Abstract
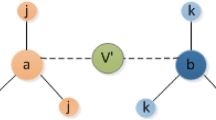
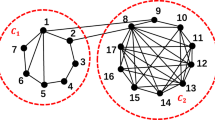
The network of networks (NONs) is a case of multiplex networks, when mining key nodes in the network, the information between the various sub-networks needs to be considered. In this paper, a weighted information fusion (WIF) method is proposed to identify the influential nodes of NONs. We first divide NONs into many individual networks and then perform weighted fusion. In the process, relevant information of nodes is measured to construct the basic probability assignment (BPA) for every single network. Besides, by considering the topological structure of the network, the method of effective distance is used to describe the weight of each BPA. Finally, to measure the influential nodes of NONs, the information of all single networks is fused to obtain structural information of NONs through WIF method. More than that, the influential nodes of four real-world NONs (including Neuronal and Social two types) are measured by the proposed method, and the results are compared with other five methods, which shows that WIF method is effective in identifying the influence of nodes of NONs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang H, Fang Y-P, Zio E (2022) Resilience-oriented optimal post-disruption reconfiguration for coupled traffic-power systems. Reliability Engineering & System Safety:108408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2022.108408
Bovet A, Makse HA (2019) Influence of fake news in twitter during the 2016 us presidential election. Nat Commun 10(1):1–14
Xiong L, Su X, Qian H (2021) Conflicting evidence combination from the perspective of networks. Inf Sci 580:408–418
Guo L, Liu Z, Chen Z (2021) A novel bilateral protocol in the bipartite network based on the public goods game. Knowl-Based Syst 214:106721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106721
Wang Z, Li Z, Wang R, Nie F, Li X (2021) Large graph clustering with simultaneous spectral embedding and discretization. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(12):4426–4440
Cheong KH, Koh JM, Jones MC (2019) Paradoxical survival: examining the parrondo effect across biology. BioEssays 41(6):1900027. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201900027
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature 393:440–442
Barabási AL, Albert R (1999) Emergence of scaling in random graphs. Science 286:509–512
Wen T, Cheong KH (2021) The fractal dimension of complex networks: a review. Inf Fusion 73:87–102
Wen T, Song M, Jiang W (2018) Evaluating topological vulnerability based on fuzzy fractal dimension. Int J Fuzzy Syst 20(6):1956–1967
Song X, Xiao F (2022) Combining time-series evidence: a complex network model based on a visibility graph and belief entropy. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489--021--02956--5
Cui H, Zhou L, Li Y, Kang B (2022) Belief Entropy-of-Entropy and its application in the cardiac interbeat interval time series analysis. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 155:111736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111736
Wang Z, Wang C, Li X, Gao C, Li X, Zhu J (2022) Evolutionary markov dynamics for network community detection. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 34(3):1206–1220
Wang Z, Jusup M, Guo H, Shi L, Geček S, Anand M, Perc M, Bauch CT, Kurths J, Boccaletti S et al (2020) Communicating sentiment and outlook reverses inaction against collective risks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117(30):17650–17655
Wang Z, Wang C, Gao C, Li X, Li X (2020) An evolutionary autoencoder for dynamic community detection. Sci China Inf Sci 63(11):1–16
Wei B, Xiao F, Shi Y (2020) Synchronization in kuramoto oscillator networks with sampled-data updating law. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(6):2380–2388
Wei B, Xiao F, Shi Y (2020) Fully distributed synchronization of dynamic networked systems with adaptive nonlinear couplings. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(7):2926–2934
Qu J, Tang M, Liu Y, Guan S (2020) Identifying influential spreaders in reversible process. Chaos Solitons & Fractals 140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110197
Zhou F, Wang T, Zhong T, Trajcevski G (2022) Identifying user geolocation with hierarchical graph neural networks and explainable fusion. Inf Fusion 81:1–13
Chen L, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2021) Probability transformation of mass function: a weighted network method based on the ordered visibility graph. Eng Appl Artif Intell 105:104438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104438
Ruan Z, Yu B, Shu X, Zhang Q, Xuan Q (2020) The impact of malicious nodes on the spreading of false information. Chaos: Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 30(8):083101. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0005105
Mohammed A, Zhu F, Ahmed S, Soufiana M, Sheng H (2020) Efficient algorithms based on centrality measures for identification of top-k influential users in social networks. Inf Sci 527:88–107
Liu H, Xu X, Lu J, Chen G, Zeng Z (2021) Optimizing pinning control of complex dynamical networks based on spectral properties of grounded laplacian matrices. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern: Syst 51 (2):786–796
Lü L, Chen D, Ren X, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Zhou T (2016) Vital nodes identification in complex networks. Phys Rep 650:1–63
Shang Q, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2021) Identifying influential nodes in complex networks: effective distance gravity model. Inf Sci 577:162–179
Xu X, Zhu C, Wang Q, Zhu X, Zhou Y (2020) Identifying vital nodes in complex networks by adjacency information entropy. Scientific Reports 10(1):1–12
Delellis P, Porfiri M (2021) Detection of influential nodes in network dynamical systems from time-series. IEEE Trans Control Netw Syst 99:3061953. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCNS.2021.3061953
Holzinger A, Malle B, Saranti A, Pfeifer B (2021) Towards multi-modal causability with Graph Neural Networks enabling information fusion for explainable AI. Inf Fusion 71:28–37
Zhao G, Jia P, Zhou A, Zhang B (2020) InfGCN: identifying influential nodes in complex networks with graph convolutional networks. Neurocomputing 414:18–26
Boccaletti S, Bianconi G, Criado R, del Genio C, Gómez-Gardenes J, Romance M, Sendina-Nadal I, Wang Z, Zanin M (2014) The structure and dynamics of multilayer networks. Phys Rep 544 (1):1–122
Böttcher L, Porter MA (2021) Classical and quantum random-walk centrality measures in multilayer networks. SIAM J Appl Math 81(6):2704–2724
Kivelä M, Arenas A, Barthelemy M, Gleeson JP, Moreno Y, Porter MA (2014) Multilayer networks. J Complex Netw 2(3):203–271
Wang D, Yu W, Zou X (2020) Tensor-based mathematical framework and new centralities for temporal multilayer networks. Inf Sci 512:563–580
Yuvaraj M, Dey AK, Lyubchich V, Gel YR, Poor HV (2021) Topological clustering of multilayer networks. Proc National Academy of Sci:118(21). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2019994118https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2019994118
Danziger MM, Barabási A-L (2022) Recovery coupling in multilayer networks. Nat Commun 13(1):1–8
Liu M, Xu L, Liao P (2021) haracter-based hazard warning mechanics: a network of networks approach. Adv Eng Inf 47:101240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2020.101240
Dong S, Wang H, Mostafizi A, Song X (2020) A network-of-networks percolation analysis of cascading failures in spatially co-located road-sewer infrastructure networks. Phys: Statist Mechanics Appl 538:122971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.122971
Li M, Zhang Q, Deng Y (2018) Evidential identification of influential nodes in network of networks. Chaos Solitons & Fractals 117:283–296
Zhao J, Deng Y (2020) Complex network modeling of evidence theory. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3023760https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3023760
Brockmann D, Helbing D (2013) The hidden geometry of complex, network-driven contagion phenomena. Science 342(6164):1337–1342
Deng Y (2020) Uncertainty measure in evidence theory. Sci China Inf Sci 63(11):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3006-9
Dempster AP (1967) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann Math Stat 38(2):325–339
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence, vol 1. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Bonacich PF (1972) Factoring and weighting approaches to status scores and clique identification. J Math Sociol 2(1):113–120
Smets P (2005) Decision making in the TBM: the necessity of the pignistic transformation. Int J Approx Reason 38(2):133–147
Deng Y (2022) Random permutation set. Int J Comput Commun Control 17(1):4542. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2022.1.4542
Deng Y (2020) Information volume of mass function. Int J Comput Commun Control 15(6):3983
Gao Q, Wen T, Deng Y (2021) Information volume fractal dimension. Fractals 29(8):2150263. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X21502637
Li Y, Deng Y (2018) Generalized ordered propositions fusion based on belief entropy. Int J Comput Commun Control 13(5):792–807
Wu Q, Deng Y, Xiong N (2021) Exponential negation of a probability distribution. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06658-5https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06658-5
Gao X, Su X, Qian H, Pan X (2022) Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis under uncertain and dynamic situations. Nucl Eng Technol 54(3):948–958
Xiao F, Pedrycz W (2022) Negation of the quantum mass function for multisource quantum information fusion with its application to pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3167045
Cheng C, Xiao F (2021) A distance for belief functions of orderable set. Pattern Recogn Lett 145:165–170
Babajanyan S, Allahverdyan A, Cheong KH (2020) Energy and entropy: Path from game theory to statistical mechanics. Phys Rev Res 2(4):043055. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.2.043055
Wang Z, Xiao F, Ding W (2022) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy Jenson-Shannon divergence and its application in multi-attribute decision making. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489--022--03347--0https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489--022--03347--0
Xiao F, Wen J, Pedrycz W (2022) Generalized divergence-based decision making method with an application to pattern classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2022.3177896https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2022.3177896
Xie D, Xiao F, Pedrycz W (2021) Information quality for intuitionistic fuzzy values with its application in decision making. Eng Appl Artif Intell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104568
Lai JW, Chang J, Ang L, Cheong KH (2020) Multi-level information fusion to alleviate network congestion. Inf Fusion 63:248–255
Zhang L, Xiao F (2022) A novel belief χ2 divergence for multisource information fusion and its application in pattern classification. Int J Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22912
Zhu C, Xiao F, Cao Z (2022) A generalized Rényi divergence for multi-source information fusion with its application in EEG data analysis. Inf Sci 605:225–243
Brandes U, Fleischer D (2009) Centrality measures based on current flow. In: Proceedings of the 22nd annual conference on theoretical aspects of computer science
Newman MEJ (2005) A measure of betweenness centrality based on random walks. Soc Networks 27(1):39–54
De Domenico M, Porter MA, Arenas A (2015) Muxviz: a tool for multilayer analysis and visualization of networks. J Complex Netw 3(2):159–176
Kapferer B (1972) Strategy and transaction in an African factory. Manchester University Press
Snijders TA, Pattison PE, Robins GL, Handcock MS (2006) New specifications for exponential random graph models. Socio Method 36(1):99–153
Vickers M, Chan S (1981) Representing classroom social structure Melbourne: Victoria Institute of Secondary Education
Wang D, Wang H, Zou X (2017) Identifying key nodes in multilayer networks based on tensor decomposition. Chaos: Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 27(6):063108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4985185
Yang M, Chen G, Fu X (2011) A modified sis model with an infective medium on complex networks and its global stability. Phys: Stat Mechanics Appl 390(12):2408–2413
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.62003280), and Chongqing Talents: Exceptional Young Talents Project (No.cstc2022ycjh-bgzxm0070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, M., Liu, L. & Xiao, F. Identify influential nodes in network of networks from the view of weighted information fusion. Appl Intell 53, 8005–8023 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03856-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03856-y