Abstract
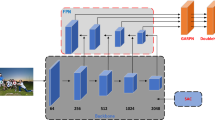
Pedestrian detection is a canonical problem in computer vision. Motivated by the observation that the major bottleneck of pedestrian detection lies on the different scales of pedestrian instances in images, our effort is focused on improving the detection rate, especially for small-sized pedestrians who are relatively far from the camera. In this paper, we introduce a novel context-aware pedestrian detection method by developing the Deconvolution Integrated Faster R-CNN (DIF R-CNN), in which we integrate a deconvolutional module to bring additional context information which is helpful to improve the detection accuracy for small-sized pedestrian instances. Furthermore, the state-of-the-art CNN-based model (Inception-ResNet) is exploited to provide a rich and discriminative hierarchy of feature representations. With these enhancements, a new synthetic feature map can be generated with a higher resolution and more semantic information. Additionally, atrous convolution is adopted to enlarge the receptive field of the synthetic feature map. Extensive evaluations on two challenging pedestrian detection datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DIF R-CNN. Our new approach performs 12.29% better for detecting small-sized pedestrians (those below 50 pixels in bounding-box height) and 6.87% better for detecting all case pedestrians of the Caltech benchmark than the state-of-the-art method. For aerial-view small-sized pedestrian detection, our method achieve 8.9% better performance when compared to the baseline method on the Okutama human-action dataset.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang X, Cheng L, Li B, Hu H-M (2018) Too far to see? Not really!—pedestrian detection with scale-aware localization policy. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(8):3703–3715
Du X, El-Khamy M, Lee J, Davis L (2017) Fused DNN: a deep neural network fusion approach to fast and robust pedestrian detection. In: 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 953-961. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2017.111
Brazil G, Yin X, Liu X (2017) Illuminating pedestrians via simultaneous detection & segmentation. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, pp 4950–4959. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.530
Cai Z, Fan Q, Feris RS, Vasconcelos N (2016) A unified multi-scale deep convolutional neural network for fast object detection. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. ECCV 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9908. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_22
Barekatain M, Marti M, Shih H-F, Murray S, Nakayama K, Matsuo Y, Prendinger H (2017) Okutama-action: an aerial view video dataset for concurrent human action detection. In: 30th IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, pp 2153–2160. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.267
Li J, Liang X, Shen S, Xu T, Feng J, Yan S (2018) Scale-aware fast R-CNN for pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans Multimedia 20(4):985–996
Dollár P, Wojek C, Schiele B, Perona P (2009) Pedestrian detection: a benchmark. In: 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 304–311. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206631
Sermanet P, Kavukcuoglu K, Chintala S, LeCun Y (2013) Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multi-stage feature learning. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 3626–3633. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.465
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 39(6):1137-1149. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
Fu C-Y, Liu W, Ranga A, Tyagi A, Berg AC (2017) DSSD: deconvolutional single shot detector. arXiv:1701.06659 [cs.CV]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.06659. Accessed 23 Jan 2017
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2017) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 39(4):640-651. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683
Hariharan B, Arbeláez P, Girshick R, Malik J (2015) Hypercolumns for object segmentation and fine-grained localization. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 447–456. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298642
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2017) DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834-848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Holschneider M., Kronland-Martinet R., Morlet J., Tchamitchian P. (1990) A Real-Time Algorithm for Signal Analysis with the Help of the Wavelet Transform. In: Combes JM., Grossmann A., Tchamitchian P. (eds) Wavelets. inverse problems and theoretical imaging. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 286–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-75988-8_28
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS). Commun. ACM, pp 1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556 [cs.CV]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. Accessed 4 Sep 2014
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi AA (2017) Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-First Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI Press, pp 4278–4284. http://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI17/paper/view/14806. Accessed 12 Feb 2017
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Zhang L, Lin L, Liang X, He K (2016) Is faster R-CNN doing well for pedestrian detection?. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. ECCV 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9906. Springer, Cham, pp 443–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_28
Pinheiro PO, Lin TY, Collobert R, Dollár P (2016) Learning to refine object segments. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. ECCV 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9905. Springer, Cham, pp 75–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_5
Huang J, Rathod V, Sun C, Zhu M, Korattikara A, Fathi A, Fischer I, Wojna Z, Song Y, Guadarrama S (2017) Speed/accuracy trade-offs for modern convolutional object detectors. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 3296–3297. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.351
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M (2015) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 886–893. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.177
Ess A, Leibe B, Schindler K, Van Gool L (2008) A mobile vision system for robust multi-person tracking. In: 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587581
Wojek C, Walk S, Schiele B (2009) Multi-cue onboard pedestrian detection. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 794–801. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206638
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Basic Research Project in Science and Engineering through the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea and National Research Foundation of Korea (National Research Foundation of Korea 2017-R1D1A1B04-031040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, H., Chen, Y. & Shin, H. Context-aware pedestrian detection especially for small-sized instances with Deconvolution Integrated Faster RCNN (DIF R-CNN). Appl Intell 49, 1200–1211 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1326-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1326-8