Abstract
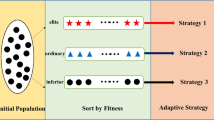
Since many PSO variants are easily trapped in local optima from which they can barely break free, this paper proposes an adaptive hierarchical update particle swarm optimization (AHPSO) algorithm. The new term “local optimum early warning” is first defined to reflect the risk of being trapped in a local optimum. It plays a key role in the global coordinated control to determine the paradigm evolution direction and adjust the trajectory of particles in different risk environments. After that, the adaptive hierarchical update method generates two-layer and three-layer update formulas for the global exploration subpopulation and the local exploitation subpopulation, respectively, in order to improve the capability to resist the temptation of local optima. Consisting of the weighted synthesis sub-strategy and the mean evolution sub-strategy, the multi-choice comprehensive learning strategy is then employed to develop the most suitable learning paradigm to guide the motion path. Moreover, 18 benchmark functions and one real-world optimization problem are employed to evaluate the AHPSO against eight typical PSO variants. According to the experimental results, the AHPSO outperformed other methods in solving different types of functions by yielding high solution accuracy and high convergence speed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95-international conference on neural networks, vol 4. IEEE, pp 1942–1948
van den Bergh F, Engelbrecht AP (2006) A study of particle swarm optimization particle trajectories. Inf Sci 176(8):937–971
Bai Q (2010) Analysis of particle swarm optimization algorithm. Comput Inf Sci 3(1):180
Mohammad RB (2019) A theoretical guideline for designing an effective adaptive particle swarm. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 24(1):57–68
Chen Y-P, Jiang P (2010) Analysis of particle interaction in particle swarm optimization. Theor Comput Sci 411(21):2101–2115
Wang D, Tan D, Liu L (2018) Particle swarm optimization algorithm: an overview. Soft Comput 22(2):387–408
Tan TY, Li Z, Lim CP, Fielding B, Yu Y, Anderson E (2019) Evolving ensemble models for image segmentation using enhanced particle swarm optimization. IEEE Access 7:34004–34019
Valle YD, Venayagamoorthy GK, Mohagheghi S, Hernandez J-C, Harley RG (2008) Particle swarm optimization: basic concepts, variants and applications in power systems. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12 (2):171–195
Alswaitti M, Albughdadi M, Isa NAM (2018) Density-based particle swarm optimization algorithm for data clustering. Expert Syst Appl 91:170–186
Mapetu JPB, Chen Z, Kong L (2019) Low-time complexity and low-cost binary particle swarm optimization algorithm for task scheduling and load balancing in cloud computing. Appl Intell 49(9):3308–3330
Yang L, Chen H (2019) Fault diagnosis of gearbox based on rbf-pf and particle swarm optimization wavelet neural network. Neural Comput Appl 31(9):4463–4478
Wang D, Wang H, Liu L (2016) Unknown environment exploration of multi-robot system with the fordpso. Swarm Evol Comput 26:157–174
Du B, Wei Q, Liu R (2019) An improved quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization for endmember extraction. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57(8):6003–6017
Ye Z. (2019) Coverage optimization and simulation of wireless sensor networks based on particle swarm optimization. Int J Wireless Inf Networks :1–10
Liang J, Ge S, Qu B, Yu K, Liu F, Yang H, Wei P, Li Z (2020) Classified perturbation mutation based particle swarm optimization algorithm for parameters extraction of photovoltaic models. Energy Convers Manag 203:112138
Liang J-J, Suganthan PN (2005) Dynamic multi-swarm particle swarm optimizer. In: Proceedings 2005 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium, 2005. SIS 2005., pages 124–129. IEEE
Niu B, Zhu Y, He X, Wu H (2007) Mcpso: a multi-swarm cooperative particle swarm optimizer. Appl Math Comput 185(2):1050–1062
Zhang J, Ding X (2011) A multi-swarm self-adaptive and cooperative particle swarm optimization. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24(6):958–967
Tanweer MR, Suresh S, Sundararajan N (2016) Dynamic mentoring and self-regulation based particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving complex real-world optimization problems. Inf Sci 326:1–24
Ye W, Feng W, Fan S (2017) A novel multi-swarm particle swarm optimization with dynamic learning strategy. Appl Soft Comput 61:832–843
Shi Y, Eberhart R (1998) A modified particle swarm optimizer. In: 1998 IEEE International conference on evolutionary computation proceedings. IEEE world congress on computational intelligence (cat. no. 98TH8360). IEEE, pp 69–73
Lu J, Hu H, Bai Y (2015) Generalized radial basis function neural network based on an improved dynamic particle swarm optimization and adaboost algorithm. Neurocomputing 152:305–315
Maurice C (1999) The swarm and the queen: towards a deterministic and adaptive particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 1999 congress on evolutionary computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406), vol 3. IEEE, pp 1951–1957
Ratnaweera A, Halgamuge SK, Watson HC (2004) Self-organizing hierarchical particle swarm optimizer with time-varying acceleration coefficients. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 8(3):240–255
Zhan Z-H, Zhang J, Li Y, Chung HS-H (2009) Adaptive particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B (Cybern) 39(6):1362–1381
Liang JJ, Kai Qin A, Suganthan PN, Baskar S (2006) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10(3):281–295
Li C, Yang S, Nguyen TT (2011) A self-learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization problems. IEEE Trans Systems Man Cybern B (Cybern) 42(3):627–646
Zhou J, Fang W, Xiaojun W u, Sun J, Cheng S (2016) An opposition-based learning competitive particle swarm optimizer. In: 2016 IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation (CEC). IEEE, pp 515–521
Zhang K, Huang Q, Zhang Y (2019) Enhancing comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization with local optima topology. Inf Sci 471:1–18
Xu G, Cui Q, Shi X, Ge H, Zhan Z-H, Lee HP, Liang Y, Tai R, Chunguo W u (2019) Particle swarm optimization based on dimensional learning strategy. Swarm Evol Comput 45:33–51
Li W, Meng X, Huang Y, Fu Z-H (2020) Multipopulation cooperative particle swarm optimization with a mixed mutation strategy. Inf Sci
James K. (2003) Bare bones particle swarms. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium. SIS’03 (Cat. No. 03EX706). IEEE, pp 80–87
Richer TJ, Blackwell TM (2006) The lévy particle swarm. In: 2006 IEEE International conference on evolutionary computation. IEEE, pp808–815
Peram T, Veeramachaneni K, Mohan CK (2003) Fitness-distance-ratio based particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE swarm intelligence symposium. SIS’03 (Cat. No. 03EX706). IEEE, pp 174–181
Ho SL, Yang S, Ni G, Wong H-CC (2006) A particle swarm optimization method with enhanced global search ability for design optimizations of electromagnetic devices. IEEE Trans Magn 42(4):1107–1110
Lu Y, Zeng N, Liu Y, Zhang N (2015) A hybrid wavelet neural network and switching particle swarm optimization algorithm for face direction recognition. Neurocomputing 155:219–224
Ning Y, Peng Z, Dai Y, Bi D, Wang J (2019) Enhanced particle swarm optimization with multi-swarm and multi-velocity for optimizing high-dimensional problems. Appl Intell 49(2):335–351
Olorunda O, Engelbrecht AP (2008) Measuring exploration/exploitation in particle swarms using swarm diversity. In: 2008 IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation (IEEE world congress on computational intelligence). IEEE, pp 1128–1134
Dukic ML, Dobrosavljevic ZoS (1990) A method of a spread-spectrum radar polyphase code design. IEEE J Select Areas Commun 8(5):743–749
Gil-López S, Del Ser J, Salcedo-Sanz S, Pérez-Bellido ÁM, Marı J, Portilla-Figueras JA et al (2012) A hybrid harmony search algorithm for the spread spectrum radar polyphase codes design problem. Expert Syst Appl 39(12):11089–11093
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by NSFC Grant Nos. 61701060 and 61801067, Guangxi Colleges and Universities Key Laboratory of Intelligent Processing of Computer Images and Graphics Project No. GIIP1806, and the Science and Technology Research Project of Higher Education of Hebei Province (Grant No. QN2019069), and Chongqing Key Lab of Computer Network and Communication Technology (CY-CNCL-2017-02), and the Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission Grant No. KJQN201801905 & KJZD-K201901902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Sha, L., Zhu, S. et al. Adaptive hierarchical update particle swarm optimization algorithm with a multi-choice comprehensive learning strategy. Appl Intell 52, 1853–1877 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02413-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02413-3