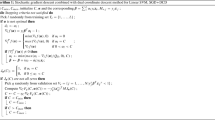
Abstract
Support vector machines (SVMs) training may be posed as a large quadratic program (QP) with bound constraints and a single linear equality constraint. We propose a (block) coordinate gradient descent method for solving this problem and, more generally, linearly constrained smooth optimization. Our method is closely related to decomposition methods currently popular for SVM training. We establish global convergence and, under a local error bound assumption (which is satisfied by the SVM QP), linear rate of convergence for our method when the coordinate block is chosen by a Gauss-Southwell-type rule to ensure sufficient descent. We show that, for the SVM QP with n variables, this rule can be implemented in O(n) operations using Rockafellar’s notion of conformal realization. Thus, for SVM training, our method requires only O(n) operations per iteration and, in contrast to existing decomposition methods, achieves linear convergence without additional assumptions. We report our numerical experience with the method on some large SVM QP arising from two-class data classification. Our experience suggests that the method can be efficient for SVM training with nonlinear kernel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, P., Kovoor, N., Pardalos, P.M.: Algorithms for the least distance problem. In: Pardalos, P.M. (ed.) Complexity in Numerical Optimization, pp. 33–56. World Scientific, Singapore (1993)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Nonlinear Programming, 2nd edn. Athena Scientific, Belmont (1999)
Brucker, P.: An O(n) algorithm for quadratic knapsack problems. Oper. Res. Lett. 3, 163–166 (1984)
Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-J.: LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines (2001). Available from http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm
Chang, C.-C., Hsu, C.-W., Lin, C.-J.: The analysis of decomposition methods for support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 11, 1003–1008 (2000)
Chen, P.-H., Fan, R.-E., Lin, C.-J.: A study on SMO-type decomposition methods for support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 17, 893–908 (2006)
Cristianini, N., Shawe-Taylor, J.: An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Fan, R.-E., Chen, P.-H., Lin, C.-J.: Working set selection using second order information for training support vector machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 6, 1889–1918 (2005)
Ferris, M.C., Munson, T.S.: Interior-point methods for massive support vector machines. SIAM J. Optim. 13, 783–804 (2003)
Ferris, M.C., Munson, T.S.: Semismooth support vector machines. Math. Program. 101, 185–204 (2004)
Fine, S., Scheinberg, K.: Efficient SVM training using low-rank kernel representations. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2, 243–264 (2001)
Fletcher, R.: Practical Methods of Optimization, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1987)
Glasmachers, T., Igel, C.: Maximum-gain working set selection for SVMs. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7, 1437–1466 (2006)
Hush, D., Scovel, C.: Polynomial-time decomposition algorithms for support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 51, 51–71 (2003)
Hush, D., Kelly, P., Scovel, C., Steinwart, I.: QP algorithms with guaranteed accuracy and run time for support vector machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7, 733–769 (2006)
Joachims, T.: Making large-scale SVM learning practical. In: Schölkopf, B., Burges, C.J.C., Smola, A.J. (eds.) Advances in Kernel Methods—Support Vector Learning, pp. 169–184. MIT Press, Cambridge (1999)
Keerthi, S.S., Gilbert, E.G.: Convergence of a generalized SMO algorithm for SVM classifier design. Mach. Learn. 46, 351–360 (2002)
Keerthi, S.S., Ong, C.J.: On the role of the threshold parameter in SVM training algorithm. Technical Report CD-00-09, Department of Mathematical and Production Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore (2000)
Keerthi, S.S., Shevade, S.K.: SMO algorithm for least-squares SVM formulations. Neural Comput. 15, 487–507 (2003)
Keerthi, S.S., Shevade, S.K., Bhattacharyya, C., Murthy, K.R.K.: Improvements to Platt’s SMO algorithm for SVM classifier design. Neural Comput. 13, 637–649 (2001)
Kiwiel, K.C.: On linear time algorithms for the continuous quadratic knapsack problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 134, 549–554 (2007)
Lin, C.-J.: On the convergence of the decomposition method for support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 12, 1288–1298 (2001)
Lin, C.-J.: Linear convergence of a decomposition method for support vector machines. Technical Report, Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan (2001)
Lin, C.-J.: Asymptotic convergence of an SMO algorithm without any assumptions. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 13, 248–250 (2002)
Lin, C.-J., Lucidi, S., Palagi, L., Risi, A., Sciandrone, M.: A decomposition algorithm model for singly linearly constrained problems subject to lower and upper bounds. Technical Report, DIS-Università di Roma “La Sapienza”, Rome, January (2007). To appear in J. Optim. Theory Appl.
List, N., Simon, H.U.: A general convergence theorem for the decomposition method. In: Proceedings of the 17th Annual Conference on Learning Theory, pp. 363–377 (2004)
List, N., Simon, H.U.: General polynomial time decomposition algorithms. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3559, pp. 308–322. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Lucidi, S., Palagi, L., Risi, A., Sciandrone, M.: On the convergence of hybrid decomposition methods for SVM training. Technical Report, DIS-Università di Roma “La Sapienza”, Rome, July 2006. Submitted to IEEE Trans. Neural Netw.
Luo, Z.-Q., Tseng, P.: Error bounds and the convergence analysis of matrix splitting algorithms for the affine variational inequality problem. SIAM J. Optim. 2, 43–54 (1992)
Luo, Z.-Q., Tseng, P.: Error bounds and convergence analysis of feasible descent methods: a general approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 46, 157–178 (1993)
Mangasarian, O.L., Musicant, D.R.: Successive overrelaxation for support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 10, 1032–1037 (1999)
Nocedal, J., Wright, S.J.: Numerical Optimization. Springer, New York (1999)
Osuna, E., Freund, R., Girosi, F.: Improved training algorithm for support vector machines. In: Proc. IEEE NNSP’97 (1997)
Palagi, L., Sciandrone, M.: On the convergence of a modified version of SVMlight algorithm. Optim. Methods Softw. 20, 317–334 (2005)
Platt, J.: Sequential minimal optimization: A fast algorithm for training support vector machines. In: Schölkopf, B., Burges, C.J.C., Smola, A.J. (eds.) Advances in Kernel Methods-Support Vector Learning, pp. 185–208. MIT Press, Cambridge (1999)
Rockafellar, R.T.: The elementary vectors of a subspace of R N. In: Bose, R.C., Dowling, T.A. (eds.) Combinatorial Mathematics and Its Applications, Proc. of the Chapel Hill Conference 1967, pp. 104–127. Univ. North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill (1969)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Network Flows and Monotropic Optimization. Wiley, New York, 1984. Republished by Athena Scientific, Belmont (1998)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.-B.: Variational Analysis. Springer, New York (1998)
Saunders, C., Stitson, M.O., Weston, J., Bottou, L., Schölkopf., B., Smola, A.J.: Support vector machine—reference manual. Report CSD-TR-98-03, Department of Computer Science, Royal Holloway, University of London, Egham, UK (1998)
Scheinberg, K.: An efficient implementation of an active set method for SVM. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7, 2237–2257 (2006)
Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.J., Williamson, R.C., Bartlett, P.L.: New support vector algorithms. Neural Comput. 12, 1207–1245 (2000)
Simon, H.U.: On the complexity of working set selection. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Algorithmic Learning Theory, pp. 324–337 (2004)
Suykens, J.A.K., Van Gestel, T., De Brabanter, J., De Moor, B., Vandewalle, J.: Least Squares Support Vector Machines. World Scientific, Singapore (2002)
Tseng, P., Yun, S.: A coordinate gradient descent method for nonsmooth separable minimization. Math. Program. B 117, 387–423 (2009)
Vapnik, V.: Estimation of Dependences Based on Empirical Data. Springer, New York (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported by the National Science Foundation, Grant No. DMS-0511283.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tseng, P., Yun, S. A coordinate gradient descent method for linearly constrained smooth optimization and support vector machines training. Comput Optim Appl 47, 179–206 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-008-9215-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-008-9215-4