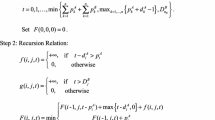Abstract
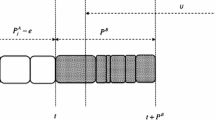
In the current research papers on multi-agent (multi-person) scheduling, a person’s objective function is always considered as a cost function on scheduling, whereas a cooperative profit function is defined to serve as his objective one in this paper. In the two-person scheduling problem addressed in this paper, the two persons jointly order a common operational time interval of a single machine. Each person needs to process a set of his own jobs in that time window. The same objective function of each person still relies on the sequence of all the jobs of both persons since each part of the function is determined by some given parameters except one part assumed to be a given multiple of the total completion time of his own jobs. The two persons have to negotiate a job sequence and determine the (related) final solution on cooperative profit allocation. Such a two-person scheduling problem is essentially a cooperative game. An algorithm is designed to yield the cooperative-profit-based Pareto efficient solution set acting as the first game-based solution concept in this paper. The parallelized version of the algorithm is also developed. The second game-based solution concept is the Shapley value appropriate for the above cooperative-game situation on two-person scheduling. Several instances are presented and analyzed to reveal the necessity to employ the two solution concepts together.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gu, Y.H., Tang, G.C.: Scheduling game: new development of Nash bargaining solution. J. Chongqing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 29(2), 1–6 (2012)
Tang, G.C., Fan, B.Q., Liu, L.L.: Classifications, advances and prospects of scheduling games. J. Chongqing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 31(1), 6–14 (2014)
Baker, K.: Introduction to sequencing and scheduling. Wiley, New York (1974)
Bilbao, J.M.: Cooperative games on combinatorial structures. Kluwer Academic, Boston (2000)
Curiel, I., Pederzoli, G., Tijs, S.: Sequencing games. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 40(3), 344–351 (1989)
Curiel, I., Potters, J., Prasad, R., et al.: Sequencing and cooperation. Oper. Res. 42(3), 566–568 (1994)
Cai, X.Q., Vairaktarakis, G.L.: Coordination of outsourced operations at a third-party facility subject to booking, overtime, and tardiness costs. Oper. Res. 60(6), 1436–1450 (2012)
Aydinliyim, T., Vairaktarakis, G.L.: Coordination of outsourced operations to minimize weighted flow time and capacity booking costs. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 12(2), 236–255 (2010)
Gibbons, A., Spirakis, P.: Lectures in parallel computation. Cambridge University, Cambridge (2005)
Hwang, K., Dongarra, J., Fox, C.G.: Distributed and cloud computing: from parallel processing to the internet of things. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington (2011)
Baker, K., Smith, J.: A multiple-criterion model for machine scheduling. J. Schedul. 6(1), 7–16 (2003)
Agnetis, A., Mirchandani, P.B., Pacciarelli, D., et al.: Scheduling problems with two competing agents. Oper. Res. 52(2), 229–242 (2004)
Lee, K., Choi, B.C., Leung, J., et al.: Approximation algorithms for multi-agent scheduling to minimize total weihted completion time. Inf. Process. Lett. 109(16), 913–917 (2009)
Mor, B., Mosheiov, G.: Single machine batch scheduling with two competing agents to minimize total flowtime. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 215(3), 524–531 (2011)
Wu, C.C., Wu, W.H., Chen, J.C., et al.: A study of the single-machine two-agent scheduling problem with release times. Appl. Soft Comput. 13(2), 998–1006 (2013)
Tuong, N.H., Soukhal, A., Billaut, J.C.: Single-machine multi-agent scheduling problems with a global objective function. J. Schedul. 15(3), 311–321 (2012)
Agnetis, A., Billaut, J.C., Gawiejnowicz, S., et al.: Multiagent scheduling: models and algorithms. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Pinedo, M.: “Multiagent scheduling—models and algorithms” by A. Agnetis, J.-C. Billaut, S. Gawiejnowicz, D. Pacciarelli, A. Soukhal. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 245(3), 877 (2015)
Yin, Y., Wu, C.C., Wu, W.H., et al.: A branch-and-bound procedure for a single-machine earliness scheduling problem with two agents. Appl. Soft Comput. 13(2), 1042–1054 (2013)
Liu, P., Yi, N., Zhou, X., et al.: Scheduling two agents with sum-of-processing-times-based deterioration on a single machine. Appl. Math. Comput. 219(17), 8848–8855 (2013)
Cheng, T.C.E., Chung, Y.H., Liao, S.C., et al.: Two-agent single-machine scheduling with release times to minimize the total weighted completion time. Comput. Oper. Res. 40(1), 353–361 (2013)
Zhao, K., Lu, X.: Approximation schemes for two-agent scheduling on parallel machines. Theor. Comput. Sci. 468, 114–121 (2013)
Gerstl, E., Mosheiov, G.: Scheduling problems with two competing agents to minimized weighted earliness-tardiness. Comput. Oper. Res. 40(1), 109–116 (2013)
Fan, B.Q., Cheng, T.C.E., Li, S.S., et al.: Bounded parallel-batching scheduling with two competing agents. J. Schedul. 16(3), 261–271 (2013)
Gawiejnowicz, S., Suwalski, C.: Scheduling linearly deteriorating jobs by two agents to minimize the weighted sum of two criteria. Comput. Oper. Res. 52(Part A), 135–146 (2014)
Gerstl, E., Mosheiov, G.: Single machine just-in-time scheduling problems with two competing agents. Naval Res. Logist. 61(1), 1–16 (2014)
Lee, W.C., Wang, J.Y.: A scheduling problem with three competing agents. Comput. Oper. Res. 51, 208–217 (2014)
Gu, Y.H., Goh, M., Chen, Q.L., et al.: A new two-party bargaining mechanism. J. Comb. Optim. 25(1), 135–163 (2013)
Gu, Y.H., Fan, J., Tang, G.C., et al.: Maximum latency scheduling problem on two-person cooperative games. J. Comb. Optimiz. 26(1), 71–81 (2013)
Luo, X., Xu, Z., Yu, J., Chen, X.: Building association link network for semantic link on web resources. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 8(3), 482–494 (2011)
Xu, Z., Luo, X., Wang, L.: Incremental building association link network. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 26(3), 153–162 (2011)
Xu, Z., Luo, X., Lu, W.: Association link network: an incremental semantic data model on organizing web resources. In: ICPADS pp. 793–798. (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editor and the anonymous referees for their constructive comments and suggestions. This paper was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61273220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Gu, Y., Ruan, Y. et al. Two game-based solution concepts for a two-agent scheduling problem. Cluster Comput 19, 769–781 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-016-0557-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-016-0557-x