Abstract
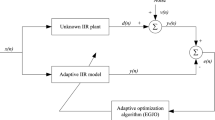
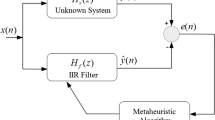
In this paper, optimal coefficients of unknown infinite impulse response (IIR) system are computed by utilizing a new population based algorithm called teacher learner based optimization (TLBO) for system identification problem. TLBO algorithm is inspired by the teaching learning process in the classroom and is free from algorithmic specific parameters. In TLBO, difference mean is calculated for each learner, which is the difference between the existing mean result of the class and the teacher. This difference mean is updated in each iteration and is responsible for maintaining the diversity of this algorithm. System identification problem is based on minimizing the mean square error (MSE) function and finding the optimal coefficients of an unknown IIR system. The MSE is the difference between the outputs of an adaptive IIR system and an unknown IIR system. Exhaustive simulations have been done for finding the unknown system coefficients of same order and reduced order case. Four benchmark functions are tested using TLBO algorithm to verify its efficacy for system identification problem. In order to prove the effectiveness of the applied algorithm, evaluated coefficients and MSE values are compared with that of the genetic algorithm (GA), particle swarm optimization (PSO), cat swarm optimization (CSO), cuckoo search algorithm (CSA), firefly algorithm (FFA), bat algorithm (BAT), differential evolution with wavelet mutation (DEWM), harmony search (HS) and opposition based harmony search (OHS) algorithm.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pai PF, Nguyen BA, Sundaresan MJ (2013) Nonlinearity identification by time-domain-only signal processing. Int J Non-Linear Mech 54:85–98
Zhou X, Yang C, Gui W (2014) Nonlinear system identification and control using state transition algorithm. Appl Math Comput 226:169–179
Chung HC, Liang J, Kushiyama S, Shinozuka M (2004) Digital image processing for non-linear system identification. Int J Non-linear Mech 39(5):691–707
Albaghdadi M, Briley B, Evens M (2006) Event storm detection and identification in communication systems. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 91(5):602–613
Mitra SK (2011) Digital signal processing:a computer-based approach. McGraw-Hill, New York
Barreto GA, Souza LGM (2016) Novel approaches for parameter estimation of local linear models for dynamical system identification. Appl Intell 44(1):149–165
Lu Y, Yan D, Levy D (2015) Friction coefficient estimation in servo systems using neural dynamic programming inspired particle swarm search. Appl Intell 43(1):1–14
Widrow B, Strearns SD (1985) Adaptive signal processing. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Yang XS (2010) Nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms. Luniver Press
Yao L, Sethares WA (1994) Nonlinear parameter estimation via the genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process 42(4):927–935
Aggarwal A, Rawat TK, Kumar M, Upadhyay DK (2015) Optimal design of FIR high pass filter based on l 1 error approximation using real coded genetic algorithm. Eng Sci Technol 18(4):594–602
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Piscataway, pp 1942–1948
Chen S, Luk BL (2010) Digital IIR filter design using particle swarm optimisation. International Journal of Modelling. Identif Control 9(4):327–335
Krusienski DJ, Jenkins WK (2004) Particle swarm optimization for adaptive IIR filter structure. In: IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation, CEC 2004, vol 1, pp 965–970
Durmus B, Gun A (2011) Parameter identification using particle swarm optimization. In: International advanced technologies symposium, IATS, pp 188–192
Fang W, Sun J, Xu W (2006) Analysis of adaptive IIR filter design based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. In: The IEEE sixth world congress on intelligent control and automation, WCICA 2006, vol 1, pp 3396–3400
Panda G, Pradhan PM, Majhi B (2011) IIR System identification using cat swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 38(10):12,671–12,683
Saha SK, Ghoshal SP, Kar R, Mandal D (2013) Cat Swarm Optimization algorithm for optimal linear phase FIR filter design. ISA T 52(6):781–794
Singh S, Ashok A, Rawat TK, Kumar M (2016) Optimal IIR system identification using flower pollination algorithm. In: IEEE International conference on power electronics, intelligent control and energy systems ICPEICES, pp 1–6
Karaboga N (2005) Digital IIR filter design using differential evolution algorithm. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing 8:1269–1276
Yang XS, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via lévy flights. In: IEEE World Congress on Nature and Biologically Inspired Computing, NaBIC 2009, pp 210–214
Kumar M, Rawat TK (2015) Optimal design of FIR fractional order differentiator using cuckoo search algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 42(7):3433–3449
Kumar M, Rawat TK (2015) Optimal Fractional delay-IIR Filter Design Using Cuckoo Search Algorithm. ISA T 59:39–54
Kumar M, Aggarwal A, Rawat TK, Parthasarathy H (2016) Optimal Nonlinear System Identification Using Fractional Delay Second-Order Volterra System. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica. https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2016.7510184
Dai C, Chen W, Zhu Y (2010) Seeker optimization algorithm for digital IIR filter design. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(5):1710– 1718
Kumar M, Aggarwal A, Rawat TK (2016) Bat algorithm: application to adaptive infinite impulse response system identification. Arab J Sci Eng 41(9):3587–3604
Karaboga N (2009) A new design method based on artificial bee colony algorithm for digital IIR filters. J Frankl Inst 346(4):328–348
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2011) Filter modeling using gravitational search algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24(1):117–122
Saha SK, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP (2014) Harmony search algorithm for infinite impulse response system identification. Comput Electr Eng 40(4):1265–1285
Upadhyay P, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP, Mukherjee V (2014) A novel design method for optimal IIR system identification using opposition based harmony search algorithm. J Frankl Inst 351(5):2454–2488
Upadhyay P, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP (2016) A new design method based on firefly algorithm for IIR system identification problem. J King Saud Univ-Eng Sci 28(2):174–198
Upadhyay P, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP (2014) IIR System identification using differential evolution with wavelet mutation. Inst J Eng Sci Technol 17(1):8–24
Upadhyay P, Kar R, Mandal D, Ghoshal SP (2014) Craziness based particle swarm optimization algorithm for IIR system identification problem. Int J Electron Commun 68(5):369–378
Jiang S, Wang Y, Ji Z (2015) A new design method for adaptive IIR system identification using hybrid particle swarm optimization and gravitational search algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn 79(4):2553–2576
Yang Y, Yang B, Niu M (2018) Adaptive infinite impulse response system identification using opposition based hybrid coral reefs optimization algorithm. Appl Intell 48(7):1689–1706
Lagos-Eulogio P, Seck-Tuoh-Mora JC, Hernandez-Romero N, Medina-Marin J (2017) A new design method for adaptive IIR system identification using hybrid CPSO and DE. Nonlinear Dyn 88(4):2371–2389
Mohammadi A, Zahiri SH, Razavi SM (2018) Infinite impulse response systems modeling by artificial intelligent optimization methods. Evolving Systems:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-018-9218-z
Rao RV (2016) Teaching-learning-based Optimization algorithm. In: Teaching learning based optimization algorithm and its engineering applications. Springer, Cham, pp 9–39
Wenchao Y, Gao L, Li X, Zhou Y (2015) A new differential evolution algorithm with a hybrid mutation operator and self-adapting control parameters for global optimization problems. Appl Intell 42(4):642–660
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
This is to state that the authors have no conflict of interest with anyone.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Ashok, A., Kumar, M. et al. Adaptive infinite impulse response system identification using teacher learner based optimization algorithm. Appl Intell 49, 1785–1802 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1354-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1354-4