: probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data. In: Proceedings of the eighteenth international conference on machine learning, ICML, pp 282–289
Lee A, Shikano K, Kawahara T (2004) Real-time word confidence scoring using local posterior probabilities on tree trellis search. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’04), vol 791, pp I-793–796
Lengerich C, Hannun A (2016) An end-to-end architecture for keyword spotting and voice activity detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:161109405
Li K, Naylor J, Rossen M (1992) A whole word recurrent neural network for keyword spotting. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP-92), pp 81–84
Li J, Deng L, Gong Y, Haeb-Umbach R (2014) An overview of noise-robust automatic speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 22:745–777
Lin CY, Jang JSR, Chen KT (2005) Automatic segmentation and labeling for Mandarin Chinese speech corpora for concatenation-based TTS. Int J Comput Linguist Chin Lang Process Spec Issue Annot Speech Corpora 10:145–166
Lin H, Bilmes J, Vergyri D, Kirchhoff K (2007) OOV detection by joint word/phone lattice alignment. In: IEEE workshop on automatic speech recognition & understanding, (ASRU), pp 478–483
Linguistic Data Consortium (1994) CSR-II (wsj1) complete, vol LDC94S13A. Linguistic Data Consortium, Philadelphia
Manos AS, Zue VW (1997) A segment-based wordspotter using phonetic filler models. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP-97), pp 899–902
Marcus JN (1992) A novel algorithm for HMM word spotting performance evaluation and error analysis. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP-92), IEEE, pp 89–92
Martin A, Doddington G, Kamm T, Ordowski M, Przybocki M (1997) The DET curve in assessment of detection task performance DTIC document. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg
Matejka P, Zhang L, Ng T, Mallidi HS, Glembek O, Ma J, Zhang B (2014) Neural network bottleneck features for language identification. In: Proceedings of Odyssey, pp 299–304
Metze F, Anguera X, Barnard E, Davel M, Gravier G (2014) Language independent search in MediaEval’s spoken web search task. Comput Speech Lang 28:1066–1082
Michel M, Ajot J, Fiscus J (2006) The NIST meeting room corpus 2 phase 1. In: International workshop on machine learning for multimodal interaction, Springer, pp 13–23
Miki M, Kitaoka N, Miyajima C, Nishino T, Takeda K (2014) Improvement of multimodal gesture and speech recognition performance using time intervals between gestures and accompanying speech. EURASIP J Audio Speech Music Process 2014:1–7
Miller DR et al. (2007) Rapid and accurate spoken term detection. In: Annual conference of the international speech communication association (INTERSPEECH), pp 314–317
Moattar MH, Homayounpour MM (2012) A review on speaker diarization systems and approaches. Speech Commun 54:1065–1103
Molau S, Hilger F, Ney H (2003) Feature space normalization in adverse acoustic conditions. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’03), pp I-656–I-659
Motlicek P, Valente F, Szoke I (2012) Improving acoustic based keyword spotting using LVCSR lattices. In: 2012 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 4413–4416
Nehe NS, Holambe RS (2012) DWT and LPC based feature extraction methods for isolated word recognition. EURASIP J Audio Speech Music Process 2012:1–7
Ngo K, Spriet A, Moonen M, Wouters J, Jensen SH (2012) A combined multi-channel Wiener filter-based noise reduction and dynamic range compression in hearing aids. Sig Process 92:417–426
NIST (2013) NIST open keyword search 2013 evaluation (OpenKWS13), 1st edn. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Washington DC
NIST (2014) NIST open keyword search 2014 evaluation (OpenKWS14), 1st edn. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Washington DC
NIST (2015) NIST open keyword search 2015 evaluation (OpenKWS15), 1st edn. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Washington DC
NIST (2016) NIST open keyword search 2016 evaluation (OpenKWS16), 1st edn. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Washington DC
Ou Z, Luo H (2012) CRF-based confidence measures of recognized candidates for lattice-based audio indexing. In: 2012 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 4933–4936
Panayotov V, Chen G, Povey D, Khudanpur S (2015) Librispeech: an ASR corpus based on public domain audio books. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 5206–5210
Peeters G (2004) A large set of audio features for sound description (similarity and classification) in the CUIDADO project, Cuidado project report. IRCAM, Paris
Plátek O (2014) Automatic speech recognition using Kaldi. Charles University in Prague, Prague
Platt JC (1999) Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. In: Advances in kernel methods: support vector learning. MIT Press, pp 185–208
Povey D, Woodland PC (2002) Minimum phone error and I-smoothing for improved discriminative training. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’02), pp I-105–I-108
Powers DM (2011) Evaluation: from precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. J Mach Learn Technol 2:37–63
Rabiner L, Juang B-H (1993) Fundamentals of speech recognition. PTR Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Ramabhadran B, Sethy A, Mamou J, Kingsbury B, Chaudhari U (2009) Fast decoding for open vocabulary spoken term detection. In: Proceedings of human language technologies: the 2009 annual conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, companion, volume: short papers, Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 277–280
Rastrow A, Sethy A, Ramabhadran B (2009) A new method for OOV detection using hybrid word/fragment system. In: 2009 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, IEEE, pp 3953–3956
Roark B, Saraclar M, Collins M (2007) Discriminative n-gram language modeling. Comput Speech Lang 21:373–392
Rose R (1995) Keyword detection in conversational speech utterances using hidden Markov model based continuous speech recognition. Comput Speech Lang 9:309–333
Rose RC, Paul DB (1990) A hidden Markov model based keyword recognition system. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP-90), pp 129–132
Sainath TN, Parada C (2015) Convolutional neural networks for small-footprint keyword spotting. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 1478–1482
Schuster M, Paliwal KK (1997) Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Signal Process 45:2673–2681
Seigel MS, Woodland PC, Gales M (2013) A confidence-based approach for improving keyword hypothesis scores. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’13), pp 8565–8569
Shan C, Zhang J, Wang Y, Xie L (2018) Attention-based end-to-end models for small-footprint keyword spotting. arXiv preprint arXiv:180310916
Sharma R et al (2003) Speech-gesture driven multimodal interfaces for crisis management. Proc IEEE 91:1327–1354
Shokri A, Tabibian S, Akbari A, Nasersharif B, Kabudian J (2011) A robust keyword spotting system for Persian conversational telephone speech using feature and score normalization and ARMA filter. In: GCC conference and exhibition (GCC), pp 497–500
Shudong Huang JL, Xuling Wu, Lei Wu, Yan Yongmin, Qin Zhoakai (1998) 1997 Mandarin broadcast news speech (HUB4-NE) LDC98S73. Linguistic Data Consortium, Philadelphia
Sun M et al. (2016) Max-pooling loss training of long short-term memory networks for small-footprint keyword spotting. In: Spoken language technology workshop (SLT), IEEE, pp 474–480
Sun M, Schwarz A, Wu M, Strom N, Matsoukas S, Vitaladevuni S (2017a) An empirical study of cross-lingual transfer learning techniques for small-footprint keyword spotting. In: International conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA), IEEE, pp 255–260
Sun M et al. (2017b) Compressed time delay neural network for small-footprint keyword spotting. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 3607–3611
Szöke I (2010) Hybrid word-subword spoken term detection. Faculty of Information Technology, BUT, Brno
Szöke I, Schwarz P, Matějka P, Burget L, Karafiát M, Černocký J (2005a) Phoneme based acoustics keyword spotting in informal continuous speech. In: International conference on text, speech and dialogue. Springer, pp 302–309
Szöke I, Schwarz P, Matejka P, Burget L, Karafiát M, Fapso M, Cernocký J (2005b) Comparison of keyword spotting approaches for informal continuous speech. In: Interspeech, Citeseer, pp 633–636
Tabibian S, Shokri A, Akbari A, Nasersharif B (2011) Performance evaluation for an HMM-based keyword spotter and a large-margin based one in noisy environments. Proc Comput Sci 3:1018–1022
Tabibian S, Akbari A, Nasersharif B (2013) Keyword spotting using an evolutionary-based classifier and discriminative features. Eng Appl Artif Intell 26:1660–1670
Tabibian S, Akbari A, Nasersharif B (2014) Extension of a kernel-based classifier for discriminative spoken keyword spotting. Neural Process Lett 39:195–218
Tabibian S, Akbari A, Nasersharif B (2015) Speech enhancement using a wavelet thresholding method based on symmetric Kullback–Leibler divergence. Sig Process 106:184–197
Tabibian S, Akbari A, Nasersharif B (2016) A fast hierarchical search algorithm for discriminative keyword spotting. Inf Sci 336:45–59
Tabibian S, Akbari A, Nasersharif B (2018) Discriminative keyword spotting using triphones Information and N-best Search. Inf Sci 423:157–171
Tamura S, Iwano K, Furui S (2005) Toward robust multimodal speech recognition. In: Symposium on large scale knowledge resources (LKR2005), pp 163–166
Tang R, Lin J (2018) Deep residual learning for small-footprint keyword spotting. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 5484–5488
Tejedor J, Wang D, Frankel J, King S, Colás J (2008) A comparison of grapheme and phoneme-based units for Spanish spoken term detection. Speech Commun 50:980–991
Tejedor J et al (2017) ALBAYZIN 2016 spoken term detection evaluation: an international open competitive evaluation in Spanish. EURASIP J Audio Speech Music Process 2017:1–22
Thambiratnam AJ (2005) Acoustic keyword spotting in speech with applications to data mining. Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane
Toh AM, Togneri R, Nordholm S (2005) Spectral entropy as speech features for speech recognition. Paper presented at the proceedings of post graduate electrical engineering and computing symposium (PEECS)
Toledano DT, Gómez LAH, Grande LV (2003) Automatic phonetic segmentation. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 11:617–625
Tsochantaridis I, Joachims T, Hofmann T, Altun Y (2005) Large margin methods for structured and interdependent output variables. J Mach Learn Res 6:1453–1484
Tucker G, Wu M, Sun M, Panchapagesan S, Fu G, Vitaladevuni S (2016) Model compression applied to small-footprint keyword spotting. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 1878–1882
Tüske Z, Golik P, Schlüter R, Drepper FR (2011) Non-stationary feature extraction for automatic speech recognition. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’11), pp 5204–5207
Vapnik VN, Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory, vol 1. Wiley, New York
Vaseghi SV (2008) Advanced digital signal processing and noise reduction. Wiley, London
Viikki O, Bye D, Laurila K (1998) A recursive feature vector normalization approach for robust speech recognition in noise. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’98), pp 733–736
Vimala C, Radha V (2014) Suitable feature extraction and speech recognition technique for isolated tamil spoken words. Int J Comput Sci Inf Technol (IJCSIT) 5:378–383
Wang D (2010) Out-of-vocabulary spoken term detection. University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh
Wang D, Tejedor J, Frankel J, King S, Colás J (2009) Posterior-based confidence measures for spoken term detection. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing(ICASSP’09), pp 4889–4892
Wang D, Tejedor J, King S, Frankel J (2012) Term-dependent confidence normalisation for out-of-vocabulary spoken term detection. J Comput Sci Technol 27:358–375
Wang Y, Yang J, Lu J, Liu H, Wang L (2015) Hierarchical deep belief networks based point process model for keywords spotting in continuous speech. Int J Commun Syst 28:483–496
Wang Z, Li X, Zhou J (2017) Small-footprint keyword spotting using deep neural network and connectionist temporal classifier. arXiv preprint arXiv:170903665
Weintraub M (1995) LVCSR log-likelihood ratio scoring for keyword spotting. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP-95), pp 297–300
Wolf JJ (1980) Speech signal processing and feature extraction. In: Spoken language generation and understanding. Springer, pp 103–128
Wollmer M, Eyben F, Keshet J, Graves A, Schuller B, Rigoll G (2009) Robust discriminative keyword spotting for emotionally colored spontaneous speech using bidirectional LSTM networks. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’09), pp 3949–3952
Wollmer M, Marchi E, Squartini S, Schuller B (2011) Multi-stream LSTM-HMM decoding and histogram equalization for noise robust keyword spotting. Cognit Neurodyn 5:253–264
Wollmer M, Schuller B, Rigoll G (2013) Keyword spotting exploiting long short-term memory. Speech Commun 55:252–265
Wu M et al. (2018) Monophone-based background modeling for two-stage on-device wake word detection. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 5494–5498
Xiong X (2009) Robust speech features and acoustic models for speech recognition. Nanyang Technological University, Ph.D. Thesis
Xu Y, Zhang D, Jin Z, Li M, Yang J-Y (2006) A fast kernel-based nonlinear discriminant analysis for multi-class problems. Pattern Recogn 39:1026–1033
Xu H, Su H, Chng ES, Li H (2014) Semi-supervised training for bottle-neck feature based DNN-HMM hybrid systems. In: Fifteenth annual conference of the international speech communication association, pp 2078–2082
Yang J, Frangi AF (2004) Yang J-y. A new kernel Fisher discriminant algorithm with application to face recognition Neurocomputing 56:415–421
Yapanel Ü (2000) Garbage modeling techniques for a Turkish keyword spotting system. Boğaziçi University, Istanbul
Yoshizawa S, Hayasaka N, Wada N, Miyanaga Y (2004) Cepstral gain normalization for noise robust speech recognition. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP’04), pp I-209–I-212
Yu D, Deng L (2014) Automatic speech recognition: a deep learning approach. Springer, New York
Zacharie DG, Pinto JP (2007) Keyword spotting on word lattices. IDIAP, Martigny
Zhang S-X (2014) Structured support vector machines for speech recognition. University of Cambridge, Department of Engineering, Doctor of Philosophy thesis
Zhang Y, Glass JR (2009) Unsupervised spoken keyword spotting via segmental DTW on Gaussian posteriorgrams. In: IEEE workshop on automatic speech recognition & understanding, IEEE, pp 398–403
Zhang R, Wang W (2011) Learning linear and nonlinear PCA with linear programming. Neural Process Lett 33:151–170
Zhang S-X, Liu C, Yao K, Gong Y (2015) Deep neural support vector machines for speech recognition. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP’15), pp 4275–4279
Zhang Y, Suda N, Lai L, Chandra V (2017) Hello edge: keyword spotting on microcontrollers. arXiv preprint arXiv:171107128
Zhao H, Xiao Y (2012) A novel robust MFCC extraction method using sample-ISOMAP for speech recognition. Int J Digit Content Technol Appl 6:393–400
Zheng W, Zou C, Zhao L (2005) An improved algorithm for kernel principal component analysis. Neural Process Lett 22:49–56
Zhuang Y, Chang X, Qian Y, Yu K (2016) Unrestricted vocabulary keyword spotting using LSTM-CTC. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 938–942
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabibian, S. A survey on structured discriminative spoken keyword spotting. Artif Intell Rev 53, 2483–2520 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09739-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09739-y