Abstract
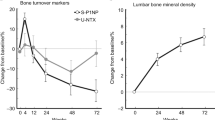
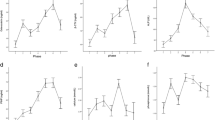
The changes in biochemical marker level of bone turnover of women before and after menopause and the relationship between it and bone mineral density (BMD) are analyzed. At the same time, the level of biochemical markers of bone metabolism of women with decreased BMD at premenopause and postmenopause is discussed. In this paper, the lumbar vertebrae (L1–L4) and femoral neck BMD of 225 female outpatients with osteoporosis were measured by dual-energy X ray bone sonometer. Among them, 185 menopause women at age of 45–65 were selected, and they were divided into normal bone mass group (50), decreased bone mass group (35) and osteoporosis group (100) according to BMD; in addition, 45 menopause women with decreased BMD at age of 51–70 were selected as postmenopause decreased-BMD group, and 25 non-menopause decreased-BMD women at age of 42–50 were selected as premenopause decreased-BMD group. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was carried out to measure the level of serum cathespin K (Cathe K), bone alkaline phosphatase (B-ALP) and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) of all patients; and electrochemiluminescence immunoassay is used to detect the level of osteocalcin, β-crosslaps and type-I procollagen N-terminal propeptide(PINP). The Cathe K, PINP, β-crosslaps, osteocalcin and TRAP level of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis are obviously higher than those of normal bone mass group (P < 0.05), and they are in negative correlation to lumbar vertebrae (L1–L4) or femoral neck BMD (P < 0.05); B-ALP level is slightly lower than that of normal bone mass group, however, such difference is of no statistical significance (P > 0.05). The Cathe K and TRAP level of serum in postmenopause decreased-BMD group were significantly lower than those in premenopausal women (P < 0.01), and the PINP and osteocalcin level of serum were significantly higher than those in premenopause decreased-BMD group (P < 0.01). However, the differences of lumbar vertebrae (L1–L4), femoral neck BMD and β-crosslaps, B-ALP level between the two groups are of no statistical significance (P > 0.05). Osteoporosis of postmenopausal women is high turnover. The changes in the levels of serum osteocalcin, β-crosslaps, PINP, B-ALP, TRAP and Cathe K could reflect the bone metabolism activity. The joint detection of BMD and bone-turnover biochemical marker is beneficial to the prevention, treatment and efficacy observation of the patients with osteoporosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan, Weisen, Chen, Shizhan, Feng, Zhiyong: Automatic clustering of social tag using community detection. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 7(2), 675–681 (2013)
Zhang, Yingyue, Mintzer, Evan, Uhrich, Kathryn E.: Synthesis and characterization of PEGylated bolaamphiphiles with enhanced retention in liposomes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 482, 19–26 (2016)
Arunkumar, N., Mohamed Sirajudeen, K.M.: Approximate entropy based ayurvedic pulse diagnosis for diabetics—a case study In: TISC 2011—Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Trendz in Information Sciences and Computing, pp. 133–135 (2011)
Arunkumar, N., Ramkumar, K., Hema, S., Nithya, A., Prakash, P., Kirthika, V.: Fuzzy Lyapunov exponent based onset detection of the epileptic seizures. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Information and Communication Technologies, ICT, pp. 701–706 (2013)
Faig, Jonathan J., Moretti, Alysha, Joseph, Laurie B., Zhang, Yingyue, Nova, Mary Joy, Smith, Kervin, Uhrich, Kathryn E.: Biodegradable kojic acid-based polymers: controlled delivery of bioactives for melanogenesis inhibition. Biomacromol 18(2), 363–373 (2017)
Arunkumar, N., Venkataraman, V., Thivyashree, L.: A moving window approximate entropy based neural network for detecting the onset of epileptic seizures. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 8(15), 1841–1847 (2013)
Chan, Jennifer W., Zhang, Yingyue, Uhrich, Kathryn E.: Amphiphilic macromolecule self-assembled monolayers suppress smooth muscle cell proliferation. Bioconjug. Chem. 26(7), 1359–1369 (2015)
Zhao, Yijiu, Wang, Li, Wang, Houjun, Liu, Changjian: Minimum rate sampling and spectrum blind reconstruction in random equivalent sampling. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 34(8), 2667–2680 (2015)
Fernandes, S.L., Gurupur, V.P., Sunder, N.R., Arunkumar, N., Kadry, S.A.: Novel nonintrusive decision support approach for heart rate measurement. Pattern Recognit. Lett. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2017.07.002
Arunkumar, N., Ramkumar, K., Venkatraman, V., Abdulhay, E., Fernandes, S.L., Kadry, S., Segal, S.: Classification of focal and non focal EEG using entropies. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 94, 112–117 (2017)
Chan, J.W., Zhang, Y., Uhrich, K.E.: Amphiphilic macromolecule self-assembled monolayers suppress smooth muscle cell proliferation. Bioconjug. Chem. 26(7), 1359–1369 (2015)
Malarkodi, M.P., Arunkumar, N., Venkataraman, V.: Gabor wavelet based approach for face recognition. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 8(15), 1831–1840 (2013)
Stephygraph, L.R., Arunkumar, N.: Brain-actuated wireless mobile robot control through an adaptive human-machine interface. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 397, 537–549 (2016)
Acknowledgements
Foundation project of Guizhou Provincial Health Planning Commission: Establishment and application of a conservative treatment prognosis model for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis(GZWJKJ2014-2-131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Guo, J. Markov chain based simulation analysis of bone mineral density and changes in the level of biochemical markers of bone transformation in postmenopausal women. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 2), 4737–4744 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2320-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2320-y