Abstract
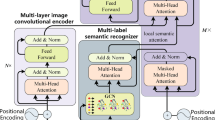
Understanding scene image includes detecting and recognizing objects, estimating the interaction relationships of the detected objects, and describing image regions with sentences. However, since the complexity and variety of scene image, existing methods take object detection or vision relationship estimate as the research targets in scene understanding, and the obtained results are not satisfactory. In this work, we propose a Multi-level Semantic Tasks Generation Network (MSTG) to leverage mutual connections across object detection, visual relationship detection and image captioning, to solve jointly and improve the accuracy of the three vision tasks and achieve the more comprehensive and accurate understanding of scene image. The model uses a message pass graph to mutual connections and iterative updates across the different semantic features to improve the accuracy of scene graph generation, and introduces a fused attention mechanism to improve the accuracy of image captioning while using the mutual connections and refines of different semantic features to improve the accuracy of object detection and scene graph generation. Experiments on Visual Genome and COCO datasets indicate that the proposed method can jointly learn the three vision tasks to improve the accuracy of those visual tasks generation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang Y, Kuan K, Lin J et al (2017) Object detection meets knowledge graphs. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. IEEE, Sydney, pp 1661–1667
Marino K, Salakhutdinov R, Gupta A (2017) The more you know: using knowledge graphs for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 2673–2681
Chao Y-W, Wang A, He Y et al (2015) Hico: A benchmark for recognizing human-object interactions in images. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE. Santiago, pp 1017–1025
Lu C, Krishna R, Bernstein M, Li F-F (2016) Visual relationship detection with language priors. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, Amsterdam, pp 852–869
Donahue J, Hendricks LA, Rohrbach M et al (2017) Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition and Description. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 677–691
Karpathy A, Li F-F (2016) Deep Visual-Semantic Alignments for Generating Image Descriptions [J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. IEEE, Boston, USA, pp 664–676
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R et al (2015) Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. IEEE, Lille, pp 2048–2057
Johnson J, Krishna R, Stark M et al (2015) Image retrieval using scene graphs. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Boston, 3668–3678
Shen W, Zhao K, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Bai X, Yuille A (2017) DeepSkeleton: learning multi-task scale-associated deep side outputs for object skeleton extraction in natural images[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(11):5298–5311
Yatskar M, Zettlemoyer L, Farhadi A et al (2016) Situation recognition: visual semantic role labeling for image understanding. In: IEEE computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, Las Vegas, pp 5534–5542
Zitnick C, Parikh VL (2013) Learning the visual interpretation of sentences. In International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Sydney, pp 1681–1688
Liu Y, Yu J, Han Y et al (2018) Understanding the effective receptive field in semantic image segmentation[J]. Multimed Tools Appl 77(17):22159–22171
Przelaskowski A (2010) The role of sparse data representation in semantic image understanding. In: International Conference on Computer Vision & Graphics: Part I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T et al (2014) Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Columbus, pp 580–587
Cao Y, Fu G, Yang J, Cao Y, Yang MY (2019) Accurate salient object detection via dense recurrent connections and residual-based hierarchical feature integration[J]. Signal Process Image Commun 78:103–112
Li Y, Tarlow D, Brockschmidt M et al (2016) Gated graph sequence neural networks[J]. In: IEEE International Conference on Learning Representations. IEEE, San Juan, pp 1–20
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(6):1137–1149
Bochkovskiy A, Wang C-Y, Liao H-Y (2020) YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXivpreprint arXiv 2004:10934
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D et al (2016) SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Amsterdam, pp 21–37
Li Y, Ou Y, Wang X et al (2017) Vip-cnn: visual phrase guided convolutional neural network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 1347–1356
Xu D-F, Zhu Y-K et al (2017) Scene graph generation by iterative message passing. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 5410–5419
Elhoseiny M, Cohen S, Chang W et al (2015) Sherlock: Scalable fact learning in images. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IEEE. San Francisco 31(1)
Anderson P, He X-D, Chris B et al (2018) Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In: In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 2018. IEEE, Salt Lake, pp 6077–6086
Kulkarni G, Premraj V, Ordonez V, Dhar S, Li S, Choi Y, Berg AC, Berg TL (2013) Babytalk: understanding and generating simple image descriptions[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(12):2891–2903
Elliott D, Keller F (2013) Image description using visual dependency representations. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. IEEE, Seattle, Washington, DC, pp 1292–1302
Verma Y, Gupta A, Mannem P et al (2013) Generating image descriptions using semantic similarities in the output space. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Portland, pp 288–293
Devlin J, Cheng H, Fang H et al (2015) Language models for image captioning: The quirks and what works. In: Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. IEEE, Beijing, pp 100–105
Chen L, Zhang H, Xiao J et al (2017) SCA-CNN: spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 6298–6306
Oriol V, Alexander T, Samy B et al (2015) Show and tell: a neural image caption generator. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Boston, pp 3156–3164
Steven J, Etienne M, Mroueh Y et al (2017) Self-critical sequence training for image captioning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 7008–7024
Yao T, Pan Y-W, Li Y-H et al (2017) Boosting image captioning with attributes. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Venice, pp 4894–4902
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R et al (2015) Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. IEEE, Lille, pp 2048–2057
You Q, Jin H, Wang Z et al (2016) Image captioning with semantic attention. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Las Vegas, pp 4651–4659
Lu J, Xiong C, Parikh D et al (2017) Knowing when to look: adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 375–383
Li Y, Ouyang W, Wang X et al (2017) Vip-cnn: visual phrase guided convolutional neural network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Honolulu, pp 1347–1356
Yang J, Lu J, Lee S et al (2018) Graph RCNN for scene graph generation. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Munich, pp 670–685
Li Y, Ouyang W, Zhou B et al (2018) Factorizable net: an efficient subgraph-based framework for scene graph generation. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Munich, pp 335–351
Zellers R, Yatskar M, Thomson S et al (2017) Neural motifs: Scene graph parsing with global context. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Salt Lake, pp 5831–5840
Qi X, Liao R, Jia J et al (2017) 3D graph neural networks for RGBD semantic segmentation. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Venice, pp 5199–5208
Kenneth M, Ruslan S, Abhinav G (2017) The more you know: using knowledge graphs for image classification. arXiv preprint arXiv 1612:04844
Krishna R, Zhu Y, Groth O, Johnson J, Hata K, Kravitz J, Chen S, Kalantidis Y, Li LJ, Shamma DA, Bernstein MS, Fei-Fei L (2017) Visual genome: connecting language and vision using Crowdsourced dense image annotations[J]. Int J Comput Vis 123(1):32–73
Lin T-Y, Maire M, Belongie S et al (2014) Microsoft coco: common objects in context. In: IEEE European conference on computer vision. IEEE, Zurich, pp 740–755
Karpathy A, Li F-F (2015) Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Boston, pp 3128–3137
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Li Y, Ouyang W, Zhou B et al (2017) Scene graph generation from objects, phrases and region captions. In IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Venice, pp 1261–1270
Wang W, Wang R, Shan S et al (2019) Exploring context and visual pattern of relationship for scene graph generation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, Long Beach, pp 8188–8197
Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T et al (2002) BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: IEEE 40th annual meeting on association for computational linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics. IEEE, Philadelphia, pp 311–318
Banerjee S, Lavie A (2005) METEOR: an automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In: Proceedings of the Acl Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization. IEEE, Michigan, pp 65–72
Lin C-Y, Hovy E (2003) Automatic evaluation of summaries using n-gram co-occurrence statistics. In: IEEE Human Language Technology Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. IEEE, Edmonton, pp 71–78
Vedantam R, Lawrence Zitnick C, Parikh D (2015) Cider: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, Boston, pp 4566–4575
Anderson P, Fernando B, Johnson M et al (2016) Spice: Semantic propositional image caption evaluation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, IEEE, Amsterdam, pp 382–398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, P., Mo, H. & Jiang, L. Scene graph generation by multi-level semantic tasks. Appl Intell 51, 7781–7793 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02115-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02115-2