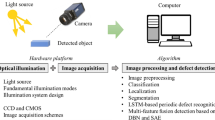
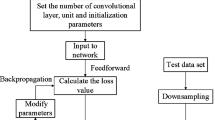
Abstract
Pattern classification is a fundamental problem in many data-driven application domains. New-labeled data refers to the data with the labels that are new and different from source labels. How to learn the new-labeled data is a crucial research in the data classification. In this paper, an evolved fuzzy min-max neural network for new-labeled data classification (FMM-NLA) is proposed. In FMM-NLA, the network can be self-evolved. Unlike the traditional FMM methods, the trained network of FMM-NLA can be expanded when new-labeled data added. FMM-NLA is a continuing-learning method, which can realize the continuing training process without retraining all the data. In order to verify the superiority of the proposed method, benchmark data sets are used. The experimental results show that FMM-NLA is effective in handling new-labeled data. Moreover, the application result on the pipeline defect recognition in depth shows that FMM-NLA is effective in solving the new-labeled defect recognition problem.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khari M, Garg AK, Gonzalez-Crespo R, Verd E (2019) Gesture Recognition of RGB and RGB-D Static Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Int J Interact Multimed Artif Intell 5(7):22–27. https://doi.org/10.9781/ijimai.2019.09.002
Bouchra N, Aouatif A, Mohammed N, Nabil H (2019) Auto-Encoder For face classification deep belief Network and international. J Interact Multimed Artif Intell 5(5):22–29. https://doi.org/10.9781/ijimai.2018.06.004
Kumar NA, Sanjay C, Chakravarthy M (2019) Mamdani Fuzzy Expert System Based Directional Relaying Approach for Six-Phase Transmission Line. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence. In: Press:1-11. https://doi.org/10.9781/ijimai.2019.06.002
Jain AK (1999) Data clustering: a review[J]. Acm Comput Surv 31(3):264–323
Chen Y, Lin Z, Zhao X et al (2014) Deep Learning-Based classification of hyperspectral Data[J]. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Observ Remote Sens 7(6):2094–2107
Kim HM, Choi DH (2016) Defects detection of gas pipeline near the welds based on self quotient image and discrete cosine transform. Russ J Nondestruct Test 52(3): 175C183
Liu J, Zang D, Liu C, Ma Y, Fu M (2019) A leak detection method for oil pipeline based on markov feature and two-stage decision scheme. Measurement 138:433-445, ISSN:0263-2241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.01.029
Antipov AG, Markov AA (2018) 3D simulation and experiment on high speed rail MFL inspection. NDT E Int 98:177–185, ISSN:0963-8695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2018.04.011
Wu D, Liu Z, Wang X, Su L (2017) Composite magnetic flux leakage detection method for pipelines using alternating magnetic field excitation. NDT E Int 91:148–155. ISSN:0963-8695, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2017.07.002
Han W, Wu Z, Zhou M, et al. (2017) Magnetic flux leakage signal inversion based on improved efficient population utilization strategy for particle swarm Optimization[J]. Russ J Nondestruct Test 53(12):862–873
Polikar R, et al. (2001) Learn++: an incremental learning algorithm for supervised neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C (Appl Rev) 31(4):497–508
Ahmed AA, Mohammed MF (2018) SAIRF: A similarity approach for attack intention recognition using fuzzy min-max neural network. J Comput Sci 25:467–473. ISSN:1877-7503, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2017.09.007
Jawarkar NP (2007) Emotion Recognition using Prosody Features and a Fuzzy Min-Max Neural Classifier[J]. IETE Tech Rev 24(5):369–373
Schlimmer JC, Granger RH (1986) Incremental learning from noisy data. Mach Learn 1 (3):317–354
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern recognition and machine learning (information science and Statistics)[M]. Springer, New York
Al Sayaydeh ON, Mohammed MF, Lim CP (2019) Survey of Fuzzy minCMax Neural Network for Pattern Classification Variants and Applications. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(4):635–645. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2865950
Shinde S, Kulkarni U (2017) Extended fuzzy hyperline-segment neural network with classification rule extraction. Neurocomputing 260(oct.18):79–91, ISSN:0925-2312, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.03.036
Simpson PK (1992) Fuzzy min-max neural networks. I. Classification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3(5):776–786. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.159066
Simpson PK (1993) Fuzzy min-max neural networks - Part 2: Clustering. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 1(1):32-. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.1993.390282
Gabrys B, Bargiela A (2000) General fuzzy min-max neural network for clustering and classification[M]. IEEE Press
Mohammed MF, Lim CP (2016) Improving the Fuzzy Min-Max Neural Network with a K-nearest Hyperbox Expansion Rule for Pattern Classification[J]. Appl Soft Comput, pp 52
Khuat TT, Chen F (2019) Gabrys B. An Effective Multi-Resolution Hierarchical Granular Representation based Classifier using General Fuzzy Min-Max Neural Network[J]. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst PP(99):1–1
Liu J, Qu Y, Dong FZ (2019) Semi-supervised Fuzzy Min–Max Neural Network for Data Classification[J]. Neural Process Lett (Nov.14):1573-773X
Bezdek JC, Ehrlich R, Full WFCM (1984) The fuzzy c -means clustering algorithm[J]. Comput Geosci 10(2):191– 203
Liu J, Ma Y, Zhang H, Su H, Xiao G (2017) A modified fuzzy minCmax neural network for data clustering and its application on pipeline internal inspection data. Neurocomputing 238:56–66. ISSN:0925-2312, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.036
Quteishat AM, Lim CP (2007) A modified fuzzy min-max neural network and its application to fault classification[M]. Soft Computing in Industrial Applications Springer Berlin Heidelberg
Zhang H, Liu J, Ma D, Wang Z (2011) Data-Core-Based Fuzzy Min-Max neural network for pattern Classification[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(12):2339–2352. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2011.2175748
Dua D, Graff C (2019) UCI Machine Learning Repository http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml. University of California, School of Information and Computer Science, Irvine
Carvalho AA, Rebello JMA, Sagrilo LVS, et al. (2006) MFL Signals and artificial neural networks applied to detection and classification of pipe weld defects[J]. NDT E Int 39(8):661– 667
Xu J, et al. (2019) Low-Cost, Tiny-Sized MEMS Hydrophone Sensor for Water Pipeline Leak Detection. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(8):6374–6382. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2874583
Qidwai UA (2009) Autonomous corrosion detection in gas pipelines: a hybrid-fuzzy classifier approach using ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation protocols. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Frequen Control 56 (12):2650–2665. https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2009.1356
Lu S, Feng J, Zhang H, Liu J, Wu Z (2019) An estimation method of defect size from MFL image using visual transformation convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15(1):213–224. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2018.2828811
Liu J, Qu F, Hong X, Zhang H A Small-sample Wind Turbine Fault Detection Method with Synthetic Fault Data. Using Generative Adversarial Nets. IEEE Trans Ind Inf. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2018.2885365
Rostami Kandroodi M, Nadjar Araabi B, Mansoob Bassiri M, Nili Ahmadabadi M (2017) Estimation of depth and length of defects from magnetic flux leakage measurements: Verification with simulations, experiments and pigging data. IEEE Trans Magn 53(3):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2016.2631525
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFF0108800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61973071, 61627809, 61703087), the Liaoning Natural Science Foundation of China (2019 − KF − 03 − 04), the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program(XLYC1907138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Liu, J., Qu, F. et al. Evolved fuzzy min-max neural network for new-labeled data classification. Appl Intell 52, 305–320 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02259-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02259-9