Abstract
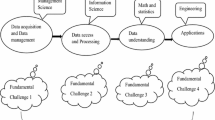
Scale space theory has been introduced into the field of big data, but its research is still not deep enough and perfect because of the lack of universal theory and method. With deepening of big data processing applications, the research becomes more and more urgent. In view of the above question, this paper studies pervasive multiscale data analysis theory and method, and proposes ARAMS (Association Rules Algorithm based on Multi Scale). On one hand, we give the definition and partition of data scale as well as the relationship of multiscale data set between the upper scale and lower scale based on concept hierarchy theory. On the other hand, we clarify the definition of multiscale data analysis, study essence and classification method. Previous studies show that the proposed method has high coverage rate, high accuracy rate, lower error rate of support estimation degree and greater improvement the efficiency than the traditional algorithm.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Felzenszwalb, P., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: A Discriminatively Trained, Multiscale, Deformable Part Model. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2008. CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on. IEEE (2008)
Kolda, T.G., Sun, J.: Scalable Tensor Decompositions for Multi-aspect Data Mining. Data Mining, 2008. ICDM’08. Eighth IEEE International Conference on. IEEE (2008)
Mierswa, I., et al.: Yale: Rapid Prototyping for Complex Data Mining Tasks. In: Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. ACM (2006)
Hu, C., et al.: Video structural description technology for the new generation video surveillance systems. Front. Comput. Sci. 9(6), 980–989 (2015)
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E.P., Bovik, A.C.: Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. Signals, Systems and Computers, 2004. Conference Record of the Thirty-Seventh Asilomar Conference on. IEEE (2003)
Hall, M., et al.: The WEKA data mining software: an update. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newslett. 11(1), 10–18 (2009)
Riedel, E., Gibson, G., Faloutsos, C.: Active storage for large-scale data mining and multimedia applications. In: Proceedings of 24th Conference on Very Large Databases. Citeseer (1998)
Huan, T., et al.: ProteoLens: a visual analytic tool for multiscale database-driven biological network data mining. BMC Bioinform. 9(Suppl 9), S5 (2008)
Eldawlatly, S., Jin, R., Oweiss, K.G.: Identifying functional connectivity in large-scale neural ensemble recordings: a multiscale data mining approach. Neural Comput. 21(2), 450–477 (2009)
Li, T., et al.: A survey on wavelet applications in data mining. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newslett. 4(2), 49–68 (2002)
Danon, L., et al.: Comparing community structure identification. J. Stat. Mech. 2005(09), P09008 (2005)
Fu, T.-C.: A review on time series data mining. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 24(1), 164–181 (2011)
Xu, Z., et al.: Generating temporal semantic context of concepts using web search engines. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 43, 42–55 (2014)
Xu, Z., et al.: Crowdsourcing based social media data analysis of urban emergency events. Multimed. Tools Appl. 1–18 (2015)
Xu, Z., et al.: Semantic based representing and organizing surveillance big data using video structural description technology. J. Syst. Softw. 102, 217–225 (2015)
Xu, Z., et al.: Crowdsourcing based description of urban emergency events using social media big data (2016)
Belkin, M., Niyogi, P.: Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation. Neural Comput. 15(6), 1373–1396 (2003)
Bell, R.M., Koren, Y.: Lessons from the Netflix prize challenge. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newslett. 9(2), 75–79 (2007)
Bellazzi, R., et al.: Temporal data mining for the quality assessment of hemodialysis services. Artif. Intell. Med. 34(1), 25–39 (2005)
Blondel, V.D., et al.: Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. 2008(10), P10008 (2008)
Burnett, C., Blaschke, T.: A multiscale segmentation/object relationship modelling methodology for landscape analysis. Ecol. Model. 168(3), 233–249 (2003)
Ding, H., et al.: Querying and mining of time series data: experimental comparison of representations and distance measures. Proc. VLDB Endow. 1(2), 1542–1552 (2008)
Džeroski, S.: Multi-relational data mining: an introduction. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newslett. 5(1), 1–16 (2003)
Huck, K.A., Malony, A.D.: Perfexplorer: a performance data mining framework for large-scale parallel computing. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing. IEEE Computer Society (2005)
Jenatton, R., et al.: Multiscale mining of fMRI data with hierarchical structured sparsity. Pattern Recognition in NeuroImaging (PRNI), 2011 International Workshop on. IEEE (2011)
Khan, S.S., Ahmad, A.: Cluster center initialization algorithm for K-means clustering. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 25(11), 1293–1302 (2004)
Knobbe, A., et al.: Multi-relational Data Mining (1999)
Kopanas, I., Avouris, N.M., Daskalaki, S.: The role of domain knowledge in a large scale data mining project. Methods and Applications of Artificial Intelligence, pp. 288–299. Springer (2002)
Lancaster, A., et al.: PyPop: a software framework for population genomics: analyzing large-scale multi-locus genotype data. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. NIH Public Access (2003)
Li, S.-T., Chou, S.-W., Pan, J.-J.: Multi-resolution spatio-temporal data mining for the study of air pollutant regionalization. In: System Sciences, 2000. Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on. IEEE (2000)
Li, S.-T., Shue, L.-Y.: Data mining to aid policy making in air pollution management. Expert Syst. Appl. 27(3), 331–340 (2004)
Low, Y., et al.: Distributed GraphLab: a framework for machine learning and data mining in the cloud. Proc. VLDB Endow. 5(8), 716–727 (2012)
Machiraju, R., et al.: EVITA—efficient visualization and interrogation of tera-scale data. Data Mining for Scientific and Engineering Applications, pp. 257–279. Springer (2001)
Mennis, J., Guo, D.: Spatial data mining and geographic knowledge discovery–An introduction. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 33(6), 403–408 (2009)
Streilein, W., et al.: Fused multi-sensor image mining for feature foundation data. In: Information Fusion, 2000. FUSION 2000. Proceedings of the Third International Conference on. IEEE (2000)
Tsytsarau, M., Palpanas, T.: Survey on mining subjective data on the web. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 24(3), 478–514 (2012)
Vespignani, A.: Predicting the behavior of techno-social systems. Science 325(5939), 425 (2009)
Pal, S.K., Mitra, P.: Pattern Recognition Algorithms for Data Mining. CRC press (2004)
Tsoumakas, G., Katakis, I., Vlahavas, I.: Mining multi-label data. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook, pp. 667–685. Springer (2009)
Mucha, P.J., et al.: Community structure in time-dependent, multiscale, and multiplex networks. Science 328(5980), 876–878 (2010)
Han, J., Kamber, M., Pei, J.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Elsevier (2011)
Acknowledgments
This research is supported in part by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LY16F020012) and Ningbo Key Laboratory of intelligent home appliances (No. 2016A22008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Gao, K. Deep data analyzing algorithm based on scale space theory. Cluster Comput 20, 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-016-0677-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-016-0677-3