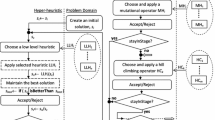
Abstract
This paper presents an iterative adaptive approach which hybridises bin packing heuristics to assign exams to time slots and rooms. The approach combines a graph-colouring heuristic, to select an exam in every iteration, with bin-packing heuristics to automate the process of time slot and room allocation for exam timetabling problems. We start by analysing the quality of the solutions obtained by using one heuristic at a time. Depending on the individual performance of each heuristic, a random iterative hyper-heuristic is used to randomly hybridise the heuristics and produce a collection of heuristic sequences to construct solutions with different quality. Based on these sequences, we analyse the way in which the bin packing heuristics are automatically hybridised. It is observed that the performance of the heuristics used varies depending on the problem. Based on these observations, an iterative hybrid approach is developed to adaptively choose and hybridise the heuristics during solution construction. The overall aim here is to automate the heuristic design process, which draws upon an emerging research theme which is concerned with developing methods to design and adapt heuristics automatically. The approach is tested on the exam timetabling track of the second International Timetabling Competition, to evaluate its ability to generalise on instances with different features. The hyper-heuristic with low-level graph-colouring and bin-packing heuristics approach was found to generalise well over all the problem instances and performed comparably to the state of the art approaches.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atsuta M, Nonobe K, Ibaraki T (2008) Itc2007 track 1: an approach using general csp solver. In: Practice and theory of automated timetabling (PATAT 2008), August 2008, pp 19–22
Burke EK, Elliman DG, Ford PH, Weare RF (1996) Examination timetabling in British universities. In: Burke EK, Ross R (eds) The practice and theory of automated timetabling. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 1153. Springer, Berlin, pp 76–92
Burke EK, McCollum B, Meisels A, Petrovic S, Qu R (2007) A graph-based hyper-heuristic for educational timetabling problems. Eur J Oper Res 176:177–192
Burke EK, Newall J (2004) Solving examination timetabling problems through adaptation of heuristic orderings. Ann Oper Res 129(2):107–134
Burke EK, Petrovic S, Qu R (2006) Case based heuristic selection for timetabling problems. J Sched 9(2):115–132
Burke EK, Qu R, Soghier A (2010) Adaptive selection of heuristics for improving constructed exam timetables. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on the practice and theory of automated timetabling (PATAT’10), pp 136–151
Carter MW, Laporte G, Lee SY (1996) Examination timetabling: algorithmic strategies and applications. J Oper Res Soc 74:373–383
De Smet G (2008) Examination track, practice and theory of automated timetabling. In: Examination track, practice and theory of automated timetabling (PATAT’08), Montreal, 19–22 August 2008
Gogos C, Alefragis P, Housos E (2008) A multi-staged algorithmic process for the solution of the examination timetabling problem. In: Practice and theory of automated timetabling (PATAT 2008), pp 19–22
McCollum B, McMullan P, Burke EK, Parkes AJ, Qu R (2012) A new model for automated examination timetabling. Ann Oper Res 194(1):291–315
McCollum B, McMullan P, Parkes AJ, Burke EK, Abdullah S (2009) An extended great deluge approach to the examination timetabling problem. In: Proceedings of the 4th multidisciplinary international scheduling: theory and applications 2009 (MISTA 2009), Dublin, Ireland, 10–12 August 2009, pp 424–434
Muller T (2008) Itc 2007 solver description: a hybrid approach. In: Practice and theory of automated timetabling (PATAT 2008), August 2008, pp 19–22
Ozcan E, Bykov Y, Birben M, Burke EK (2009) Examination timetabling using late acceptance hyper-heuristics. In: Evolutionary computation 2009 (CEC’09), pp 997–1004
Pillay N (2008) A developmental approach to the examination timetabling problem. In: Practice and theory of automated timetabling (PATAT 2008), August 2008, pp 19–22
Pillay N (2010) Evolving hyper-heuristics for a highly constrained examination timetabling problem. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on the practice and theory of automated timetabling (PATAT’10), pp 336–346
Pillay N (2010) A study into the use of hyper-heuristics to solve the school timetabling problem. In: Proceedings of the 2010 annual. Research conference of the South African institute of computer scientists and information technologists (SAICSIT’10)
Pillay N, Banzhaf W (2009) A study of heuristic combinations for hyper-heuristic systems for the uncapacitated examination timetabling problem. Eur J Oper Res 197:482–491
Pillay N, Banzhaf W (2010) An informed genetic algorithm for the examination timetabling problem. Appl Soft Comput 10(2):457–467
Qu R, Burke EK, McCollum B (2009) Adaptive automated construction of hybrid heuristics for exam timetabling and graph colouring problems. Eur J Oper Res 198(2):392–404
Qu R, Burke EK, McCollum B, Merlot LTG, Lee SY (2009) A survey of search methodologies and automated approaches for examination timetabling. J Sched 12(1):55–89
Sabar N, Ayob M, Qu R, Kendall G (2012) A graph colouring constructive hyper-heuristic for examination timetabling problems. Appl Intell 37:1–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soghier, A., Qu, R. Adaptive selection of heuristics for assigning time slots and rooms in exam timetables. Appl Intell 39, 438–450 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-013-0422-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-013-0422-z