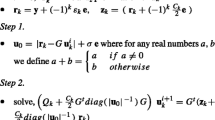Abstract
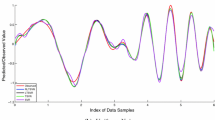
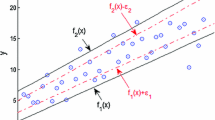
Twin support vector regression (TSVR) and Lagrangian TSVR (LTSVR) satisfy only empirical risk minimization principle. Moreover, the matrices in their formulations are always positive semi-definite. To overcome these problems, we propose an efficient implicit Lagrangian formulation for the dual regularized twin support vector regression, called IRLTSVR for short. By introducing a regularization term to each objective function, the optimization problems in our IRLTSVR are positive definite and implement the structural risk minimization principle. Moreover, the 1-norm of the vector of slack variable is replaced with 2-norm to make the objective functions strongly convex. Our IRLTSVR solves two systems of linear equations instead of solving two quadratic programming problems (QPPs) in TSVR and one large QPP in SVR, which makes the learning speed of IRLTSVR faster than TSVR and SVR. Particularly, we compare three implementations of IRLTSVR with existing approaches. Computational results on several synthetic and real-world benchmark datasets clearly indicate the effectiveness and applicability of the IRLTSVR in comparison to SVR, TSVR and LTSVR.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasundaram S, Gupta D (2014) On implicit Lagrangian twin support vector regression by Newton method. Int J Comput Intell Syst 7(1):50–64
Balasundaram S, Tanveer M (2013) On Lagrangian twin support vector regression. Neural Comput Applic 22(1):257–267
Balasundaram S, Tanveer M (2013) Smooth Newton method for implicit Lagrangian twin support vector regression, KES. IOS Press 17:267–278
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis: forecasting and control. Holden-Day, San Francisco
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 2(3):27
Claesen M, Smet FD, Suykens JAK, Moor BD (2014) EnsembleSVM: A library for ensemble learning using support vector machines. J Mach Learn Res 15(1):141–145
Chen X, Yang J, Liang J, Ye Q (2012) Smooth twin support vector regression. Neural Comput & Applic 21(3):505–513
Cortes C, Vapnik VN (1995) Support vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel based learning method. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Demsar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple datasets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30
Ebrahimi T, Garcia GN, Vesin JM (2003) Joint time-frequency-space classification of EEG in a brain-computer interface application. Journal of Applied Signal Processing 1(7):713–729
Fung G, Mangasarian OL (2003) Finite Newton method for Lagrangian support vector machine classification. Neurocomputing 55(1-2):39–55
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik VN (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machine. Mach Learn 46:389–422
Hiriart-Urruty JB, Strodiot JJ, Nguyen VH (1984) Generalized Hessian matrix and second order optimality conditions for problems with CL1 data. Appl Math Optim 11:43–56
Jayadeva, Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(5):905–910
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2008) Application of smoothing technique on twin support vector machines. Pattern Recogn Lett 29:1842–1848
Lee YJ, Hsieh WF, Huang CM (2005) 𝜖 − SSVR: A smooth support vector machine for 𝜖-insensitive regression. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 17(5):678–685
Lee YJ, Mangasarian OL (2001) SSVM: A smooth support vector machine for classification. Comput Optim Appl 20(1):5–22
Mangasarian OL, Musicant DR (2001) Lagrangian support vector machines. J Mach Learn Res 1:161–177
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2006) Multisurface proximal support vector classification via generalized eigenvalues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(1):69–74
Mukherjee S, Osuna E, Girosi F (1997) Nonlinear prediction of chaotic time series using support vector machines. In: NNSP’97: Neural Networks for Signal Processing VII: in Proc. of IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop. Amelia Island. FL, USA, pp 511–520
Muller KR, Smola AJ, Ratsch G, Schlkopf B, Kohlmorgen J (1999) Using support vector machines for time series prediction. In: Schlkopf B, Burges CJC, Smola AJ (eds) Advances in Kernel Methods- Support Vector Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 243–254
Murphy PM, Aha DW (1992) UCI repository of machine learning databases. University of California, Irvine. http://www.ics.uci.edu/mlearn
Osuna E, Freund R, Girosi F (1997) Training support vector machines: An application to face detection. In: Proceedings of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 130– 136
Peng X (2010) TSVR: An efficient twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Netw 23(3):365–372
Peng X (2010) Primal twin support vector regression and its sparse approximation. Neurocomputing 73:2846–2858
Platt J (1999) Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. In: Scholkopf B., Burges CJC, Smola AJ (eds) Advances in Kernel Methods-Support Vector Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 185–208
Shao YH, Zhang CH, Yang ZM, Jing L, Deng NY (2012) An 𝜖-twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Comput & Appl 23:175–185
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9:293–300
Tanveer M (2015) Linear programming twin support vector regression. to appear in Filomat
Tanveer M (2015) Robust and sparse linear programming twin support vector machines. Cogn Comput 7:137–149
Tanveer M (2015) Application of smoothing techniques for linear programming twin support vector machines. Knowl Inf Syst 45(1):191–214
Tanveer M, Shubham K (2015) A regularization on Lagrangian twin support vector regression. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi:10.1007/s13042-015-0361-6
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Vapnik VN (2000) The nature of statistical learning theory, 2nd Edition. Springer, New York
Xu Y, Wang L (2014) K-nearest neighbor-based weighted twin support vector regression. Appl Intell 41 (1):299– 309
Xu Y, Wang L (2012) A weighted twin support vector regression. Knowl-Based Syst 33:92–101
Zhong P, Xu Y, Zhao Y (2012) Training twin support vector regression via linear programming. Neural Comput & Appl 21(2):399–407
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University for the financial support under the project number 2015/01/4329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanveer, M., Shubham, K., Aldhaifallah, M. et al. An efficient implicit regularized Lagrangian twin support vector regression. Appl Intell 44, 831–848 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-015-0728-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-015-0728-0