Abstract
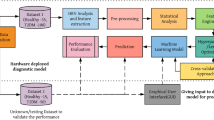
Early diagnosis of prediabetes is an effective solution to the rising cases of diabetes around the world. The heterogeneous physiological characteristics of the ECG signal recorded from the heart make it challenging to implement an efficient diagnostic system. Therefore, this paper proposes a new approach to handling the heterogeneous characteristics of heart rate variability (HRV) with an absolute magnitude deviation analysis and an integrated machine learning technique for prediabetes prediction. We conducted an oral glucose tolerance test to acquire a resting-state ECG signal and the corresponding blood glucose value. We analyzed the HRV pattern from the ECG signal with a block-sliding window technique. We proposed a hybrid model to classify normal and prediabetes based on the extent of the absolute deviation of HRV values and avoiding a single point of failure. We adopted the model from the classification and regression tree (CART) and neural network (NN) algorithms. The experimental results reveal that when the blood glucose level increases, the maximum and range values of CARTHRV decreases while the minimum value increases. The proposed hybrid model had a better performance than the two methods with 100% sensitivity, specificity, and F1-score measures against CART and NN that recorded < 100% for the same number of prediabetes in the training and test sets. The outcome from the analysis shows that the changes in blood glucose can be observed in ECG signals. The fast approximation of the proposed method to 100% accuracy suggests that it is possible to achieve the diagnosis of prediabetes and overcome the discrepancies in physiological signals among individuals.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya UR, Joseph KP, Kannathal N, Lim CM, Suri JS (2006) Heart rate variability: a review. Med Biol Eng Compu 44(12):1031–1051
Acharya UR, Faust O, Sree SV, Ghista DN, Dua S, Joseph P, Tamura T (2013a) An integrated diabetic index using heart rate variability signal features for diagnosis of diabetes. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 16(2):222–234
Acharya UR, Faust O, Kadri NA, Suri JS, Yu W (2013b) Automated identification of normal and diabetes heart rate signals using nonlinear measures. Comput Biol Med 43(10):1523–1529
ADA:American Diabetes Association (2017) Standards of medical care in diabetes—2017 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical diabetes: a publication of the American Diabetes Association, 35(1), 5
Ali JB, Hamdi T, Fnaiech N, Di Costanzo V, Fnaiech F, Ginoux JM (2018) Continuous blood glucose level prediction of Type 1 Diabetes based on Artificial Neural Network. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 38(4):828–840
Antelmi I, De Paula RS, Shinzato AR, Peres CA, Mansur AJ, Grupi CJ (2004) Influence of age, gender, body mass index, and functional capacity on heart rate variability in a cohort of subjects without heart disease. Am J Cardiol 93(3):381–385
Beloufa F, Chikh MA (2013) Design of fuzzy classifier for diabetes disease using Modified Artificial Bee Colony algorithm. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 112(1):92–103
Carnethon MR, Yan L, Greenland P, Garside DB, Dyer AR, Metzger B, Daviglus ML (2008) Resting heart rate in middle age and diabetes development in older age. Diabetes Care 31(2):335–339
Cho N, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B (2018) IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 138:271–281
Erdogan D, Yucel H, Uysal BA, Ersoy IH, Icli A, Akcay S, Tamer MN (2013) Effects of prediabetes and diabetes on left ventricular and coronary microvascular functions. Metabolism 62(8):1123–1130
Erkaymaz O, Ozer M (2016) Impact of small-world network topology on the conventional artificial neural network for the diagnosis of diabetes. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 83:178–185
Festa A, D’Agostino RALPH, Hales CN, Mykkänen L, Haffner SM (2000) Heart rate in relation to insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 23(5):624–628
Fong S, Mohammed S, Fiaidhi J, Kwoh CK (2013) Using causality modeling and fuzzy lattice reasoning algorithm for predicting blood glucose. Expert Syst Appl 40(18):7354–7366
Ganji MF, Abadeh MS (2011) A fuzzy classification system based on ant colony optimization for diabetes disease diagnosis. Expert Syst Appl 38(12):14650–14659
Gulumbe SU, Suleiman S, Badamasi S, Tambuwal AY, Usman U (2019) Predicting diabetes mellitus using artificial neural network through a simulation study. Mach Learn Res 4(2):33
Igbe T, Li J, Liu Y, Li S, Kandwal A, Nie Z, Lei W (2019, October). Analysis of ECG segments for non-invasive blood glucose monitoring. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on E-health Networking, Application & Services (HealthCom) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Kiselev AR, Shvartz VA, Bockeria OL (2016) Novel results and future perspectives of study of cardiovascular autonomic control in prediabetic patients. Anatolian J Cardiol 16(10):770–771
Li J, Xiaojing M, Igbe T, Yuhang L, Abhishek K, Lei W, Jingyi L (2020) A novel CGM metric-gradient and combining mean sensor glucose enable to improve the prediction of nocturnal hypoglycemic events in patients with diabetes. J Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8830774
Li J, Zhang B, Lu G, You J, Zhang D (2019) Body surface feature-based multi-modal learning for diabetes mellitus detection. Inf Sci 472:1–14
Liu W, Huang A, Wang P, Chu CH (2019) PbFG: Physique-based fuzzy granular modeling for non-invasive blood glucose monitoring. Inf Sci 497:56–76
Pachori RB, Avinash P, Shashank K, Sharma R, Acharya UR (2015) Application of empirical mode decomposition for analysis of normal and diabetic RR-interval signals. Expert Syst Appl 42(9):4567–4581
Pradhan N, Rani G, Dhaka VS, Poonia RC (2020). Diabetes prediction using artificial neural network. In Deep Learning Techniques for Biomedical and Health Informatics, Academic Press 327–339.
Ramasahayam S, Koppuravuri SH, Arora L, Chowdhury SR (2015) Noninvasive blood glucose sensing using near infra-red spectroscopy and artificial neural networks based on inverse delayed function model of neuron. J Med Syst 39(1):166
San PP, Ling SH, Nguyen H (2013) Evolvable rough-block-based neural network and its biomedical application to hypoglycemia detection system. IEEE Transac Cybernet 44(8):1338–1349
Schroeder EB, Chambless LE, Liao D, Prineas RJ, Evans GW, Rosamond WD, Heiss G (2005) Diabetes, glucose, insulin, and heart rate variability: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Diabetes Care 28(3):668–674
Seyd PA, Ahamed VT, Jacob J, Joseph P (2008) Time and frequency domain analysis of heart rate variability and their correlations in diabetes mellitus. Int J Biol Life Sci 4(1):24–27
Seyd A, Joseph PK, Jacob J (2012) Automated diagnosis of diabetes using heart rate variability signals. J Med Syst 36(3):1935–1941
Shu T, Zhang B, Tang YY (2018) An improved noninvasive method to detect diabetes mellitus using the probabilistic collaborative representation based classifier. Inf Sci 467:477–488
Stein PK, Barzilay JI, Domitrovich PP, Chaves PM, Gottdiener JS, Heckbert SR, Kronmal RA (2007) The relationship of heart rate and heart rate variability to non-diabetic fasting glucose levels and the metabolic syndrome: the cardiovascular health study. Diabet Med 24(8):855–863
Tiwary BK (2020) Computational medicine: quantitative modeling of complex diseases. Brief Bioinform 21(2):429–440
Tobore I, Li J, Kandwal A, Yuhang L, Nie Z, Wang L (2019) Statistical and spectral analysis of ECG signal towards achieving non-invasive blood glucose monitoring. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 19(6):266
Tobore I, Kandwal A, Li J, Yan Y, Omisore OM, Enitan E, Sinan L, Yuhang L, Wang L, Nie Z. (2020). Towards adequate prediction of prediabetes using spatiotemporal ECG and EEG feature analysis and weight-based multi-model approach. Knowledge-Based Systems, 17(209): 106464.
Topçu Ç, Frühwirth M, Moser M, Rosenblum M, Pikovsky A (2018). Disentangling respiratory sinus arrhythmia in heart rate variability records. Physiological measurement, 39(5): 054002.
Valensi P, Extramiana F, Lange C, Cailleau M, Haggui A, Maison Blanche P, DESIR Study Group (2011). Influence of blood glucose on heart rate and cardiac autonomic function The DESIR study. Diabetic medicine, 28(4): 440-449
Wang H, Shara NM, Calhoun D, Umans JG, Lee ET, Howard BV (2010) Incidence rates and predictors of diabetes in those with prediabetes: the Strong Heart Study. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 26(5):378–385
Wang L, Cui L, Wang Y, Vaidya A, Chen S, Zhang C, Gao X (2015) Resting heart rate and the risk of developing impaired fasting glucose and diabetes: the Kailuan prospective study. Int J Epidemiol 44(2):689–699
Zarkogianni K, Litsa E, Mitsis K, Wu PY, Kaddi CD, Cheng CW, Nikita KS (2015) A review of emerging technologies for the management of diabetes mellitus. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 62(12):2735–2749
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant No. 2018YFC2001002, Shenzhen Basic Research Project under Grant No. JCYJ20180507182231907 and CAS Key Laboratory of Health Informatics. The support from Chinse Academy of Sciences and The World Academy of Sciences (CAS-TWAS) president’s fellowship program
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Igbe, T., Li, J., Kandwal, A. et al. An absolute magnitude deviation of HRV for the prediction of prediabetes with combined artificial neural network and regression tree methods. Artif Intell Rev 55, 2221–2244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10040-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10040-0