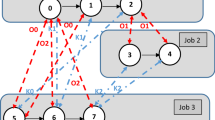
Abstract
In fields like transport or materials sourcing, it is common industrial practice nowadays to contract several partners for the fulfilment of similar sets of tasks. A typical approach is to include quotes to the contracts that specify which portion of the total volume should be given to each partner. In this study, which is inspired by a real-world problem, we examine the question of operationally distributing jobs to a set of partners in order to meet the contracted quotes in different dimensions as closely as possible. We propose the term fair task allocation problem and analyze its complexity. While the problem is NP-hard in the strong sense for the general case, we show that it is solvable in pseudopolynomial time for a given number of partners and dimensions. Besides an exact solution approach based on dynamic programming, we present an efficient Tabu Search procedure. The Tabu Search is applied to real world as well as to self-generated instances. To verify its quality, the results are compared to the solutions of a commercial MIP-solver.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cattrysse, D., & Wassenhove, L. V. (1992). A survey of algorithms for the generalized assignment problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 60(3), 260–272.
Chen, X., Sterna, M., Han, X., & Blazewicz, J. (2016). Scheduling on parallel identical machines with late work criterion: Offline and online cases. Journal of Scheduling, 19(6), 729–736.
Garey, M., & Johnson, D. (1979). Computers and intractability: A guide to the theory of NP-completeness. New York: Freeman.
Gendreau, M., & Potvin, J.-Y. (2014). Tabu search. In E. Burke & G. Kendall (Eds.), Search methodologies (pp. 243–263). Boston, MA: Springer.
Glover, F. (1989). Tabu search: Part I. ORSA Journal on Computing, 1(3), 190–206.
Graham, R., Lawler, E., Lenstra, J., & Rinnooy Kan, A. (1979). Optimization and approximation in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: A survey. Annals of Discrete Mathematics, 5, 287–326.
Huynh Tuong, N., Soukhal, A., & Billaut, J.-C. (2009). A new dynamic programming formulation for scheduling independent tasks with common due date on parallel machines. European Journal of Operational Research, 202(3), 646–653.
Jaehn, F. (2016). Sustainable operations. European Journal of Operational Research, 253(2), 243–264.
Józefowska, J. (2012). Just-in-time scheduling in modern mass production environment. In R. Ríos-Mercado & Y. Ríos-Solís (Eds.), Just-in-time systems (Vol. 60, pp. 171–190). New York: Springer.
Karp, R. (1972). Reducibility among combinatorial problems. In R. Miller & J. Thatcher (Eds.), Complexity of computer computations (pp. 85–103). NY: Plenum Press.
Karsu, Ö., & Azizoğlu, M. (2012). The multi-resource agent bottleneck generalised assignment problem. International Journal of Production Research, 50(2), 309–324.
Korf, R. E. (2009). Multi way number partitioning. In Proceedings of the twenty-first international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 538–543.
Korf, R. E. (2010). Objective functions for multi-way number partitioning. In Proceedings of the third annual symposium on combinatorial search, pp. 71–72.
Kovalyov, M. Y., & Werner, F. (2002). Approximation schemes for scheduling jobs with common due date on parallel machines to minimize total tardiness. Journal of Heuristics, 8, 415–428.
Kubiak, W. (2009). Proportional optimization and fairness (Vol. 127). New York: Springer.
Kubiak, W., Steiner, G., & Yeomans, J. (1997). Optimal level schedule for mixed-model, multi-level just-in-time assembly systems. Annals of Operations Research, 69, 241–259.
Kubiak, W., & Sethi, S. (1991). A note on “level schedule for mixed-model assembly lines in just-in-time systems”. Management Science, 37, 121–122.
Kuhn, H. (1955). The hungarian method for the assignment problem. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 2(1&2), 83–97.
Martello, S., & Toth, P. (1995a). The bottleneck generalized assignment problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 83(3), 621–638.
Martello, S., & Toth, P. (1995b). A note on exact algorithms for the bottleneck generalized assignment problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 83(3), 711–712.
Mazzola, J., & Neebe, A. (1988). Bottleneck generalized assignment problems. Engineering Costs and Production Economics, 14(1), 61–65.
Mazzola, J., & Neebe, A. (1993). An algorithm for the bottleneck generalized assignment problem. Computers & Operations Research, 20(4), 355–362.
Miltenburg, J., & Sinnamon, G. (1989). Scheduling mixed-model, multilevel assembly lines in just-in-time production systems. International Journal of Production Research, 27, 1487–1509.
Parrello, B., Kabat, W., & Wos, L. (1986). Job-shop scheduling using automated reasoning: A case study of the car-sequencing problem. Journal of Automated Reasoning, 2(1), 1–42.
Pentico, D. (2007). Assignment problems: A golden anniversary survey. European Journal of Operational Research, 176(2), 774–793.
Sterna, M. (2011). A survey of scheduling problems with late work criteria. Omega, 39, 120–129.
Zhang, J., Mouratidis, K., & Pang, H. (2011). Heuristic algorithms for balanced multi-way number partitioning. In Proceedings of the twenty-second international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 693–698.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Billing, C., Jaehn, F. & Wensing, T. Fair task allocation problem. Ann Oper Res 284, 131–146 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-3052-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-3052-3