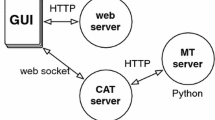
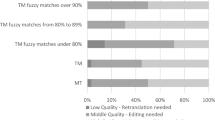
Abstract
Translation memory tools now offer the translator to insert post-edited machine translation segments for which no match is found in the databases. The Google Translator Toolkit does this by default, advising in its Settings window: “Most users should not modify this”. Post-editing of no matches appears to work on engines trained with specific bilingual data on a source written under controlled language constraints. Would this, however, work for any type of task as Google’s advice implies? We have tested this by carrying out experiments with English–Chinese trainees, using the Toolkit to translate from the source text (the control group) and by post-editing (the experimental group). Results show that post-editing gains in productivity are marginal. With regard to quality, however, post-editing produces significantly better statistical results compared to translating manually. These gains in quality are observed independently of language direction, text difficulty or translator’s level of performance. In light of these findings, we discuss whether translators should consider post-editing as a viable alternative to conventional translation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen J (2003) Post-editing. In: Somers H (ed) Computers and translation: a translator’s guide. John Benjamins, Amsterdam, pp 297–317
Beaton A, Contreras G (2010) Sharing the continental airlines and SDL post-editing experience. In: AMTA 2010: the ninth conference of the association for machine translation in the Americas, Denver, CO
Belam J (2003) Buying up to falling down: a deductive approach to teaching post-editing. In: MT Summit IX, workshop on teaching translation technologies and tools, New Orleans, USA
Campbell S (1998) Translation into the second language. Addison Wesley Longman, New York
Depraetere I (2010) What counts as useful advice in a university post-editing training context? Report on a case study. In: EAMT 2010: proceedings of the 14th annual conference of the European association for machine translation, Saint-Raphaël, France
Dragsted B, Hansen IG (2009) Exploring translation and interpreting hybrids: the case of sight translation. Meta 54(3): 588–604
Dugast L, Senellart J, Koehn P (2007) Statistical post-editing on SYSTRAN’s rule-based translation system. In: ACL 2007: proceedings of the second workshop on statistical machine translation, Prague, Czech Republic, pp 220–223
Fiederer R, O’Brien S (2009) Quality and machine translation: a realistic objective?. J Specialised Transl 11: 52–72
Garcia I (2010) Is machine translation ready yet?. Target 22(1): 7–21
Garcia I, Stevenson V (2009) Google Translator Toolkit. Free web-based translation memory for the masses. Multilingual 106: 16–18
Gerber L (2008) Recipes for success with machine translation, part 1. Clientside News, January, pp 15–17
Guerberof A (2009) Productivity and quality in the postediting of outputs from translation memories and machine translation. Localis Focus 7(1): 11–21
Hardt D, Elming J (2010) Incremental re-training for post-editing SMT. AMTA 2010: the ninth conference of the association for machine translation in the Americas, Denver, CO
Lagarda AL, Alabau V, Casacuberta F, Silva R, Díaz-de-Liaño E (2009) Statistical post-editing of a rule-based machine translation system. In: NAACL HLT 2009. Human language technologies: the 2009 annual conference of the North American chapter of the ACL, short papers, Boulder, CO, pp 217–220
Moser-Mercer B (2010) The search for neuro-physiological correlates of expertise in interpreting. In: Shreve GM, Angelone E (eds) Translation and cognition. John Benjamins, Amsterdam, pp 263–288
O’Brien S (2002) Teaching post-editing: a proposal for course content. In: Sixth EAMT workshop “Teaching machine translation”, Manchester, UK, pp 99–106
O’Brien S (2006) Eye-tracking and translation memory matches. Perspectives 14(3): 185–204
Perrino S (2009) User-generated translation: the future of translation in a Web 2.0 environment. J Specialised Transl 12: 55–78
Ramos LC (2010) Post-editing free machine translation: from a language vendor’s perspective. In: AMTA 2010: the ninth conference of the association for machine translation in the Americas, Denver, CO
SDL Research (2010) Trends in automated translation in today’s global business. http://www.sdl.com/en/language-technology/landing-pages/machine-translation-survey/. Accessed 1 May 2011
Specia L (2011) Exploiting objective annotations for measuring translation post-editing effort. In: EAMT 2011: proceedings of the 15th conference of the European association for machine translation, Leuven, Belgium, pp 73–80
TAUS (2007) Advanced leveraging. A TAUS report. http://www.translationautomation.com/technology-reviews/advanced-leveraging.html. Accessed 1 May 2011
TAUS (2010) Postediting in practice. A TAUS report. http://www.translationautomation.com/best-practices/postediting-in-practice.html. Accessed 1 May 2011
Van Ess-Dykema C, Phillips J, Reeder F, Gerber L (2010) Paralinguist assessment decision factors for machine translation output: a case study. In: AMTA 2010: the ninth conference of the association for machine translation in the Americas, Denver, CO
Wendt C (2010) Better translations with user collaboration—integrated MT at Microsoft. In: AMTA 2010: the ninth conference of the association for machine translation in the Americas, Denver, CO
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, I. Translating by post-editing: is it the way forward?. Machine Translation 25, 217–237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10590-011-9115-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10590-011-9115-8