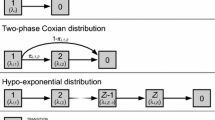
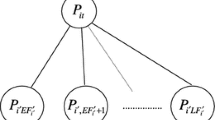
Abstract
The resource-constrained project scheduling problem (RCPSP) has been the subject of a great deal of research during the previous decades. This is not surprising given the high practical relevance of this scheduling problem. Nevertheless, extensions are needed to be able to cope with situations arising in practice such as multiple activity execution modes, activity duration changes and resource breakdowns. In this paper we analytically determine the impact of unexpected resource breakdowns on activity durations. Furthermore, using this information we develop an approach for inserting explicit idle time into the project schedule in order to protect it as well as possible from disruptions caused by resource unavailabilities. This strategy will be compared to a traditional simulation-based procedure and to a heuristic developed for the case of stochastic activity durations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artigues, C., & Roubellat, F. (2000). A polynomial activity insertion algorithm in a multi-resource schedule with cumulative constraints and multiple modes. European Journal of Operational Research, 127, 294–316.
Barlow, R., & Proschan, F. (1996). Mathematical theory of reliability. New York: Wiley.
Blumenfeld, D. (2001). Operations research calculations handbook. CRC Press: Boca Raton.
Brucker, P., Drexl, A., Möhring, R., Neumann, K., & Pesch, E. (1999). Resource-constrained project scheduling: notation, classification, models and methods. European Journal of Operational Research, 112, 3–41.
Demeulemeester, E., & Herroelen, W. (2002). In International series in operations research & management science : Vol. 49. Project scheduling—a research handbook. Boston: Kluwer Academic.
Herroelen, W., & Leus, R. (2004). The construction of stable project baseline schedules. European Journal of Operational Research, 156(3), 550–565.
Herroelen, W., De Reyck, B., & Demeulemeester, E. (1998). Resource-constrained scheduling: a survey of recent developments. Computers and Operations Research, 25, 279–302.
Kolisch, R., & Sprecher, A. (1997). PSPLIB—a project scheduling library. European Journal of Operational Research, 96, 205–216.
Lambrechts, O., Demeulemeester, E., & Herroelen, W. (2007a). Exact and suboptimal reactive strategies for resource-constrained project scheduling with uncertain resource availabilities. Research Report KBI0702, Department of Decision Sciences and Information Management, K.U. Leuven, Belgium, 36 pp.
Lambrechts, O., Demeulemeester, E., & Herroelen, W. (2007b). A tabu search procedure for developing robust predictive project schedules. International Journal of Production Economics, 111(2), 493–508.
Lambrechts, O., Demeulemeester, E., & Herroelen, W. (2008). Proactive and reactive strategies for resource-constrained project scheduling with uncertain resource availabilities. Journal of Scheduling, 11(2), 121–136.
Leus, R. (2004). The generation of stable project plans. 4OR, The Quarterly Journal of the Belgian, French and Italian Operations Research Societies, 2(3), 251–254.
Leus, R., & Herroelen, W. (2004). Stability and resource allocation in project planning. IIE Transactions, 36(7), 667–682.
O’Donovan, R., Uzsoy, R., & McKay, K. (1999). Predictable scheduling of a single machine with breakdowns and sensitive jobs. International Journal of Production Research, 37(18), 4217–4233.
Schatteman, D., Herroelen, W., Van de Vonder, S., & Boone, A. (2008). A methodology for integrated risk management and proactive scheduling of construction projects. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 134(11), 885–893.
Van de Vonder, S. (2006). Proactive-reactive procedures for robust project scheduling. Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of Economics and Applied Economics, Department of Decision Sciences and Information Management, K.U. Leuven, Belgium.
Van de Vonder, S., Demeulemeester, E., Herroelen, W., & Leus, R. (2005). The use of buffers in project management: the trade-off between stability and makespan. International Journal of Production Economics, 97(2), 227–240.
Van de Vonder, S., Demeulemeester, E., Herroelen, W., & Leus, R. (2006). The trade-off between stability and makespan in resource-constrained project scheduling. International Journal of Production Research, 44(2), 215–236.
Van de Vonder, S., Ballestin, F., Demeulemeester, E., & Herroelen, W. (2007). Heuristic procedures for reactive project scheduling. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 52(1), 11–28.
Van de Vonder, S., Demeulemeester, E., & Herroelen, W. (2008). Proactive heuristic procedures for robust project scheduling: an experimental analysis. European Journal of Operational Research, 189(3), 723–733.
Yu, G., & Qi, X. (2004). Disruption management—framework, models and applications. New Jersey: World Scientific.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambrechts, O., Demeulemeester, E. & Herroelen, W. Time slack-based techniques for robust project scheduling subject to resource uncertainty. Ann Oper Res 186, 443–464 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-010-0777-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-010-0777-z