Abstract
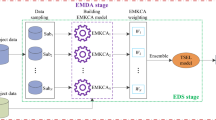
Software defect prediction aims to predict the defect proneness of new software modules with the historical defect data so as to improve the quality of a software system. Software historical defect data has a complicated structure and a marked characteristic of class-imbalance; how to fully analyze and utilize the existing historical defect data and build more precise and effective classifiers has attracted considerable researchers’ interest from both academia and industry. Multiple kernel learning and ensemble learning are effective techniques in the field of machine learning. Multiple kernel learning can map the historical defect data to a higher-dimensional feature space and make them express better, and ensemble learning can use a series of weak classifiers to reduce the bias generated by the majority class and obtain better predictive performance. In this paper, we propose to use the multiple kernel learning to predict software defect. By using the characteristics of the metrics mined from the open source software, we get a multiple kernel classifier through ensemble learning method, which has the advantages of both multiple kernel learning and ensemble learning. We thus propose a multiple kernel ensemble learning (MKEL) approach for software defect classification and prediction. Considering the cost of risk in software defect prediction, we design a new sample weight vector updating strategy to reduce the cost of risk caused by misclassifying defective modules as non-defective ones. We employ the widely used NASA MDP datasets as test data to evaluate the performance of all compared methods; experimental results show that MKEL outperforms several representative state-of-the-art defect prediction methods.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljamaan, H.I., Elish, M.O.: An empirical study of bagging and boosting ensembles for identifying faulty classes in object-oriented software. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Data Mining, Nashville, TN, USA, pp. 187–194 (2009)
Amasaki, S., Takagi, Y., Mizuno, O., Kikuno, T.: A Bayesian belief network for assessing the likelihood of fault content. In: International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering, pp. 215–226 (2003)
Bennett, K.P., Momma, M., Embrechts, M.J.: MARK: a boosting algorithm for heterogeneous kernel models. In: Proceedings of 8th ACM-SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Edmonton, Canada: ACM, pp. 24–31 (2002)
Bezerra, E. Miguel, Oliveiray, A.L.I., Adeodatoz, P.J.L.: Predicting software defects: a cost-sensitive approach. International Conference Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, pp. 2515–2522 (2011)
Bi, J., Zhang, T., Bennett, K.P.: Column-generation boosting methods for mixture of kernels. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Seattle, USA: ACM, pp. 521–526 (2004)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Catal, C., Diri, B.: A systematic review of software fault prediction studies. Expert Syst. Appl. 36, 7346–7354 (2009)
Damoulas, T., Girolami, M.A.: Probabilistic multi-class multi-kernel learning: on protein fold recognition and remote homology detection. Bioinformatics 24(10), 1264–1270 (2008)
Dietterich, T.G.: Ensemble methods in machine learning. Mult. Classier Syst. 1857, 1–15 (2000)
Elish, K., Elish, M.: Predicting defect-prone software modules using support vector machines. J. Syst. Softw. 81(5), 649–660 (2008)
Freund, Y., Schapire, R.E.: A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 55(1), 119–139 (1997)
Gao, K., Khoshgoftaar, T.M.: Software defect prediction for high-dimensional and class-imbalanced data. SEKE, pp. 89–94 (2011)
Gao, K., Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Napolitano, A.: A hybrid approach to coping with high dimensionality and class imbalance for software defect prediction. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2, 281–288 (2012)
GÄonen, M., Alpaydin, E.: Localized multiple kernel learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. Helsinki, Finland: ACM, pp. 352–359 (2008)
Gayatri, N., Nickolas, S., Reddy, A.V.: Feature selection using decision tree induction in class level metrics dataset for software defect predictions. In: The World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science, pp. 124–129 (2010)
Gehler, P.V., Nowozin, S.: On feature combination for multiclass object classification. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2, 221–228 (2009)
Gray, D., Bowes, D., Davey, N., Sun, Y., Christianson, B.: The Misuse of the NASA metrics data program data sets for automated software defect prediction. in EASE 2011. Durham (2011)
Gray, D., Bowes, D., Davey, N., Sun, Y., Christianson, B.: Using the support vector machine as a classification method for software defect prediction with static code metrics. Eng. Appl. Neural Netw. 43, 223–234 (2009)
Hall, T., Beecham, S., Bowes, D., Gray, D., Counsell, S.: A systematic literature review on fault prediction performance in software engineering. Softw. Eng. 38(6), 1276–1304 (2011)
Halstead, M.H.: Elements of Software Science (Operating and Programming Systems Series). Elsevier North-Holland, New York (1977)
He, H., Garcia, E.A.: Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 21(9), 1263–1284 (2009)
Jing, X.Y., Ying, S., Zhang, Z.W., Wu, S.S., Liu, J.: Dictionary learning based software defect prediction. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Software Engineering. Hyderabad, India: ACM, pp. 414–423 (2014)
Kembhavi, A., Siddiquie, B., Miezianko, R.: Incremental multiple Kernel learning for object recognition. Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2, 638–645 (2009)
Khoshgoftaar, M.T., Gao, K., Seliya, N.: Attribute selection and imbalanced data: problems in software defect prediction. In: International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, pp. 137–144 (2010)
Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Seliya, N.: Software quality classification modeling using the SPRINT decision tree algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 365–374 (2002)
Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Seliya, N.: Tree-based software quality estimation models for fault prediction. IEEE Symposium on Software Metrics, pp. 203–214 (2002)
Lewis, D.P., Jebara, T., Noble, W. S.: Nonstationary kernel combination. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning. Pittsburgh, USA: ACM, pp. 553–560 (2006)
Luo, G.C., Ma, Y., Qin, K.: Asymmetric learning based on Kernel partial least squares for software defect prediction. IEICE Trans. 95–D(7), 2006–2008 (2012)
Lyu, M.R.: Software reliability engineering: a roadmap. In: Proceedings of the 2007 Future of Software Engineering (FOSE’07). Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society, pp. 153–170 (2007)
Ma, Y., Luo, G.C., Chen, H.: Kernel based asymmetric learning for software defect prediction. IEICE Trans. 95–D(1), 215–226 (2012)
McCabe, T.J.: A complexity measure. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 4, 308–320 (1976)
Menzies, T., Greenwald, J., Frank, A.: Datamining static code attributes to learn defect predictors. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 33(1), 2–13 (2007)
Menzies, T., Greenwald, J., Frank, A.: Data mining static code attributes to learn defect predictors. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 33(1), 2–13 (2007)
Muller, K.R., Mika, S., Ratsch, G., Tsuda, K., Scholkopf, B.: An introduction to kernel based learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 12(2), 181–201 (2001)
Nam, J., Pany, S.J., Kim, S.: Transfer defect learning. In: International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 382–391 (2013)
Ong, C.S., Smola, A.J., Williamson, R.C.: Learning the kernel with hyperkernels. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 6(7), 1043–1071 (2005)
Paikari, E., Richter, M.M., Ruhe, G.: Defect prediction using case-based reasoning: an attribute weighting technique based upon sensitivity analysis in neural networks. Int. J. Softw. Eng. Knowl. Eng. 22(5), 747–768 (2012)
Rakotomamonjy, A., Bach, F., Canu, S.: More efficiency in multiple kernel learning. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 20(24), 775–782 (2007)
Ren, J., Qin, K., Ma, Y., Luo, G.: On software defect prediction using machine learning. J. Appl. Math. 2014(785435), 8 (2014)
Rokach, L.: Ensemble-based classifiers. Artif. Intell. Rev. 33, 1–39 (2010)
Schoelkopf, B., Smola, A., MullerK, R.: Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem. Neural Comput. 10(5), 1299–1319 (1998)
Scholkopf, B., Mika, S., Burges, C.J.C., Knirsch, P., Muller, K.R., Ratsch, G.: Input space versus feature space in kernel-based methods. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 10(5), 1000–1017 (1999)
Seiffert, C., Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Van Hulse, J.: Improving software-quality predictions with data sampling and boosting. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 39(6), 1283–1294 (2009)
Seliya, N., Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Hulse, J.V.: Predicting faults in high assurance software. In: IEEE International High Assurance Systems Engineering Symposium, pp. 26–34 (2010)
Seliya, N., Khoshgoftaar, T.M.: The use of decision trees for cost-sensitive classification an empirical study in software quality prediction. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1(5), 448–459 (2011)
Shepperd, M., Song, Q.B., Sun, Z.B., Mair, C.: Data quality: some comments on the NASA software defect data sets. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 39(9), 1208–1215 (2013)
Sun, Y., Kamel, Mohamed S., Wong, Andrew K.C., Wang, Y.: Cost-sensitive boosting for classification of imbalanced data. Pattern Recognit. 40(12), 3358–3378 (2007)
Sun, Z.B., Song, Q.B., Zhu, X.Y.: Using coding based ensemble learning to improve software defect prediction. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C 42(6), 1806–1817 (2012)
Thwin, M.M.T., Quah, T.S.: Application of neural networks for software quality prediction using object-oriented metrics. J. Syst. Softw. 76(2), 147–156 (2005)
Turhan, B., Bener, A.: Software Defect Prediction: Heuristics for Weighted Naïve Bayes. In: International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pp. 244–249 (2007)
Turhan, B., Bener, A.: Analysis of naïve bayes’ assumptions on software fault data: an empirical study. Data Knowl. Eng. 68(2), 278–290 (2009)
Valentini, G., Masulli, F.: Ensembles of learning machines. Neural Netw. 3–20 (2002)
Wang, T., Li, W.H.: Naïve Bayes software defect prediction model. International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering, pp. 1–4 (2010)
Wang, J., Shen, B.J., Chen, Y.T.: Compressed C4.5 models for software defect prediction. International Conference on Quality Software, pp. 13–16 (2012)
Wang, S., Yao, X.: Using class imbalance learning for software defect prediction. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 62(2), 434–443 (2013)
Xia, Hao, Hoi, Steven C.H.: MKBoost: a framework of multiple kernel boosting. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 25(7), 1574–1586 (2013)
Xing, F., Guo, P., Lyu, M.R.: A novel method for early software quality prediction based on support vector machine. In: Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering, Chicago, Illinois, USA, pp. 213–222 (2005)
Yambor, W.S., Draper, B.A., Beveridge, J.R.: Analyzing PCA-based face recognition algorithms: eigenvector selection and distance measures. In: Proceeding of the 2nd Workshop on Empirical Evaluation in Computer Vision, Dublin, Ireland, pp.1–15 (2000)
Yan, Z., Chen, X.Y., Guo, P.: Software defect prediction using fuzzy support vector regression. Adv. Neural Netw. 6064, 17–24 (2010)
Zheng, J.: Cost-sensitive boosting neural networks for software defect prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(6), 4537–4543 (2010)
Zhou, Z.H., Liu, X.Y.: Training cost-sensitive neural networks with methods addressing the class imbalance problem. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 18(1), 63–77 (2006)
Zien, A., Ong, C.S.: Multiclass multiple kernel learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, pp. 1191–1198 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Zhang, Z., Jing, X. et al. Multiple kernel ensemble learning for software defect prediction. Autom Softw Eng 23, 569–590 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10515-015-0179-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10515-015-0179-1