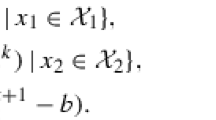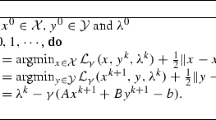Abstract
The alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) recently has found many applications in various domains whose models can be represented or reformulated as a separable convex minimization model with linear constraints and an objective function in sum of two functions without coupled variables. For more complicated applications that can only be represented by such a multi-block separable convex minimization model whose objective function is the sum of more than two functions without coupled variables, it was recently shown that the direct extension of ADMM is not necessarily convergent. On the other hand, despite the lack of convergence, the direct extension of ADMM is empirically efficient for many applications. Thus we are interested in such an algorithm that can be implemented as easily as the direct extension of ADMM, while with comparable or even better numerical performance and guaranteed convergence. In this paper, we suggest correcting the output of the direct extension of ADMM slightly by a simple correction step. The correction step is simple in the sense that it is completely free from step-size computing and its step size is bounded away from zero for any iterate. A prototype algorithm in this prediction-correction framework is proposed; and a unified and easily checkable condition to ensure the convergence of this prototype algorithm is given. Theoretically, we show the contraction property, prove the global convergence and establish the worst-case convergence rate measured by the iteration complexity for this prototype algorithm. The analysis is conducted in the variational inequality context. Then, based on this prototype algorithm, we propose a class of specific ADMM-based algorithms that can be used for three-block separable convex minimization models. Their numerical efficiency is verified by an image decomposition problem.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For the ADMM scheme, the primal variables x and y play different roles —- x is an intermediate variable which is not involved in the iteration and the only primal variable required by the iteration is y.
References
Aujol, J.F., Gilboa, G., Chan, T., Osher, S.: Structure-texture image decomposition–modeling, algorithms, and parameter selection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 67, 111–136 (2006)
Blum, E., Oettli, W.: Mathematische Optimierung. Grundlagen und Verfahren. Ökonometrie und Unternehmensforschung. Springer, Berlin (1975)
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., Peleato, B., Eckstein, J.: Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Foun. Trends Mach. Learn. 3, 1–122 (2010)
Chan, T. F., Glowinski, R.: Finite element approximation and iterative solution of a class of mildly non-linear elliptic equations. Technical Report, Stanford University (1978)
Chandrasekaran, V., Parrilo, P.A., Willsky, A.S.: Latent variable graphical model selection via convex optimization. Ann. Stat. 40, 1935–1967 (2012)
Chen, C.H., He, B.S., Ye, Y.Y., Yuan, X.M.: The direct extension of ADMM for multi-block convex minimization problems is not necessarily convergent. Math. Program. Ser. A 155, 57–79 (2016)
Eckstein, J., Yao, W.: Augmented Lagrangian and alternating direction methods for convex optimization: a tutorial and some illustrative computational results. Pac. J. Optim. 11(4), 619–644 (2015)
Esser, E., Zhang, X., Chan, T.F.: A general framework for a class of first order primal-dual algorithms for convex optimization in imaging science. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 3, 1015–1046 (2010)
Facchinei, F., Pang, J.S.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems. Springer Series in Operations Research, vol. I. Springer, New York (2003)
Gabay, D., Mercier, B.: A dual algorithm for the solution of nonlinear variational problems via finite-element approximations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2, 17–40 (1976)
Glowinski, R.: On alternating directon methods of multipliers: a historical perspective. In: Fitzgibbon, W., Kuznetsov, Y.A., Neittaanmaki, P., Pironneau, O. (eds.) Modeling, Simulation and Optimization for Science and Technology, pp. 59–82. Springer, Dordrecht (2014)
Glowinski, R., Marrocco, A.: Approximation par èlèments finis d’ordre un et résolution par pénalisation-dualité d’une classe de problèmes non linéaires, R.A.I.R.O., R2, 41–76 (1975)
Han, D.R., Yuan, X.M.: A note on the alternating direction method of multipliers. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 155, 227–238 (2012)
Hansen, P., Nagy, J., O’Leary, D.: Deblurring Images: Matrices, Spectra, and Filtering. SIAM, Philadelphia (2006)
He, B.S., Tao, M., Yuan, X.M.: Alternating direction method with Gaussian back substitution for separable convex programming. SIAM J. Optim. 22, 313–340 (2012)
He, B.S., Tao, M., Yuan, X.M.: A splitting method for separable convex programming. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35, 394–426 (2015)
He, B.S., Tao, M., Yuan, X.M.: Convergence rate and iteration complexity on the alternating direction method of multipliers with a substitution procedure for separable convex programming. Math. Oper. Res. 42(3), 662–691 (2017)
He, B.S., Yuan, X.M.: On the O(1/n) convergence rate of Douglas-Rachford alternating direction method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 700–709 (2012)
He, B.S., Yuan, X.M.: Linearized alternating direction method with Gaussian back substitution for separable convex programming. Numer. Algebra Control Optim. 3, 247–260 (2013)
Hestenes, M.R.: Multiplier and gradient methods. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 4, 303–320 (1969)
Lions, P.L., Mercier, B.: Splitting algorithms for the sum of two nonlinear operators. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 16, 964–979 (1979)
McLachlan, G.J.: Discriminant Analysis and Statistical Pattern Recognition. Wiley, Hoboken (2004)
Meyer, Y.: Oscillating Patterns in Image Processing and Nonlinear Evolution Equations. University Lecture Series. AMS, Providence (2002)
Nemirovsky, A.S., Yudin, D.B.: Problem Complexity and Method Efficiency in Optimization. Wiley-Interscience Series in Discrete Mathematics. Wiley, New York (1983)
Nesterov, Y.E.: A method for unconstrained convex minimization problem with the rate of convergence \(\cal{O}(1/{k^2})\). Doklady AN SSSR 269, 543–547 (1983)
Ng, M.K., Yuan, X.M., Zhang, W.X.: A coupled variational image decomposition and restoration model for blurred cartoon-plus-texture images with missing pixels. IEEE Trans. Imaging Proc. 22, 2233–2246 (2013)
Osher, S., Sole, A., Vese, L.: Image decomposition and restoration using total variation minimization and the \(H^{-1}\) norm. Multiscale Model. Simul. 1, 349–370 (2003)
Passty, G.B.: Ergodic convergence to a zero of the sum of monotone operators in Hilbert space. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 72, 383–390 (1979)
Peng, Y.G., Ganesh, A., Wright, J., Xu, W.L., Ma, Y.: Robust alignment by sparse and low-rank decomposition for linearly correlated images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34, 2233–2246 (2012)
Powell, M.J.D.: A method for nonlinear constraints in minimization problems. In: Fletcher, R. (ed.) Optimization, pp. 283–298. Academic Press, New York (1969)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Augmented Lagrangians and applications of the proximal point algorithm in convex programming. Math. Oper. Res. 1, 97–116 (1976)
Rudin, L., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Phys. D 60, 259–268 (1992)
Schaeffer, H., Osher, S.: A low patch-rank interpretation of texture. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 6, 226–262 (2013)
Starck, J., Elad, M., Donoho, D.L.: Image decomposition via the combination of sparse representations and a variational approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14, 1570–1582 (2005)
Tao, M., Yuan, X.M.: Recovering low-rank and sparse components of matrices from incomplete and noisy observations. SIAM J. Optim. 21, 57–81 (2011)
Vese, L., Osher, S.: Modeling textures with total variation minimization and oscillating patterns in image processing. J. Sci. Comput. 19, 553–572 (2003)
Wang, X.F., Yuan, X.M.: The linearized alternating direction method for Dantzig Selector. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 34, A2792–A2811 (2012)
Yang, J.F., Yuan, X.M.: Linearized augmented Lagrangian and alternating direction methods for nuclear norm minimization. Math. Comput. 82, 301–329 (2013)
Acknowledgements
Fundig was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10471056), NSFC/RGC Joint Research Scheme (Grant No. N_PolyU504/14) and Research Grants Council, University Grants Committee (Grant No. HKBU 12313516).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the NSFC Grant 10471056, the NSFC/RGC Joint Research Scheme: N_PolyU504/14 and the General Research Fund from Hong Kong Research Grants Council: HKBU 12313516.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, B., Yuan, X. A class of ADMM-based algorithms for three-block separable convex programming. Comput Optim Appl 70, 791–826 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-018-9994-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-018-9994-1
Keywords
- Convex programming
- Alternating direction method of multipliers
- Splitting methods
- Contraction
- Convergence rate