Abstract
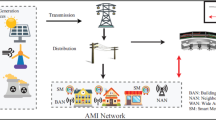
Internet of things (IoT) enables smart electrical grids (SEGs) to solve its problems and to support a lot of tasks. These tasks include power monitoring, demand-side energy management coordination of distributed storage, and the integration of renewable energy generators. Sending the complete captured data directly to the cloud would lead to resource wastage. Hence, 2-tier architecture is replaced by 3-tier one in order to include a fog computing tier. Fog tier acts as a bridge in the middle between IoT devices embedded in SEG and cloud tier to overcome the cloud challenges. The main actions of the added fog tier are collecting, computing, and storing smart meters data before transmitting it to the cloud. In this paper, a new electrical load forecasting (ELF) strategy has been proposed based on the pre-mentioned 3-tier architecture. ELF consists of two main phases, which are; (i) data pre-processing phase (DP2) and (ii) load prediction phase (LP2). Both phases are executed at cloud servers (CSs) on the collected data, which is received from all fogs connected to the entire cloud. The main objective of DP2 is to; (i) select the meaningful features and (ii) eliminate outlier items from the collected data. The main contribution of this paper lied on outlier rejection phase. The paper introduces a new outlier rejection methodology called hybrid outlier rejection methodology (HORM). HORM try to eliminate all outliers from the training dataset before start learning the prediction model during LP2. HORM involves two stages which are; (i) a new statistical based outlier rejection stage, which is called fast outlier rejection (FOR) and (ii) an accurate outlier rejection (AOR) stage using genetic algorithm (GA). Then, the filtered data is used to give fast and accurate load prediction decisions. Experimental results have shown that the proposed HORM outperforms recent outlier rejection methods in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-measure.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabie, A.S., Abo-Al-Ez, K.: A new strategy of load forecasting technique for smart grids. Int. J. Modern Trends Eng. Res. (IJMTER) 2(12), 332–341 (2015)
Saleh, A.R., Abo-Al-Ezb, K.: A data mining based load forecasting strategy for smart electrical grids. Adv. Eng. Inform. 30(3), 422–448 (2016)
Ozger, M., Cetinkaya, O., Akan, O.: Energy harvesting cognitive radio networking for iot-enabled smart grid. Mob. Netw. Appl. 23(4), 956–966 (2018)
Mahajan, V., Patil, P.: Internet of things based residential power load forecasting. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 3(7), 1362–1364 (2016)
Atlam, H., Walters, R., Wills, G.: Fog computing and the internet of things: a review. Big Data Cognit. Comput. 2(10), 1–18 (2018)
Jaradat, M., Jarrah, M., Bousselham, A., Jararweh, Y., Al-Ayyouba, M.: The internet of energy: smart sensor networks and big data management for smart grid. Procedia Comput. Sci. 56, 592–597 (2015)
Ghanbari, Z., Navimipour, N., Hosseinzadeh, M., Darwesh, A.: Resource allocation mechanisms and approaches on the internet of things. Comput Clust (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-019-02910-8
Yang, S.C., Liu, J., Liu, R., Chang, C.: On construction of an energy monitoring service using big data technology for the smart campus. Comput Clust (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-019-02921-5
Rabie, S.A., Ali, H., Saleh, A.: A fog based load forecasting strategy for smart grids using big electrical data. Clust. Comput. 22(1), 241–270 (2019)
Madhusudhanan, P.S., Karpagam, N., Mahesh, A., Suhi, P.: An hybrid metaheuristic approach for efficient feature selection. Comput Clust (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2337-2
Manoj, R., Praveena, M., Vijayakumar, K.: An ACO–ANN based feature selection algorithm for big data. Clust. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2550-z
Mao, J., Wang, T., Jin, C., Zhou, A.: Feature grouping-based outlier detection upon streaming trajectories. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(12), 2696–2709 (2017)
Rahmani, M., Atia, G.: Randomized robust subspace recovery and outlier detection for high dimensional data matrices. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(6), 1580–1594 (2017)
Vasconcelos, R.V., Olivieri, B., Roriz, M., Endler, M., Junior, M.: Smartphone-based outlier detection: a complex event processing approach for driving behavior detection. J. Internet Serv. Appl. 8(13), 1–30 (2017)
Venkatesh, G., Arunesh, K.: Map Reduce for big data processing based on traffic aware partition and aggregation. Clust. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1799-6
VeeraManickam, M., Mohanapriya, M., Pandey, B., Akhade, S., Kale, S., Patil, R., Vigneshwar, M.: Map-Reduce framework based cluster architecture for academic student’s performance prediction using cumulative dragonfly based neural network. Clust. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1553-5
Tellis V, Souza D (2018) Detecting Anomalies in Data Stream Using Efficient Techniques: A Review. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Control, Power, Communication and Computing Technologies (ICCPCCT), Kannur, India, pp. 296–298
Park, C.H.: Outlier and anomaly pattern detection on data streams. J. Supercomput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2674-1
Shou, Z., Li, S.: Large dataset summarization with automatic parameter optimization and parallel processing for local outlier detection. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 30(23), 1–13 (2018)
Chomatek L, Duraj A (2019) Efficient Genetic Algorithm for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technologies in Biomedicine, ITIB 2018: Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Springer, Cham, vol. 762, pp. 64–76
Saneja, B., Rani, R.: A scalable correlation-based approach for outlier detection in wireless body sensor networks. Int. J. Commun Syst (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.3918
Yan Y, Cao L, Rundensteiner E (2017) Distributed Top-N Local Outlier Detection in Big Data. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Boston, MA, USA, pp. 827–836
Liu, M.W., Newell, G.: Detecting outliers in species distribution data. J. Biogeogr. 45(1), 164–176 (2018)
Liu, X., Zhou, Y., Chen, X.: Mining outlier data in mobile internet-based large real-time databases. Complex. Hindawi (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9702304
Okay F, Ozdemir S (2016) A fog Computing Based Smart Grid Model. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Yasmine Hammamet, Tunisia, pp. 1–6
Yu, W., Liang, F., He, X., Hatcher, W., Lu, C., Lin, J., Yang, X.: A survey on the edge computing for the internet of things. IEEE Access IEEE 6, 6900–6919 (2018)
Aiyad, S., Saleh, A., Labib, L.: A new distributed feature selection technique for classifying gene expression data. Int. J. Biomath. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793524519500396
Posio, K.L., Ruuska, J., Ruha, P.: Outlier detection for 2D temperature data. IFAC Proc. 41(2), 1958–1963 (2008)
Raja, P., Bhaskara, V.: An effective genetic algorithm for outlier detection. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 38(6), 30–33 (2012)
Afzal, M., Ashraf, S.: Genetic algorithm for outlier detection. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. (IJCSIT) 7(2), 833–835 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Meratnia, N., Havinga, P.: Outlier detection techniques for wireless sensor networks: a survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 12(2), 159–170 (2010)
Yu, N., Zhang, L., Ren, Y.: A novel D-S based secure localization algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Sec. Commun. Netw. 7(11), 1945–1954 (2014)
Revathi, L., Appandiraj, A.: Hadoop based parallel framework for feature subset selection in big data. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 4(5), 3530–3534 (2015)
Feng, X., Li, S., Yuan, C., Zeng, P., Sun, Y.: Prediction of slope stability using naive Bayes classifier. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 22(3), 941–950 (2018)
European Network on Intelligent Technologies for Smart Adaptive Systems. Available at: http://www.eunite.org/. The competition page is: http://neuron.tuke.sk/competition/
Zhang, P., Wu, X., Wang, X., Bi, S.: Short-term load forecasting based on big data technologies. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 1(3), 59–67 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabie, A.H., Ali, S.H., Saleh, A.I. et al. A new outlier rejection methodology for supporting load forecasting in smart grids based on big data. Cluster Comput 23, 509–535 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-019-02942-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-019-02942-0