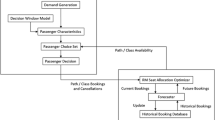
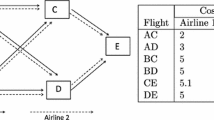
Abstract
We consider capacity management games between airlines who transport passengers over a joint airline network. Passengers are likely to purchase alternative tickets of the same class from competing airlines if they do not get tickets from their preferred airlines. We propose a Nash and a generalized Nash game model to address the competitive network revenue management problem. These two models are based on well-known deterministic linear programming and probabilistic nonlinear programming approximations for the non-competitive network capacity management problem. We prove the existence of a Nash equilibrium for both games and investigate the uniqueness of a Nash equilibrium for the Nash game. We provide some further uniqueness and comparative statics analysis when the network is reduced to a single-leg flight structure with two products. The comparative statics analysis reveals some useful insights on how Nash equilibrium booking limits change monotonically in the prices of products. Our numerical results indicate that airlines can generate higher and more stable revenues from a booking scheme that is based on the combination of the partitioned booking-limit policy and the generalized Nash game model. The results also show that this booking scheme is robust irrespective of which booking scheme the competitor takes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adida, E., Perakis, G.: Dynamic pricing and inventory control: uncertainty and competition part A: Existence of a Nash equilibrium. Technical report, MIT (2006)
Adida, E., Perakis, G.: Dynamic pricing and inventory control: uncertainty and competition part B: An algorithm for the normalized Nash equilibrium. Technical report, MIT (2006)
Andersen, P., Gill, R.: Cox’s regression model for counting processes: a large sample study. Ann. Stat. 10, 1100–1120 (1982)
Bertsimas, D., Popescu, I.: Revenue management in a dynamic network environment. Transp. Sci. 37, 257–277 (2003)
Cachon, G., Netessine, S.: Game theory in supply chain analysis. In: Simchi-Levi, S.W.D., Shen, Z. (eds.) Handbook of Quantitative Supply Chain Analysis: Modeling in the eBusiness Era. Kluwer Dordrecht (2004)
Chen, L., Homem-de-Mello, T.: An alternative discrete choice model by customer preferences. Technical report, Northwestern University. http://users.iems.northwestern.edu/tito/pubs/customer_paper_revised.pdf (2007)
Chen, L., Homem-de-Mello, T.: Re-solving stochastic programming models for airline revenue management. Ann. Oper. Res. 177, 91–114 (2010)
Cooper, W.: Asymptotic behavior of an allocation policy for revenue management. Oper. Res. 50, 720–727 (2002)
Cooper, W., Homem-de-Mello, T., Kleywegt, A.: Models of the spiral-down effect in revenue management. Oper. Res. 54, 968–987 (2006)
Dasci, A.: Dynamic pricing of perishable assets under competition: a two-period model. Technical report, School of Business, University of Alberta (2003)
de Boer, S., Freling, R., Piersma, N.: Mathematical programming for network revenue management revisited. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 37, 72–92 (2002)
Dockner, E., Horgensen, S., Long, N.V., Sorger, G.: Differential Games in Economics and Management Science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Facchinei, F., Fischer, A., Piccialli, V.: Generalized Nash equilibrium problems and Newton methods. Math. Program. 117, 163–194 (2009)
Facchinei, F., Pang, J.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems I and II. Springer, New York (2003)
Friesz, T., Mookherjee, R., Rigdon, M.: An evolutionary game theoretic model of revenue management in oligopolistic competition. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 4, 156–173 (2005)
Friesz, T., Mookherjee, R., Rigdon, M.: Formulating and solving service network pricing and resource allocation games as differential variational inequalities. In: Quincampoix, M., Vincent, T., Jorgensen, S. (eds.) Annals of Dynamic Games. Birkhauser, Basel (2006)
Gale, D., Nakaido, H.: The Jacobian matrix and global univalence of mappings. Math. Ann. 159, 81–93 (1965)
Gallego, G., Hu, M.: Dynamic pricing of perishable assets under competition. Technical report, CORC Technical Report, IEOR Department, Columbia University (2006)
Gallego, G., Huh, T., Kang, W., Phillips, R.: Price competition with the attraction demand model: existence of unique equilibrium and its stability. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 8, 359–375 (2006)
Gallego, G., Iyengar, G., Phillips, R., Dubey, A.: Managing flexible products on a network. Technical report, CORC Technical Report TR-2004-01, IEOR Department, Columbia University (2004)
Gallego, G., Krishnamoorthy, S., Phillips, R.: Competitive revenue management with forward and spot markets. Technical report, CORC Technical Report, IEOR Department, Columbia University (2005)
Gallego, G., Krishnamoorthy, S., Phillips, R.: Dynamic revenue management games with forward and spot markets. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 5, 10–31 (2006)
Gallego, G., Li, L., Ratliff, R.: Revenue management with customer choice models. Technical report, Presentation at AGIFORS RMD and Cargo Study Group, South Korea (2007)
Glasserman, P.: Perturbation analysis of production networks. In: Yao, D. (ed.) Stochastic Modeling and Analysis of Manufacturing Systems, pp. 233–280. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Gurkan, G., Pang, J.: Approximations of Nash equilibria. Math. Program. 117, 223–253 (2009)
Harker, P.: Generalized Nash games and quasi-variational inequalities. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 54, 81–94 (1991)
Jiang, H.: A Lagrangian relaxation approach for solving the network inventory control problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 59, 372–380 (2008)
Jiang, H., Miglionico, G.: Airline network revenue management with buy-up. Technical report, Judge Business School, University of Cambridge (2006)
Karjalainen, R.: The newsboy game. Technical report, Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania (1992)
Li, M., Oum, T., Anderson, C.: An airline seat allocation game. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 6, 321–330 (2007)
Li, S., Basar, T.: Distributed algorithms for the computation of noncooperative equilibria. Automatica 23, 523–533 (1987)
Lippman, S., McCardle, K.: The competitive newsboy. Oper. Res. 45, 54–65 (1997)
Liu, Q., van Ryzin, G.: On the choice-based linear programming model for network revenue management. Technical report (2008)
Mahajan, S., van Ryzin, G.: Inventory competition under dynamic consumer choice. Oper. Res. 49, 646–657 (2001)
MATLAB 6.5. The MathWorks, Inc. 24 Prime Park Way, Natick MA (2002)
Milgrom, P., Roberts, J.: Rationalizability, learning, and equilibrium in games with strategic complementarities. Economitrica 58, 1255–1278 (1990)
Milgrom, P., Shannon, C.: Monotone comparative statics. Economitrica 62, 157–180 (1994)
Mookherjee, R., Friesz, T.: Pricing, allocation and overbooking in dynamic service network competition when demand is uncertain. Technical report, The Pennsylvania State University (2005)
Netessine, S., Rudi, N.: Centralized and competitive inventory models with demand substitution. Oper. Res. 51, 329–335 (2003)
Netessine, S., Shumsky, R.: Revenue management games: horizontal and vertical competition. Manag. Sci. 51, 813–831 (2005)
Pang, J., Fukushima, M.: Quasi-variational inequalities, generalized Nash equilibria, and multi-leader-follower games. Comput. Manag. Sci. 1, 21–56 (2005)
Parlar, M.: Game theoretic analysis of the substitutable product inventory problem with random demands. Nav. Res. Logist. 35, 397–409 (1988)
Perakis, G., Sood, A.: Competitive multi-period pricing with fixed inventories. Technical report, MIT (2003)
Phillips, R.: Pricing and Revenue Optimization. Stanford Business Books, Stanford (2005)
Ratliff, R.: Multi-flight demand untruncation with recapture. Technical report, Presentation at AGIFORS RMD and Cargo Study Group, Mexico (2006)
Rosen, J.: Existence and uniqueness of the equilibrium points for concave n-person games. Econometrica 33, 520–534 (1965)
Scrimali, L.: A quasi-variational inequality approach to the financial equilibrium problem. Technical report, Università di Catania (2006)
Shapiro, A.: Monte Carlo sampling methods. In: Rusczynski, A., Shapiro, A. (eds.) Stochastic Programming. Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science, vol. 10, pp. 353–425. North-Holland, Amsterdam (2003)
Talluri, K.: On equilibria in duopolies with finite strategy spaces. Technical report, Universitat Pompeu Fabra (2003)
Talluri, K., van Ryzin, G.: A randomized linear programming method for computing network bid prices. Transp. Sci. 33, 207–216 (1999)
Talluri, K., van Ryzin, G.: The Theory and Practice of Revenue Management. Kluwer Academic, Boston (2004)
Uryasev, S., Rubinstein, R.: On relaxation algorithms in computation of noncooperative equilibria. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 39, 1263–1267 (1994)
Williamson, E.: Airline network seat inventory control: methodologies and revenue impacts. PhD thesis (1992)
Xu, H., Zhang, D.: Stochastic Nash equilibrium problems: sample average approximation and applications. Technical report, University of Southampton, December 2008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Professor Liqun Qi on the occasion of his 65th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Pang, Z. Network capacity management under competition. Comput Optim Appl 50, 287–326 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-010-9340-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-010-9340-8