Abstract
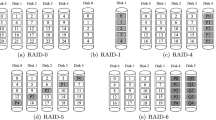
Heterogeneous Disk Arrays (HDAs) allow resource sharing of their hardware by multiple RAID levels. RAID1 (mirrored disks) and RAID5 (distributed parity arrays) are the two RAID levels considered in this study. They are both single disk failure tolerant (1DFT), but differ significantly in their efficiency in processing database workloads. The goal of the study is to maximize the number of Virtual Array (VA) allocations in HDA. We develop an analysis to estimate the load per VA based on a few parameters: the fraction of accesses to small versus large blocks and the fraction of updates versus reads. A VA is allocated according to the RAID level, which minimizes the anticipated load based on input parameters. Operation in normal and degraded mode is considered for comparison purposes, but in fact allocations are carried out using the higher load in degraded mode to ensure that single disk failures will not result in overload. We report on parametric studies to gain insight into circumstances leading to a RAID1 or RAID5 classification. An allocation experiment with a synthetic workload is used to demonstrate the superiority of HDA with respect to purely RAID1 or RAID5 disk arrays. This analytic study can be extended to 2DFT arrays, namely RAID6 versus 3-way replication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, G.A., Borowsky, E., Go, S., Romer, T.H., Becker-Szendy, R.A., Golding, R.A., Merchant, A., Spasojevic, M., Veitch, A.C., Wilkes, J.: Minerva: an automated resource provisioning tool for large-scale storage systems. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 19(4), 483–518 (2001)
Anderson, E., Kallahalla, M., Spence, S., Swaminathan, R., Wang, Q.: Ergastulum: an approach to solving the workload and device configuration problem. Technical Report SSP-2001-5, HP Labs, Palo Alto, CA
Anderson, E., Swaminathan, R., Veitch, A., Alvarez, G.A., Wilkes, J.: Selecting RAID levels for disk arrays. In: Proc. First USENIX Conf. File and Storage Technologies—FAST’02 Conf., Monterey, CA, January 2002, pp. 189–201
Anderson, E., Spence, S., Swaminathan, R., Kallahalla, M., Wang, Q.: Quickly finding near-optimal storage designs. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 23(4), 337–374 (2005)
Blaum, M., Brady, J., Bruck, J., Menon, J.: EVENODD: an optimal scheme for tolerating double disk failures in RAID architectures. IEEE Trans. Comput. 44(2), 192–202 (1995)
Borowsky, E., Golding, R., Merchant, A., Shreier, L., Shriver, E., Spasojevic, M., Wilkes, J.: Using attribute-managed storage to achieve QoS. In: Proc. 5th IFIP Int. Workshop on Quality of Service, Columbia University, New York, NY (1997)
Chen, P.M., Lee, E.K., Gibson, G.A., Katz, R.H., Patterson, D.A.: RAID: High-performance, reliable secondary storage. ACM Comput. Surv. 26(2), 145–185 (1994)
Corbett, P.F., English, B., Goel, A., Grcanac, T., Kleiman, S., Leong, J., Sankar, S.: Row-diagonal parity for double disk failure correction. In: Proc. 3rd USENIX Conf. File and Storage Technologies—FAST’04, San Francisco, CA, March–April 1994, pp. 1–14
Jacob, B., Ng, S.W., Wang, D.T., Systems, Memory: Cache, DRAM, Disk. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (2008)
Joukov, N., Krishnakumar, A.M., Patti, C., Rai, A., Satnur, S., Traeger, A., Zadok, E.: RAIF: redundant array of independent filesystems. In: Proc. 24th IEEE Conf. on Mass Storage Systems and Technologies—MSST’07, San Diego, CA, September 2007
Kleinrock, L.: Queueing Systems: Theory. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1975)
Menon, J.: A performance comparison of RAID-5 and log-structured arrays. In: Proc. 4th IEEE Int. Symp. on High-Performance Distributed Computing—HPDC, Washington, DC, August 1995, pp. 167–177
Muntz, R.R., Lui, J.C.S.: Performance analysis of disk arrays under failure. In: Proc. 16th Very Large Data Base—VLDB Conf., Brisbane, Australia, August 1990, pp. 162–173
Patterson, D.A., Gibson, G.A., Katz, R.H.: A case for redundant arrays of inexpensive disks. In: Proc. ACM SIGMOD Int. Conf. on Management of Data, Chicago, IL, June 1988, pp. 109–116
Thomasian, A., Menon, J.: RAID5 performance with distributed sparing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 8(6), 640–657 (1997)
Thomasian, A.: Reconstruct versus read-modify writes in RAID. Inf. Process. Lett. 93, 163–168 (2005)
Thomasian, A., Han, C.: Heterogeneous disk array architecture and its data allocation policies. In: Proc. Int. Symp. on Performance Evaluation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems—SPECTS’05, Cherry-Hill, NJ, July 2005, pp. 617–624
Thomasian, A., Branzoi, B.A., Han, C.: Performance evaluation of a heterogeneous disk array architecture. In: Proc. 13th IEEE Symp. Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems—MASCOTS’05, Atlanta, Georgia, July 2005, pp. 517–520
Thomasian, A.: Access costs in clustered RAID. Comput. J. 48(6), 702–713 (2005)
Thomasian, A.: Mirrored disk routing and scheduling. Cluster Comput. 9(4), 475–484 (2006)
Thomasian, A., Blaum, M.: Mirrored disk organization reliability analysis. IEEE Trans. Comput. 55(12), 1640–1644 (2006)
Thomasian, A., Fu, G., Ng, S.W.: Analysis of rebuild processing in RAID5 disk arrays. Comput. J. 50(2), 217–231 (2007)
Thomasian, A., Fu, G., Han, C.: Performance of two-disk failure-tolerant disk arrays. IEEE Trans. Comput. TC-56(6), 799–814 (2007)
Thomasian, A., Xu, J.: Reliability and performance of mirrored disk organizations. Comput. J. 51(6), 615–629 (2008)
Thomasian, A., Xu, J.: Data allocation in disk arrays with multiple RAID levels. ACM Trans. Stor. 6, (2010, to appear)
Thomasian, A., Blaum, M.: Two disk failure tolerant disk arrays: organization, operation, and coding methods. ACM Trans. Stor. 5(4): Article No. 7 (2009)
Welch, B., Unangst, M., Abbasi, Z., Gibson, G., Mueller, B., Small, J., Zelenka, J., Zhou, B.: Scalable performance of Panasas parallel file system. In: Proc. USENIX File and Storage Technologies—FAST’08 Conf., San Jose, CA, February 2008, pp. 17–33
Wilkes, J., Golding, R., Staelin, C., Sullivan, T.: The HP AutoRAID hierarchical storage system. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 14(1), 108–136 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomasian, A., Xu, J. RAID level selection for heterogeneous disk arrays. Cluster Comput 14, 115–127 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-010-0129-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-010-0129-4