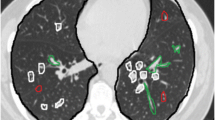
Abstract
For detection and classification of pulmonary nodules, there are two major issues exists in the existing computer aided diagnosis system. First major problem is automatic threshold to segment lungs and nodules. Threshold selection is a critical preprocessing step for medical images. Gaussian approximation based differential evolution has been used to find out the optimal threshold value for segmentation of lungs. Initially, 1-D histogram of the image is estimated using a blend of Gaussian functions whose parameters are calculated using the differential evolution method. Every Gaussian function estimating the histogram characterizes a pixel class and hence a threshold point. Second major problem is to extract the optimized features for classification of nodules. So, a novel gradient intensity feature descriptor for pulmonary nodule classification has been proposed using the multi-coordinate histogram of gradient and intensity based statistical features descriptor. Ensemble bagging trees has been used intelligently using the concepts of ensemble to classify the nodules. We have used standard dataset titled lung image consortium database for the verification and authentication of our proposed computer aided diagnostic (CAD) system. The proposed CAD system gives better results in comparison with existing CAD systems. The sensitivity of 97.5% is attained with an accuracy of 98.7%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greenlee, R.T., Murray, T., Bolden, S., Wingo, P.A.: Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J. Clin. 50, 7–33 (2000)
Jung, K.W., Won, Y.J., Park, S., Kong, H.J., Sung, J., Shin, H.R., Park, E.C., Lee, J.S.: Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality and survival in 2005. J. Korean Med. Sci. 43, 1–11 (2011)
Abbas, Qaisar: Segmentation of differential structures on computed tomography images for diagnosis lung-related diseases. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 33, 325–334 (2017)
Ozekes, S., Osman, O., Ucan, O.N.: Nodule detection in a lung region that’s segmented with using genetic cellular neural networks and 3D template matching with fuzzy rule based thresholding. Korean J. Radiol. 9, 1–9 (2008)
Ye, X., Lin, X., Dehmeshki, J., Slabaugh, G., Beddoe, G.: Shape based computer-aided detection of lung nodules in thoracic CT images. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 56, 1810–1820 (2009)
Retico, A., Fantacc, M.E., Gori, I., Kasae, P., Golosio, B., Piccioli, A., Cerello, P., Nunzio, G.D., Tangaro, S.: Pleural nodule identification in low-dose and thin-slice lung computed tomography. Comput. Biol. Med. 39, 1137–1144 (2009)
Sousa, J.R.F.S., Silva, A.C., Paiva, A.C., Nunes, R.A.: Methodology for automatic detection of lung nodules in computerized tomography images. Comput. Method Prog. Biomed. 98, 1–14 (2010)
Lee, S.L.A., Kouzani, A.Z., Hu, E.J.: Random forest based lung nodule classification aided by clustering. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 34, 535–542 (2010)
Maeda, S., Tomiyama, Y., Kim, H., Miyake, N., Itai, Y., Tan, J.K., Ishikawa, S., Yamamoto, A.: Detection of lung nodules in thoracic MDCT images based on temporal changes from previous and current images. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Inform 15, 707–713 (2011)
Tan, M., Deklerck, R., Jansen, B., Bister, M., Cornelis, J.: A novel computer-aided lung nodule detection system for CT images. Med. Phys. 38, 5630–5645 (2011)
Li, Q., Sone, S., Doi, K.: Selective enhancement filters for nodules, vessels, and airway walls in two- and three-dimensional CT scans. Med. Phys. 30(8), 2040–2051 (2003)
Song, Y., Cai, W., Zhou, Y., Feng, D.D.: Feature-based image patch approximation for lung tissue classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32(4), 797–808 (2013)
Suzuki, K., Armato, S.G., Li, F., Sone, S.: Massive training artificial neural network (MTANN) for reduction of false positives in computerized detection of lung nodules in low-dose computed tomography. Med. Phys. 30, 1602–1617 (2003)
Rubin, G.D., Lyo, J.K., Paik, D.S., Sherbondy, A.J., Chow, L.C., Leung, A.N., Mindelzun, R., Schraedley-Desmond, P.K., Zinck, S.E., Naidich, D.P., et al.: Pulmonary nodules on multi-detector row CT scans: performance comparison of radiologists and computer-aided detection. Radiology 234, 274–283 (2005)
Dehmeshki, J., Ye, X., Lin, X., Valdivieso, M., Amin, H.: Automated detection of lung nodules in CT images using shape-based genetic algorithm. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 31, 408–417 (2007)
Suárez-Cuenca, J.J., Tahoces, P.G., Souto, M., Lado, M.J., Remy-Jardin, M., Remy, J., Vidal, J.J.: Application of the iris filter for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules on computed tomography images. Comput. Biol. Med. 39, 921–933 (2009)
Opfer, R., Wiemker, R.: Performance analysis for computer-aided lung nodule detection on LIDC data. In: Medical Imaging 2007: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment, Volume 6515 of Proceedings of the SPIE, San Diego, CA, p. 65151C (2007)
Sahiner, B., Hadjiiski, L.M., Chan, H., Shi, J., Cascade, P.N., Kazerooni, E.A., Zhou, C., Wei, J., Chughtai, A.R., Poopat, C., et al.: Effect of CAD on radiologists’ detection of lung nodules on thoracic CT scans: observer performance study. In: Proceedings of SPIE 6515, Medical Imaging 2007: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment, Volume 6515 of Proceedings of the SPIE, San Diego, CA, p. 65151D (2007)
Messay, T., Hardie, R.C., Rogers, S.K.: A new computationally efficient CAD system for pulmonary nodule detection in CT imagery. Med. Image Anal. 14, 390–406 (2010)
Choi, W.J., Choi, T.S.: Genetic programming-based feature transform and classification for the automatic detection of pulmonary nodules on computed tomography images. Inf. Sci. 212, 57–78 (2012)
Choi, W.J., Choi, T.S.: Automated pulmonary nodule detection system in computed tomography images: a hierarchical block classification approach. Entropy 15, 507–523 (2013)
Akram, S., Javed, M.Y., Hussain, A., Riaz, F., Akram, M.U.: Intensity-based statistical features for classification of lungs CT scan nodules using artificial intelligence techniques. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 27(6), 737–751 (2015)
Akram, Sheeraz, Javed, M.Y., Qamar, U., Khanum, A., Hassan, A.: Artificial neural network based classification of lungs nodule using hybrid features from computerized tomographic images. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 9(1), 183–195 (2015)
Reeves, A.P., Biancardi, A.M., Apanasovich, T.V., Meyer, C.R., MacMahon, H., Beek, E.J., Kazerooni, E.A., Yankelevitz, D., McNitt-Gray, M.F., McLennan, G., et al.: The lung image database consortium (LIDC): a comparison of different size metrics for pulmonary nodule measurements. Acad. Radiol. 14, 1475–1485 (2007)
Masoumi, H., Behrad, A., Pourmina, M.A., Roosta, A.: Automatic liver segmentation in MRI images using an iterative watershed algorithm and artificial neural network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 7(5), 429–437 (2012)
Arfan, M., Jaffar, A.M., Hussain, A., Mirza, A.M.: Fuzzy entropy based optimization of clusters for the segmentation of lungs in CT scanned images. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 24(1), 91–111 (2010)
Liao, X., Zhao, J., Jiao, C., Lei, L., Qiang, Y., Cui, Q.: A segmentation method for lung parenchyma image sequences based on superpixels and a self-generating neural forest. PLoS ONE (2016). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0160556
Polikar, R.: Ensemble based systems in decision making. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 6(3), 21–45 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaffar, M.A., Siddiqui, A.B. & Mushtaq, M. Ensemble classification of pulmonary nodules using gradient intensity feature descriptor and differential evolution. Cluster Comput 21, 393–407 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0876-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0876-6