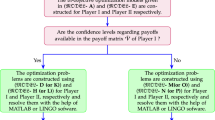
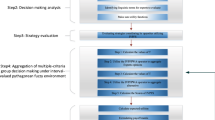
Abstract
In this study, a new Linguistic Pythagorean Hesitant Fuzzy Set (LPHFS) is introduced by considering the notions of linguistic fuzzy set and Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy set. LPHFS is a suitable path to deal with the hesitant situation in decision making, which is characterized by linguistic membership and non-membership degrees. Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) process determines multiple competing criteria in decision making. The traditional decision making approaches assume that each player is independent. But in real world competitive situation, the real fact is that each player tries to maximize individual benefit which causes a negative impact on other player. Here we propose a Linguistic Pythagorean Hesitant Fuzzy (LPHF) distance measure based on game theoretical framework to terminate the cross-influence problem. So our intention is to explore the generalized hybrid Euclidean distance measures of LPHFS. Then we analyze the application of LPHFS to MCDM game by using Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS). The LPHFS is assumed to explore the uncertainty of Decision Makers (DMs), and the game theory is used to optimize the combination of criteria in interactive conditions. A modified version of TOPSIS and Ambika method are designed in the context of MCDM game with LPHFS. Finally, two real-life problems are considered to illustrate the applicability and feasibility of our proposed method, and then a comparison analysis is drawn among the obtained results with the existing methods to depict the usefulness of it.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Systs 20(1):87–96
Bector CR, Chandra S, Vijay V (2004) Duality in linear programming with fuzzy parameters and matrix games with fuzzy payoffs. Fuzzy Sets Systs 46:253–269
Beg I, Rashid T (2013) TOPSIS For hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Int J Intell Syst 28:1162–1171
Bhaumik A, Roy SK, Li DF (2021) (α,β,γ)-cut set based ranking approach to solving bi-matrix games in neutrosophic environment. Soft Comput 25 (4):2729–2739
Bhaumik A, Roy SK, Weber GW (2020) Hesitant interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy-linguistic term set approach in Prisoners’ dilemma game theory using TOPSIS: a case study on Human-trafficking. Central Euro J Oper Res 28:797–816
Bhaumik A, Roy SK (2021) Intuitionistic interval-valued hesitant fuzzy matrix games with a new aggregation operator for solving management problem. Granular Comput 6:359–375
Bhaumik A, Roy SK, Weber GW (2021) Multi-objective linguistic-neutrosophic matrix game and its applications to tourism management. J Dynam Games 8(2):101–118
Campos L (1989) Fuzzy linear programming models to solve fuzzy matrix games. Fuzzy Sets Systs 32(3):275–289
Chen YW, Larbani M (2005) Two-person zero-sum game approach for fuzzy multiple attribute decision making problems. Fuzzy Sets Systs 157(1):34–51
Cagman N, Karatas S (2013) Intuitionistic fuzzy soft set theory and its decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 24(4):829–836
Du YQ, Hou F, Zafar W, Yu Q, Zhai Y (2017) A novel method for multiattribute decision making with interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy linguistic information. Int J Intell Syst 32(10):1085–1112
Garg H (2016) A new generalized Pythagorean fuzzy information aggregation using Einstein operations and its application to decision making. Int J Intell Syst 31(9):886–920
Garg H (2018) Linguistic Pythagorean fuzzy sets and its applications in multi attribute decision-making process. Int J Intell Syst 33(6):1234–1263
Garg H (2020) Linguistic interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy sets and their applications to multiple attribute group decision-making process. Cogni Comput 12:1313–1337
Herrera F, Martinez L (2001) A model based on linguistic 2-tuples for dealing with multigranular hierarchical linguistic contexts in multi-expert decision-making. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybern) 31 (2):227–234
Hwang CL, Yoon KS (1981) Multiple attribute decision methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Jana J, Roy SK (2018) Solution of matrix games with generalized trapezoidal fuzzy payoffs. Fuzzy Inform Engin 10(2):213–224
Jana J, Roy SK (2019) Dual hesitant fuzzy matrix games: based on new similarity measure. Soft Comput 23(18):8873–8886
Jana J, Roy SK (2021) Soft matrix game: a hesitant fuzzy MCDM approach. American J Mathe Manage Sci 40(2):107–119
Joshi D, Kumar S (2016) Interval-valued intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy Choquet integral based TOPSIS method for multi-criteria group decision making. Euro J Oper Res 248:183–191
Liao HC, Xu ZS, Zeng XJ (2014) Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their application in multi-criteria decision making. Inform Sci 271:125–142
Liang D, Xu ZS (2017) The new extension of TOPSIS method for multiple criteria decision making with hesitant Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Appl Soft Comput 60:167–179
Liu C, Tang G, Liu P (2017) An approach to multi-criteria group decision making with unknown weight information based on Pythagorean fuzzy uncertain linguistic aggregation operators. Mathemat Prob Engi 5:1–18
Mendel JM, John RIB (2002) Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10 (2):117–127
Monroy L, Fernandez FR (2011) The Shapely-Shubik index for multi-criteria simple games. Euro J Oper Res 209:122–128
Nishizaki I, Sakawa M (2001) Fuzzy and multiobjective games for conflict resolution. Physica, Heidelberg
Rodriguez RM, Martinez L, Herrera F (2012) Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision makings. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 20(1):109–119
Peng XD, Yang Y (2015) Some results for Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 30 (11):1133–1160
Ren PJ, Xu ZS, Gou XJ (2016) Pythagorean fuzzy TODIM approach to multi-criteria decision making. Appl Soft Comput 42:246–259
Reneke JA (2009) A game theory formulation of decision making under conditions of uncertainty and risk. Nonlinear Anal 71:1239–1246
Roy SK (2010) Game theory under MCDM and fuzzy set theory VDM (Verlag Dr. Müller, Germany
Roy SK, Mula P (2016) Solving matrix game with rough payoffs using genetic algorithm. Oper Res An Int J 16(1):117–130
Roy SK, Bhaumik A (2018) Intelligent water management: A triangular type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy matrix games approach. Water Resour Manage 32(3):949–968
Roy SK, Maiti SK (2020) Reduction method of type-2 fuzzy variables and their applications to Stackelberg game. Appl Intelligence 50:1398–1415
Roy SK, Jana J (2021) The multi-objective linear production planning games in triangular hesitant fuzzy set. Sadhana 46:176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-021-01683-4
Sakawa M, Nishizaki I (1994) Max-min solution for fuzzy multiobjective matrix games. Fuzzy Sets Syst 67(1):53–69
Singh P (2014) A new method for solving dual hesitant fuzzy assignment problems with restrictions based on similarity measure. Appl Soft Comput 24:559–571
Song Q, Kandel A (1999) A fuzzy approach to strategic games. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 7:634–642
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25:529–539
Torra V, Narukawa Y (2009) On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. IEEE Int Confe Fuzzy Syst, Jeju Island, Korea, 1378–1382
Verma T, Kumar A (2018) Ambika methods for solving matrix games with Atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy payoffs. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 26(1):270–283
Xia MM, Xu ZS, Chen N (2013) Some hesitant fuzzy aggregation operators with their application in group decision making. Group Deci Negot 22(2):259–279
Xu ZS, Xia MM (2011) Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy sets. Inform Sci 181(11):2128–2138
Xu ZS (2007) Some similarity measures of intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications to multiple attribute decision making. Fuzzy Optim Deci Making 6:109–121
Xu ZS (2004) A method based on linguistic aggregation operators for group decision making under linguistic preference relations. Inform Sci 166:19–30
Xue W, Xu Z, Zeng XJ (2021) Solving matrix games based on Ambika method with hesitant fuzzy information and its application in the counter-terrorism issue. Appl Intell 51:1227– 1243
Yager RR (2013) Pythagorean fuzzy subsets. In: Proceed joint IFSA world cong NAFIPS annual meeting. Edmonton, Canada, pp 57–61
Yager RR, Abbasov AM (2013) Pythagorean membership grades, complex numbers, and decision making. Int J Intell Syst 28:436–452
Yager RR (2014) Pythagorean membership grades in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22:958–965
Yang Y, Ding H, Chen ZS, Li YL (2016) A note on extension of TOPSIS to multiple criteria decision making with Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 31(1):68–72
Yang J, Xu Z, Dai Y (2021) Simple noncooperative games with intuitionistic fuzzy information and application in ecological management. Appl Intelligence. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-002215-7https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021- https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-002215-7002215-7
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inform Cont 8(3):338–356
Zhang H (2014) Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy sets and application in MAGDM. J Appl Math, https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/432092
Zhang XL (2015) A novel approach based on similarity measure for Pythagorean fuzzy multiple criteria group decision making. Int J Intell Syst, 31(6). https://doi.org/10.1002/int.21796
Zhang XL, Xu ZS (2014) Extension of TOPSIS to multiple criteria decision making with Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 29:1061–1078
Zhang XL (2016) Multicriteria Pythagorean fuzzy decision analysis: a hierarchical QUALIFLEX approach with the closeness index-based ranking methods. Inform Sci 330:104–124
Zhang C, Li D (2016) Pythagorean fuzzy rough sets and its applications in multi-attribute decision making. J Chinese Computer Syst 37(7):1531–1535
Zhang XL, Xu ZS (2015) Hesitant fuzzy QUALIFLEX approach with a signed distance-based comparison method for multiple criteria decision analysis. Exp Syst Appli 42:873–884
Zhu B, Xu Z, Xia M (2012) Dual hesitant fuzzy sets. J Appl Math. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/879629
Zhu B, Xu ZS (2014) Some results for dual hesitant fuzzy sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26:1657–166
Acknowledgements
The authors are very much thankful to the respected Editor-in-Chief, Associate Editor and anonymous Reviewers for the precious comments that helped us so much too rigorously improve the quality of the paper. The research of Jishu Jana is partially supported by the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR) under JRF scheme with sanctioned no. 09/599(0067)/2016-EMR-I dated 20/10/2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of the paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jana, J., Roy, S.K. Linguistic Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy matrix game and its application in multi-criteria decision making. Appl Intell 53, 1–22 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03442-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03442-2