Abstract
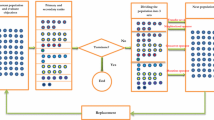
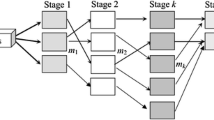
In this paper, we propose a bi-criteria optimization model for a flow shop scheduling problem with permutation, blocking and sequence dependent setup time. Indeed, these constraints are the most encountered in the industrial field, which demands high command flexibility. The objective is the minimization of two criteria, in our case the makespan and the total tardiness combined in a single objective function with a weighting coefficient for each criterion. To solve this problem, we propose a mixed integer linear programming method and a set of different metaheuristics. The suggested metaheuristics are; the genetic algorithm, the iterated greedy metaheuristic and the iterative local search algorithm. This last algorithm is proposed in two ways of exploration of the neighborhood. To verify the effectiveness of our resolution algorithms, a set of instances with n jobs and m machines is randomly generated from small instances to relatively large size ones. The analysis of the suggested simulation model allowed us to note that the iterative local search algorithm gives good results compared to the iterative greedy algorithm. Moreover, it was found that the weighting parameter plays an essential role in the problem decision making. However, it was established that it is difficult to find a good solution that minimizes both criteria at once, a suitable compromise will be necessary to be adopted using the weighting coefficient.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Basset, M., Manogaran, G., El-Shahat, D., & Mirjalili, S. (2018). A hybrid whale optimization algorithm based on local search strategy for the permutation flow shop scheduling problem. Future Generation Computer Systems, 85, 129–145.
Dong, X., Chen, P., Huang, H., & Nowak, M. (2013). A multi-restart iterated local search algorithm for the permutation flow shop problem minimizing total flow time. Computers & Operations Research, 40(2), 627–632.
Dong, X., Huang, H., & Chen, P. (2009). An iterated local search algorithm for the permutation flowshop problem with total flowtime criterion. Computers & Operations Research, 36(5), 1664–1669.
Fernandez-Viagas, V., Valente, J. M., & Framinan, J. M. (2018). Iterated-greedy-based algorithms with beam search initialization for the permutation flowshop to minimise total tardiness. Expert Systems with Applications, 94, 58–69.
Jiang, E., & Wang, L. (2019). An improved multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for energy-efficient permutation flow shop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup time. International Journal of Production Research, 57(6), 1756–1771.
Johnson, S. M. (1954). Optimal two-and three-stage production schedules with setup times included. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 1(1), 61–68.
Li, X., & Li, M. (2015). Multiobjective local search algorithm-based decomposition for multiobjective permutation flow shop scheduling problem. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 62(4), 544–557.
Li, X., & Ma, S. (2017). Multiobjective discrete artificial bee colony algorithm for multiobjective permutation flow shop scheduling problem with sequence dependent setup times. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 64(2), 149–165.
Li, X., Yang, Z., Ruiz, R., Chen, T., & Sui, S. (2018). An iterated greedy heuristic for no-wait flow shops with sequence dependent setup times, learning and forgetting effects. Information Sciences, 453, 408–425.
Liu, G. S., Zhou, Y., & Yang, H. D. (2017). Minimizing energy consumption and tardiness penalty for fuzzy flow shop scheduling with state-dependent setup time. Journal of Cleaner Production, 147, 470–484.
Meziani, N., Oulamara, A., & Boudhar, M. (2019). Two-machine flowshop scheduling problem with coupled-operations. Annals of Operations Research, 275(2), 511–530.
Miyata, H. H., & Nagano, M. S. (2019). The blocking flow shop scheduling problem: a comprehensive and conceptual review. Expert Systems with Applications, 137, 130–156.
Moslehi, G., & Khorasanian, D. (2013). Optimizing blocking flow shop scheduling problem with total completion time criterion. Computers & Operations Research, 40(7), 1874–1883.
M’Hallah, R. (2014). Minimizing total earliness and tardiness on a permutation flow shop using vns and mip. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 75, 142–156.
Nawaz, M., Enscore, E. E, Jr., & Ham, I. (1983). A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow-shop sequencing problem. Omega, 11(1), 91–95.
Newton, M. H., Riahi, V., Su, K., & Sattar, A. (2019). Scheduling blocking flowshops with setup times via constraint guided and accelerated local search. Computers & Operations Research, 109, 64–76.
Nouri, N., & Ladhari, T. (2018). Evolutionary multiobjective optimization for the multi-machine flow shop scheduling problem under blocking. Annals of Operations Research, 267(1–2), 413–430.
Pan, Q. K., & Ruiz, R. (2014). An effective iterated greedy algorithm for the mixed no-idle permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Omega, 44, 41–50.
Pan, Q. K., & Wang, L. (2012). Effective heuristics for the blocking flowshop scheduling problem with makespan minimization. Omega, 40(2), 218–229.
Rajendran, C., & Ziegler, H. (1997). An efficient heuristic for scheduling in a flowshop to minimize total weighted flowtime of jobs. European Journal of Operational Research, 103(1), 129–138.
Riahi V, Newton MH, Su K, Sattar A (2018) Local search for flowshops with setup times and blocking constraints. In Twenty-eighth international conference on automated planning and scheduling
Ribas, I., & Companys, R. (2015). Efficient heuristic algorithms for the blocking flow shop scheduling problem with total flow time minimization. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 87, 30–39.
Rifai, A. P., Nguyen, H. T., & Dawal, S. Z. M. (2016). Multi-objective adaptive large neighborhood search for distributed reentrant permutation flow shop scheduling. Applied Soft Computing, 40, 42–57.
Ronconi, D. P. (2005). A branch-and-bound algorithm to minimize the makespan in a flowshop with blocking. Annals of Operations Research, 138(1), 53–65.
Ronconi DP, Birgin EG (2012) Mixed-integer programming models for flowshop scheduling problems minimizing the total earliness and tardiness. In R. Z. Rios-Mercado & Y. A. Ríos-Solís (Eds.), Just-in-time systems, Springer Optimization and its Applications (Vol. 60, pp. 91–105). New York, NY: Springer.
Rossi, F. L., Nagano, M. S., & Sagawa, J. K. (2017). An effective constructive heuristic for permutation flow shop scheduling problem with total flow time criterion. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 90(1–4), 93–107.
Ruiz, R., Pan, Q. K., & Naderi, B. (2019). Iterated greedy methods for the distributed permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Omega, 83, 213–222.
Ruiz, R., & Stützle, T. (2007). A simple and effective iterated greedy algorithm for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 177(3), 2033–2049.
Shao, Z., Pi, D., & Shao, W. (2018). A novel discrete water wave optimization algorithm for blocking flow-shop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 40, 53–75.
Shoaardebili, N., & Fattahi, P. (2015). Multi-objective meta-heuristics to solve three-stage assembly flow shop scheduling problem with machine availability constraints. International Journal of Production Research, 53(3), 944–968.
Sun, Y., Zhang, C., Gao, L., & Wang, X. (2011). Multi-objective optimization algorithms for flow shop scheduling problem: a review and prospects. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 55(5–8), 723–739.
Ta, Q. C., Billaut, J. C., & Bouquard, J. L. (2018). Matheuristic algorithms for minimizing total tardiness in the m-machine flow-shop scheduling problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 29(3), 617–628.
Takano, M. I., & Nagano, M. S. (2017). A branch-and-bound method to minimize the makespan in a permutation flow shop with blocking and setup times. Cogent Engineering, 4(1), 1389638.
Takano, M., & Nagano, M. (2019). Evaluating the performance of constructive heuristics for the blocking flow shop scheduling problem with setup times. International Journal of Industrial Engineering Computations, 10(1), 37–50.
Tasgetiren, M. F., Kizilay, D., Pan, Q. K., & Suganthan, P. N. (2017). Iterated greedy algorithms for the blocking flowshop scheduling problem with makespan criterion. Computers & Operations Research, 77, 111–126.
Tellache, N. E. H., & Boudhar, M. (2018). Flow shop scheduling problem with conflict graphs. Annals of Operations Research, 261(1–2), 339–363.
Trabelsi, W., Sauvey, C., & Sauer, N. (2012). Heuristics and metaheuristics for mixed blocking constraints flowshop scheduling problems. Computers & Operations Research, 39(11), 2520–2527.
Xu, J., Wu, C. C., Yin, Y., & Lin, W. C. (2017). An iterated local search for the multi-objective permutation flowshop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times. Applied Soft Computing, 52, 39–47.
Yenisey, M. M., & Yagmahan, B. (2014). Multi-objective permutation flow shop scheduling problem: Literature review, classification and current trends. Omega, 45, 119–135.
Ying, K. C. (2008). Solving non-permutation flowshop scheduling problems by an effective iterated greedy heuristic. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 38(3–4), 348.
Yu, A. J., & Seif, J. (2016). Minimizing tardiness and maintenance costs in flow shop scheduling by a lower-bound-based ga. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 97, 26–40.
Zhang, W., Wang, Y., Yang, Y., & Gen, M. (2019). Hybrid multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on differential evolution for flow shop scheduling problems. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 130, 661–670.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aqil, S., Allali, K. On a bi-criteria flow shop scheduling problem under constraints of blocking and sequence dependent setup time. Ann Oper Res 296, 615–637 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-019-03490-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-019-03490-x