Abstract
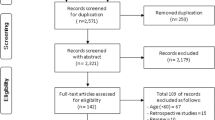
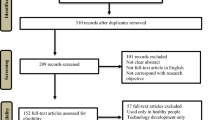
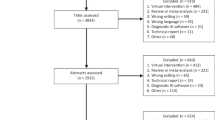
Technological advances that involve computing and artificial intelligence (AI) have led to advances in analysis methods. Fuzzy logic (FL) serves as a qualitative interpretation tool for AI. The objective of this systematic review is to investigate the methods of human movement (HM) analysis using AI through FL to understand the characteristics of the movement of healthy people. To identify relevant studies published up to April 19, 2019, we conducted a study of the PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and IEEE Xplore databases. We included studies that evaluated HM through AI using FL in healthy people. A total of 951 articles were examined, of which six were selected because they met the criteria presented in the methods. The protocols had high heterogeneity, yet all articles selected presented statistically satisfactory results, in addition to low errors or a false positive index. Only one selected article presented protocol applicability within the free-living model. Generally, AI using FL is a good tool to help assess HM in healthy people, but the model still needs new data acquisition entries to make it applicability within the free-living model.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data supporting the conclusions of this article are included in the article itself.
Abbreviations
- AI:
-
Artificial intelligence
- FL:
-
Fuzzy logic
- HM:
-
Human movement
- ANNs:
-
Artificial neural networks
- MUs:
-
Motor units
- MUAP:
-
Motor units action potential
- EMG:
-
Electromyography
References
Ahamed NU, Benson L, Clermont C, Osis ST, Ferber R (2017) Fuzzy inference system-based recognition of slow, medium and fast running conditions using a triaxial accelerometer. Procedia Comput Sci 114:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.09.054
Ahmadi H, Gholamzadeh M, Shahmoradi L, Nilashi M, Rashvand P (2018) Diseases diagnosis using fuzzy logic methods: a systematic and meta-analysis review. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 161:145–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.04.013
Ahn D (2018) Optimization algorithms for integrating advanced facility-level healthcare technologies into personal healthcare devices. DGIST, Daegu
Akash K, Hu W-L, Jain N, Reid T (2018) A classification model for sensing human trust in machines using EEG and GSR. arXiv:180309861
Baca A, Dabnichki P, Heller M, Kornfeind P (2009) Ubiquitous computing in sports: a review and analysis. J Sports Sci 27:1335–1346. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640410903277427
Bastawrous S, Wake N, Levin D, Ripley B (2018) Principles of three-dimensional printing and clinical applications within the abdomen and pelvis. Abdom Radiol (New York) 43:2809–2822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1554-8
Calmet J, Campbell JA (2010) A revisited perspective on symbolic mathematical computing and artificial intelligence. In: International conference on intelligent computer mathematics. Springer, pp 14–18
Cippitelli E, Gasparrini S, Gambi E, Spinsante S (2016) A human activity recognition system using skeleton data from RGBD sensors. Comput Intell Neurosci 2016:21. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4351435
Cust EE, Sweeting AJ, Ball K, Robertson S (2019) Machine and deep learning for sport-specific movement recognition: a systematic review of model development and performance. J Sports Sci 37:568–600. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2018.1521769
Deshpande A, Kumar M (2018) Artificial intelligence for big data: complete guide to automating big data solutions using artificial intelligence techniques. Packt Publishing Ltd, Birmingham
Farzandipour M, Nabovati E, Saeedi S, Fakharian E (2018) Fuzzy decision support systems to diagnose musculoskeletal disorders: a systematic literature review. Comput Methods Progr Biomed 163:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.06.002
Garza-Rodríguez A, Sánchez-Fernández LP, Sánchez-Pérez LA, Ornelas-Vences C, Ehrenberg-Inzunza M (2018) Pronation and supination analysis based on biomechanical signals from Parkinson’s disease patients. Artif Intell Med 84:7–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2017.10.001
Golabchi A, Han S, Fayek A, AbouRizk S (2017) Stochastic modeling for assessment of human perception and motion sensing errors in ergonomic analysis. J Comput Civ Eng 31:04017010. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000655
Gopalai AA, Arosha Senanayake SMNA (2011) A wearable real-time intelligent posture corrective system using vibrotactile feedback IEEE/ASME. Trans Mechatron 16:827–834. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2011.2161486
Kermany DS et al (2018) Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 172:1122–1131.e1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010
Kutilek P, Viteckova S, Svoboda Z (2013) Characterization of human gait using fuzzy logic. Acta Polytech 53:88–92
Ma X, Liu Q, Zhan J (2017) A survey of decision making methods based on certain hybrid soft set models. Artif Intell Rev 47:507–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-016-9490-x
Manoj T, Thyagaraju G (2018) Active and assisted living: a comprehensive review of enabling technologies and scenarios. Int J Adv Res Comput Sci 9:461–471. https://doi.org/10.26483/ijarcs.v9i1.5284
McBee MP et al (2018) Deep learning in radiology. Acad Radiol 25:1472–1480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2018.02.018
Mebarkia K, Bekka REh, Reffad A, Disselhorst-Klug C (2014) Fuzzy MUAP recognition in HSR-EMG detection basing on morphological features. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 24:473–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2014.04.006
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg (London, England) 8:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
Montoye AHK, Dong B, Biswas S, Pfeiffer KA (2016) Validation of a wireless accelerometer network for energy expenditure measurement. J Sports Sci 34:2130–2139. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2016.1151924
Morales-Orcajo E, de Bengoa Becerro, Vallejo R, Losa Iglesias M, Bayod J, de Las Barbosa, Casas E (2018) Foot internal stress distribution during impact in barefoot running as function of the strike pattern. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 21:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2018.1480760
Mostafa SA, Mustapha A, Mohammed MA, Ahmad MS, Mahmoud MA (2018) A fuzzy logic control in adjustable autonomy of a multi-agent system for an automated elderly movement monitoring application. Int J Med Inform 112:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2018.02.001
Ng H, Tan WH, Abdullah J, Tong HL (2014) Development of vision based multiview gait recognition system with MMUGait database. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/376569
Nowshiravan Rahatabad F, Jafari AH, Fallah A, Razjouyan J (2012) A fuzzy-genetic model for estimating forces from electromyographical activity of antagonistic muscles due to planar lower arm movements: the effect of nonlinear muscle properties. BioSystems 107:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2011.09.004
Pan Y (2016) Heading toward artificial intelligence 2.0. Engineering 2:409–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2016.04.018
Peulic A, Sustersic T, Peulic M (2018) Non-invasive improved technique for lumbar discus hernia classification based on fuzzy logic. Biomed Tech Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmt-2018-0013
Sakthivel G, Saravanakumar D, Muthuramalingam T (2018) Application of failure mode and effect analysis in manufacturing industry-an integrated approach with FAHP-fuzzy TOPSIS and FAHP-fuzzy VIKOR. Int J Product Qual Manag 24:398–423. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJPQM.2018.092984
Sarowar M (2018) Emergence-of-automated-computing-technologies-in-biomedical-diseaseand-drug-discovery-117. J Biomed Syst Emerg Technol 5:1–13
Savino MM, Battini D, Riccio C (2017) Visual management and artificial intelligence integrated in a new fuzzy-based full body postural assessment. Comput Ind Eng 111:596–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.06.011
Acknowledgements
We offer special thanks to the members of the Occupational Biomechanics and Quality of Life Research Center (Nucleo de Pesquisa em Biomecânica Ocupacional e Qualidade de Vida - NPBOQV). We thank Maxine Garcia, PhD, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
There was no external funding for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BL together with the advisor GV defined the theme of the paper. BL performed the search on the Scopus, PubMed, IEEEXplore, and ScienceDirect databases and withdrew duplicate articles. The inclusion and exclusion criteria for the title and abstract were applied by BL, CN, CF, FV, and LB, and then compared and debated. The inclusion and exclusion criteria for the full text were applied by BL, RP, and PB, and then compared and debated. The text was written by BL and revised by RP, PB, CN, FC, FV, LB, and GV in meetings coordinated by GV. The translation was performed by BL, PB, and GV.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, B.N., Balducci, P., Passos, R.P. et al. Artificial intelligence based on fuzzy logic for the analysis of human movement in healthy people: a systematic review. Artif Intell Rev 54, 1507–1523 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09885-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09885-8