Abstract
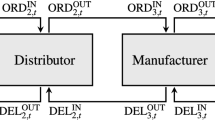
In this paper, we study the joint pricing and inventory replenishment problem for a periodic-review inventory system with random demand and dual suppliers, one of the suppliers is reliable but more expensive, the other supplier is less expensive but is unreliable with random yield. We characterize the firm’s optimal policies that simultaneously determine the optimal ordering and pricing decisions in each period over a finite planning horizon, and investigate the impacts of supply source diversification and supplier reliability on the firm and on its customers. We show that having source diversification or higher reliability of suppliers not only increases the firm’s expected profit, but also results in a lower optimal selling price, thus they benefit both the firm and its customers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anupindi, R., & Akella, R. (1993). Diversification under supply uncertainty. Management Science, 39(8), 944–963.
Argoneto, P., Perrone, G., Renna, P., Nigro, G. L., Bruccoleri, M., & Diega, S. N. L. (2010). Production planning in production networks: models for medium and short term planning. Berlin: Springer.
Chao, X., Chen, H., & Zheng, S. (2008). Joint replenishment and pricing decisions in inventory systems with stochastically dependent supply capacity. European Journal of Operational Research, 191(1), 142–155.
Chen, W., Feng, Q., & Seshadri, S. (2013). Sourcing from suppliers with random yield for price dependent demand. Annals of Operations Research, 208, 557–579.
Chen, J., Yao, D. D., & Zheng, S. (2001). Optimal replenishment and rework with multiple unreliable supply sources. Operations Research, 49(3), 430–443.
Chen, X., & Simchi-Levi, D. (2004). Coordinating inventory control and pricing strategies with random demand and fixed ordering cost: The finite horizon case. Operations Research, 52(6), 887–896.
Chen, X., & Simchi-Levi, D. (2012). Pricing and inventory management. In R. Philips, & O. Ozalp (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of pricing management. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Dada, M., Petruzzi N. C., & Schwarz, L. B. (2007). A newsvendor’s procuremnt problem when suppliers are unreliable. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management, 9(1), 9–32.
Federgruen, A., & Heching, A. (1999). Combined pricing and inventory control under uncertainty. Operations Research, 47(3), 454–475.
Federgruen, A., & Yang, N. (2011). Procurement strategies with unreliable suppliers. Operations Research, 59(4), 1033–1039.
Feng, Q. (2010). Integrating dynamic pricing and replenishment decisions under supply capacity uncertainty. Management Science, 56(12), 2154–2172.
Gong, X., Chao X., & Zheng, S. (2013). Dynamic pricing and inventory management with dual suppliers of different leadtimes and disruption risks. Production and Operations Management. (forthcoming).
Gupta, D., & Cooper, W. L. (2005). Stochastic comparisons in production yield management. Operations Research, 53(2), 377–384.
Henig, M., & Gerchak, Y. (1990). The structure of periodic review policies in the presence of random yield. Operations Research, 38(4), 634–643.
Heyman, D. P., & Sobel, M. J. (1984). Stochastic models in operations research (Vol. 2). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hsu, A., & Bassok, Y. (1999). Random yield and random demand in a production system with downward substitution. Operations Research, 47, 277–290.
Li Q., & Zheng, S. (2006). Joint inventory replenishment and pricing control for systems with uncertain yield and demand. Operations Research, 54(4), 696–705.
Qi, L., & Shen, Z.-J. M. (2007). A supply chain design model with unreliable supply. Naval Research Logistics, 54, 829–844.
Ross, S. M. (2003). Stochastic processes (2nd ed.). New York: Academic Press.
Shaked, M., & Shanthikumar, G. (1994). Stochastic orders and their applications. New York: Academic Press.
Sheffi, Y. (2005). The resilient enterprise: Overcoming vulnerability for competitive advantage. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Tomlin, B., & Wang, Y. (2005). On the value of mix flexibility and dual sourcing in unreliable newsvendor networks. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management., 7(1), 37–57.
Tomlin, B. (2006). On the value of mitigation and contingency strategies for managing supply chain disruption risks. Management Science, 52(5), 639–657.
Topkis, D. M. (1998). Supermodularity and complementarity. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Yano, C. A., & Gilbert, S. M. (2003). Coordinated pricing and production/procurement decisions: A review. In J. Eliashberg, & A. Chakravarty (Eds.), Managing business interfaces: Marketing, engineering, and manufacturing perspectives. Norwell, MA: Kluwer.
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to two anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions. In particular, the study on the case with correlated supply yield and demand was suggested by a reviewer. The research of Xiuli Chao is supported by NSF under CMMI-0927631 and CMMI-1131249. The research of Xiting Gong is supported in part by CUHK Direct Grant under No. 4055022. The research of Shaohui Zheng is supported by Hong Kong Research Grants Council under Grants #647611 and #645212, and by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant #71131003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, X., Gong, X. & Zheng, S. Optimal pricing and inventory policies with reliable and random-yield suppliers: characterization and comparison. Ann Oper Res 241, 35–51 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1547-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-014-1547-0