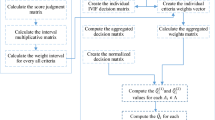
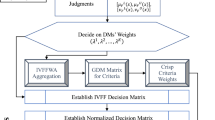
Abstract
With the rapid development of the economy, the competition among enterprises is increasingly intensifying and the internal contradictions of the enterprise are prominent, which pose many challenges to the sustainable development of small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Therefore, the scientific assessment of an enterprise’s sustainable development capability is important, as it reflects the current development status and the potential future opportunities. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations (HFLPRs), a combination of linguistic term sets and hesitant fuzzy preference relations are useful in solving group decision-making (GDM) problems. HFLTS can tackle situations in which decision makers (DMs) consider multiple potential linguistic terms at the same time than a single term for an indicator, alternative, variable, etc., to express their preferences without the use of numerical values. This paper introduces a new GDM approach under the hesitant fuzzy linguistic environment based on a multiplicative consistency adjustment algorithm and a Charnes-Cooper-Rhodes Data Envelopment Analysis (CCR-DEA) model to assess the sustainable development of SMEs. First, the concepts of HFLPR and multiplicative consistency, including the consistency index and consistency checking approach, are reviewed. Then, a new consistency-improving method for achieving an acceptable HFLPR is introduced, which ensures that each HFLPR satisfies the requirements for multiplicative consistency. After this transformation, an innovative CCR-DEA model is developed using the input–output technique to determine the final ranking of alternatives and to achieve an optimal decision-making solution. Finally, the hesitant fuzzy linguistic decision-making method is intended to be used to assess the economic growth of SMEs. The advantages and applicability of the proposed approach are determined by comparative analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamenko M, Mishchuk I, Zinchenko O (2020) Economic security and innovation activity of personnel-determinants of sustainable development of enterprises. E3S web of conferences 166: 13009
Lai Y Q (2019) Research on implementation path of mobile new media marketing strategy for small and medium-sized micro-enterprises based on Chinese market. DEStech transactions on computer science and engineering. Institute of Management Science and Industrial Engineering. Proceedings of 2019 2nd international workshop on advances in social sciences, 2019: 9
Wang WB, Lin WL, Dai XY, Yan YZ, Xuan AP (2020) Evaluating the sustainable growth of small- and medium-sized construction enterprises using the multicriteria decision-making method. Discret Dyn Nat Soc 3:1–13
Debashree D, Soumyadeb C, Prasanta KD, Sadhan KG (2018) Impact of lean and sustainability oriented innovation on sustainability performance of small and medium sized enterprises: a data envelopment analysis-based framework. Int J Prod Econ 219:416–430
Jansson J, Nilsson J, Modig F, Vall GH (2017) Commitment to sustainability in small and medium-sized enterprises: the influence of strategic orientations and management values. Bus Strateg Environ 26(1):69–83
Halme M, Korpela M (2014) Responsible innovation toward sustainable development in small and medium-sized enterprises: a resource perspective. Bus Strateg Environ 23(8):547–566
Anisse T (2017) International trade as an engine for sustainable development: the ITFC experience in supporting SMEs. Global Policy 8(3):392–396
Wu J, Zhao ZW, Sun Q, Fujita H (2021) A maximum self-esteem degree based feedback mechanism for group consensus reaching with the distributed linguistic trust propagation in social network. Information Fusion 67:80–93
Wu J, Chiclana F, Fujita H, Herrera-Viedma E (2017) A visual interaction consensus model for social network group decision making with trust propagation. Knowl-Based Syst 122:39–50
Dong YC, Zha QB, Zhang HJ, Kou G, Fujita H, Chiclana F, Herrera-Viedma E (2018) Consensus reaching in social network group decision making: research paradigms and challenges. Knowl-Based Syst 162:3–13
Rahman K, Sanam A, Saleem A, Muhammad Y (2020) Some induced generalized Einstein aggregating operators and their application to group decision-making problem using intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Annals of Optimization Theory and Practice 3(3):15–49
Zhou XY, Ji FP, Wang LQ, Ma YF, Fujita H (2020) Particle swarm optimization for trust relationship based social network group decision making under a probabilistic linguistic environment. Knowl-Based Syst 200:105999
Wu J, Sun Q, Fujita H, Chiclana F (2019) An attitudinal consensus degree to control feedback mechanism in group decision making with different adjustment cost. Knowl-Based Syst 164:265–273
Capuano N, Chiclana F, Herrera-Viedma E, Fujita H, Loia V (2019) Fuzzy group decision making for influence-aware recommendations. Comput Hum Behav 101:371–379
Bhattacharya K, De S (2020) Decision making under intuitionistic fuzzy metric distances. Annals of Optimization Theory and Practice 3(2):49–64
Garg H, Chen SM (2020) Multi-attribute group decision making based on neutrality aggregation operators of q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 517(5):427–447
Luo X, Li WM, Wang XZ (2019) Fuzzy interval linguistic sets with applications in multi-attribute group decision making. J Syst Eng Electron 29(6):1237–1250
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Inf Sci 8(2):99–249
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25(6):529–539
Wu P, Zhou LG, Chen HY, Tao ZF (2020) Multi-stage optimization model for hesitant qualitative decision making with hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Appl Intell 50(1):222–240
Liu HB, Jiang L, Xu ZS (2017) Improving the additive and multiplicative consistency of hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 33(6):3677–3693
Li SL, Wei CP (2020) A large scale group decision making approach in healthcare service based on sub-group weighting model and hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Comput Ind Eng 144(6):106444
Meng FY, Chen SY, Zhang SL (2020) Group decision making based on acceptable consistency analysis of interval linguistic hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Inf Sci 530(3):66–84
Hao JJ, Chiclana F (2020) Attitude quantifier based possibility distribution generation method for hesitant fuzzy linguistic group decision making. Inf Sci 518(1):341–360
Krishankumar R, Ravichandran KS, Aggarwal M, Tyagi SK (2020) Extended hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set with fuzzy confidence for solving group decision-making problems[J]. Neural Comput & Applic 32(4):2879–2896
Jin FF, Ni ZW, Pei LD, Chen HY (2018) Goal programming approach to derive intuitionistic multiplicative weights based on intuitionistic multiplicative preference relations. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 9(4):641–650
Krishankumar R, Ravichandran KS, Liao HC, Kar S (2020) An integrated decision framework for group decision-making with double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic information and unknown weights. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems 13(1):624–637
Wang XX, Xu ZS, Gou XJ, Miao X (2019) Distance and similarity measures for nested probabilistic-numerical linguistic term sets applied to evaluation of medical treatment. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems 21(5):1306–1329
Liu HB, Jiang L (2020) Optimizing consistency and consensus improvement process for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations and the application in group decision making. Information Fusion 56(4):114–127
Jin FF, Ni ZW, Chen H et al (2016) Approaches to decision making with linguistic preference relations based on additive consistency. Appl Soft Comput 49(12):71–80
Wu P, Zhu JM, Zhou LG, Chen HY (2019) Automatic iterative algorithm with local revised strategies to improve the consistency of hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems 21(7):2283–2298
Farhadinia B, Xu ZS (2018) Novel hesitant fuzzy linguistic entropy and cross-entropy measures in multiple criteria decision making. Appl Intell 48(11):3915–3827
Liao HC, Xu ZS, Herrera-Viedma E, Francisco H (2018) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and its application in decision making: a state-of-the-art survey. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems 20(7):2084–2110
Meng FY, Tan CQ, Chen XH (2017) Multiplicative consistency analysis for interval fuzzy preference relations: a comparative study. Omega 68(4):17–38
Talukdar P, Goala S, Dutta P, Limboo B (2020) Fuzzy multicriteria decision making in medical diagnosis using an advanced distance measure on linguistic Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Annals of Optimization Theory and Practice 3(4):113–131
Li CC, Rodríguez RM, Martínez L, Dong YC, Herrera F (2018) Consistency of hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations: an interval consistency index. Inf Sci 432:347–361
Zhu B, Xu ZS (2014) A fuzzy linear programming method for group decision making with additive reciprocal fuzzy preference relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst 246(4):19–33
Zhu B, Xu ZS (2014) Stochastic preference analysis in numerical preference relations. Eur J Oper Res 237(2):628–633
Liu JP, Xu Q, Chen HY, Zhou LG, Zhu JM, Tao ZF (2019) Group decision making with interval fuzzy preference relations based on DEA and stochastic simulation. Neural Comput & Applic 31(7):3095–3106
Yue C (2019) A normalized projection-based group decision-making method with heterogeneous decision information and application to software development effort assessment. Appl Intell 49(10):3587–3605
Jin FF, Ni ZW, Langari R, Chen HY (2020) Consistency improvement-driven decision-making methods with probabilistic multiplicative preference relations. Group Decis Negot 29(2):371–397
Javad G (2019) An interactive procedure to improve estimate of value efficiency in DEA. Expert Syst Appl 149(9):29–45
Rodriguez RM, Martinez L, Herrera F (2012) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(1):109–119
Zhang Q, Wang CJ (2019) DEA efficiency prediction based on IG–SVM. Neural Comput & Applic 31(12):8369–8378
Zhang ZM, Wu C (2014) On the use of multiplicative consistency in hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Knowl-Based Syst 72:13–27
Liu JP, Fang SC, Chen HY (2020) Multiplicative data envelopment analysis cross-efficiency and stochastic weight space acceptability analysis for group decision making with interval multiplicative preference relations. Inf Sci 514:339–332
Xu YJ, Wen X, Sun H, Wang H (2018) Consistency and consensus models with local adjustment strategy for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems 20(7):2216–2233
Zhang ZM (2016) Deriving the priority weights from incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations based on multiplicative consistency. Appl Soft Comput 99(5):37–59
Liao HC, Jiang L, Lev B (2019) Novel operations of PLTSs based on the disparity degrees of linguistic terms and their use in designing the probabilistic linguistic ELECTRE III method. Appl Soft Comput 80(7):450–464
Zhu B, Xu Z, Xu J (2014) Deriving a ranking from hesitant fuzzy preference relations under group decision making. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 44(8):1328–1337
Zhang ZM, Chen SY, Wang C (2020) Group decision making based on multiplicative consistency and consensus of fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Inf Sci 509(9):71–86
Chen HP, Xu GQ (2019) Group decision making with incomplete intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations based on additive consistency. Comput Ind Eng 516(4):560–567
Zhang ZM, Wu C (2014) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic aggregation operators and their applications to multiple attribute group decision making. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 26(5):2185–2202
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71901001, 72071001, 71871001, 71771001, 72001001), Humanities and Social Sciences Planning Project of the Ministry of Education (No. 20YJAZH066), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Nos. 2008085QG333, 2008085MG226, 2008085QG334), Key Research Project of Humanities and Social Sciences in Colleges and Universities of Anhui Province (Nos. SK2020A0038, SK2019A0013), Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Anhui Province (No. 1908085 J03), Research Funding Project of Academic and technical leaders and reserve candidates in Anhui Province (No. 2018H179), Top Talent Academic Foundation for University Discipline of Anhui Province (No. gxbjZD2020056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, ., Zhang, Y., Garg, H. et al. Evaluation of small and medium-sized enterprises’ sustainable development with hesitant fuzzy linguistic group decision-making method. Appl Intell 52, 4940–4960 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02372-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02372-9