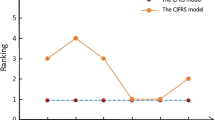
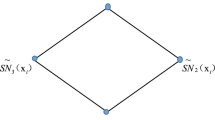
Abstract
Covering-based rough set is an important extended type of classical rough set model. In this model, concepts are approximated through substitution of a partition in classical rough set theory with a covering in covering-based rough set theory. Various generalized covering-based rough sets have been investigated, however, little work has been done on extending four classical covering-based rough set to intuitionistic fuzzy (IF) settings. In this study, four novel IF covering-based rough set models are developed by combining an IF \(\beta \)-covering with four classical covering-based rough set models. First, we present the concept of IF \(\beta \)-minimal description, and then construct four order relations on IF \(\beta \) approximation space. Second, we propose four IF \(\beta \)-covering-based rough set models and derive that they are generalizations of four existing covering-based rough sets in IF settings. We also discuss the properties of these IF \(\beta \)-covering-based rough sets and reveal their relationships. We use the existing distance between two IF sets to characterize the uncertainty of the presented IF \(\beta \)-covering-based rough sets. Third, we define the reducts of IF \(\beta \)-covering decision systems and examine their discernibility-function-based reduction methods for these IF \(\beta \)-covering-based rough sets. Fourth, we present four optimistic and pessimistic multi-granulation IF \(\beta \)-covering-based rough sets and analyze their properties and uncertainty measures from multi-granulation perspective. Fifth, we study the discernibility-function-based reduction methods for the presented multi-granulation IF \(\beta \)-covering-based rough sets. Finally, we discuss another two neighborhood-based IF covering-based rough sets. This study can provide a covering-based rough set method for acquiring knowledge from IF decision systems.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Atanassov K (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:87–96
Atanassov K (1999) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets: theory and applications. Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg
Bonikowski Z, Bryniarski E, Wybraniec-Skardowska U (1998) Extensions and intensions in rough set theory. Inf Sci 107:149–167
Chen DG, Wang CZ, Hu QH (2007) A new approach to attribute reduction of consistent and inconsistent covering decision systems with covering rough sets. Inf Sci 177(17):3500–3518
Chen DG, Zhang XX, Li WL (2015) On measurements of covering rough sets based on granules and evidence theory. Inf Sci 317:329–348
Cornelis C, Cock MD, Kerre EE (2003) Intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets: at the crossroads of imperfect knowledge. Expert Syst 20(5):260–270
Dai J-H, Hu H, Wu W-Z, Qian Y-H, Huang D-B (2018) Maximal discernibility pairs based approach to attribute reduction in fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26:2174–2187
D’eer L, Cornelis C (2018) A comprehensive study of fuzzy covering-based rough set models: definitions, properties and interrelationships. Fuzzy Sets Syst 336:1–26
Diker M (2018) Textures and fuzzy unit operations in rough set theory: an approach to fuzzy rough set models. Fuzzy Sets Syst 336:27–53
Dübois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 17:191–208
Feng T, Zhang SP, Mi JS (2012) The reduction and fusion of fuzzy covering systems based on the evidence theory. Int J Approx Reason 53:87–103
Hu QH, Zhang L, Zhang D, Pan W, An S, Pedrycz W (2011) Measuring relevance between discrete and continuous features based on neighborhood mutual information. Expert Syst Appl 38:10737–10750
Huang B, Li HX, Wei DK (2012) Dominance-based rough set model in intuitionistic fuzzy information systems. Knowl-Based Syst 28:115–123
Huang B, Wei DK, Li HX, Zhuang YL (2013) Using a rough set model to extract rules in dominance-based interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information systems. Inf Sci 221:215–229
Huang B, Guo CX, Zhuang YL, Li HX, Zhou XZ (2014) Intuitionistic fuzzy miltigranulation rough sets. Inf Sci 277:299–320
Huang B, Guo CX, Li HX, Feng GF, Zhou XZ (2016) Hierarchical structures and uncertainty measures for intuitionistic fuzzy approximation space. Inf Sci 336:92–114
Huang B, Guo CX, Li HX, Feng GF, Zhou XZ (2016) An intuitionistic fuzzy graded covering rough set. Knowl-Based Syst 107:155–178
Jena SP, Ghosh SK, Tripathy BK (2002) Intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets. Notes Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets 8(1):1–18
Li TJ, Leung Y, Zhang WX (2008) Generalized fuzzy rough approximation operators based on fuzzy coverings. Int J Approx Reason 48:836–856
Li JH, Kumar CA, Mei CL, Wang XZ (2017) Comparison of reduction in formal decision contexts. Int J Approx Reason 80:100–122
Lin GP, Qian YH, Li JJ (2012) NMGRS: Neighborhood-based multigranulation rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 53:1080–1093
Lin GP, Liang JY, Qian YH (2013) Multigranulation rough sets: from partition to covering. Inf Sci 241:101–118
Liu GL (2013) The relationship among different covering approximations. Inf Sci 250:178–183
Liu CH, Miao DQ, Qian J (2014) On multi-granulation covering rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 55:1404–1418
Ma LW (2016) Two fuzzy covering rough set models and their generalizations over fuzzy lattices. Fuzzy Sets Syst 294:1–17
Meng F, Tang J, Fujita H (2019) Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations and their application to multi-criteria decision making. Inf Fus 46:77–90
Miao DQ, Zhao Y, Yao YY, Li HX, Xu FF (2009) Relative reducts in consistent and inconsistent decision tables of the Pawlak rough set model. Inf Sci 179:4140–4150
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Inf Comput Sci 11:341–356
Pomykala JA (1987) Approximation operations in approximation space. Bull Pol Acad Sci 35(9–10):653–662
Qian YH, Liang JY, Yao YY, Dang CY (2010) MGRS: A multi-granulation rough set. Inf Sci 180:949–970
Restrepo M, Cornelis C, Gómez J (2014) Partial order relation for approximation operators in covering based rough sets. Inf Sci 284:44–59
Samanta SK, Mondal TK (2001) Intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets and rough intuitionistic fuzzy sets. J Fuzzy Math 9(3):561–582
Shen F, Ma X, Li Z, Xu Z, Cai D (2018) An extended intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method based on a new distance measure with an application to credit risk evaluation. Inf Sci 428:105–119
Skowron A, Rauszer C (1992) The discernibility matrices and functions in information systems. In: Slowiński R (ed) Intelligent decision support. Handbook of applications and advances of the rough sets theory. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Susmaga R (1997) Analyzing discretizations of continuous attributes given a monotonic discrimination function. Intell Data Anal 1:157–179
Tan AH, Li JJ, Lin GP, Lin YJ (2015) Fast approach to knowledge acquisition in covering information systems using matrix operations. Knowl-Based Syst 79:90–98
Tan AH, Wu W-Z, Tao YZ (2018) A unified framework for characterizing rough sets with evidence theory in various approximation spaces. Inf Sci 454–455:144–160
Tiwari SP, Srivastava AK (2013) Fuzzy rough sets, fuzzy preorders and fuzzy topologies. Fuzzy Sets Syst 210:63–68
Tiwari AK, Shreevastava S, Som T, Shukla KK (2018) Tolerance-based intuitionistic fuzzy-rough set approach for attribute reduction. Expert Syst Appl 101:205–212
Tsang ECC, Chen DG, Lee J, Yeung DS (2004) On the upper approximations of covering generalized rough sets. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on machine learning and cybernetics, pp. 4200–4203
Vlachos IK, Sergiadis GD (2007) Intuitionistic fuzzy information-applications to pattern recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 28:197–206
Wang W, Xin X (2005) Distance measure between intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Pattern Recogn Lett 26:2063–2069
Wang SP, Zhu W, Zhu QH, Min F (2014) Characteristic matrix of covering and its application to Boolean matrix decomposition and axiomatization. Inf Sci 263:186–197
Wang C, Shao M, Sun B, Hu Q (2015) An improved attribute reduction scheme with covering based rough sets. Appl Soft Comput 26:235–243
Wang ZH, Wang H, Feng QR, Shu L (2015) The approximation number function and the characterization of covering approximation space. Inf Sci 305:196–207
Wang C, Hu Q, Wang X, Chen D, Qian Y (2018) Feature selection based on neighborhood discrimination index. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29:2986–2999
Yang B, Hu BQ (2016) A fuzzy covering-based rough set model and its generalization over fuzzy lattice. Inf Sci 367–368:463–486
Yang XB, Song XN, Dou HL, Yang JY (2011) Multi-granulation rough set: from crisp to fuzzy case. Ann Fuzzy Math Inform 1:55–70
Yang XB, Qian YH, Yang JY (2012) Hierarchical structures on multigranulation spaces. J Comput Sci Technol 27:1169–1183
Yang T, Li QG, Zhou BL (2013) Related family: A new method for attribute reduction of covering information systems. Inf Sci 228:175–191
Yao YY, Yao BX (2012) Covering based rough set approximations. Inf Sci 200:91–107
Yao YY, Zhao Y (2009) Discernibility matrix simplification for constructing attribute reducts. Inf Sci 179:867–882
Zakowski W (1983) Approximations in the space \((U,\amalg )\). Demonstr Math 16:761–769
Zhang ZM (2012) Generalized intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets based on intuitionistic fuzzy coverings. Inf Sci 198:186–206
Zhang YL, Luo MK (2013) Relationships between covering-based rough sets and relation-based rough sets. Inf Sci 225:55–71
Zhang XH, Zhou B, Li P (2012) A general frame for intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets. Inf Sci 216:34–49
Zhou L, Wu W-Z (2008) On generalized intuitionistic fuzzy rough approximation operators. Inf Sci 178:2448–2465
Zhu W (2009) Relationship between generalized rough sets based on binary relation and covering. Inf Sci 179:210–225
Zhu W, Wang FY (2003) Reduction and axiomization of covering generalized rough sets. Inf Sci 152:217–230
Zhu W, Wang FY (2007) On three types of covering rough sets. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 19:1131–1144
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the EssayStar Company (http://essaystar.com/) for their assistance in improving the English language of this paper. We appreciate the support provided by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 61473157, 71671086, 61170105, and 71201076) and A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Li, H., Feng, G. et al. Intuitionistic fuzzy \(\beta \)-covering-based rough sets. Artif Intell Rev 53, 2841–2873 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09748-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09748-x