Abstract
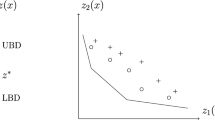
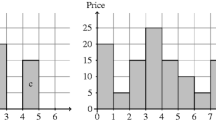
The AtMostNValue global constraint, which restricts the maximum number of distinct values taken by a set of variables, is a well known NP-Hard global constraint. The weighted version of the constraint, AtMostWValue, where each value is associated with a weight or cost, is a useful and natural extension. Both constraints occur in many industrial applications where the number and the cost of some resources have to be minimized. This paper introduces a new filtering algorithm based on a Lagrangian relaxation for both constraints. This contribution is illustrated on problems related to facility location, which is a fundamental class of problems in operations research and management sciences. Preliminary evaluations show that the filtering power of the Lagrangian relaxation can provide significant improvements over the state-of-the-art algorithm for these constraints. We believe it can help to bridge the gap between constraint programming and linear programming approaches for a large class of problems related to facility location.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beldiceanu, N., & Carlsson, M. (2001). Pruning for the minimum constraint family and for the number of distinct values constraint family. In Walsh, T. (Ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming – CP 2001, volume 2239 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 211–224). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Beldiceanu, N., Carlsson, M., & Thiel, S. (2002). Cost-filtering algorithms for the two sides of the sum of weights of distinct values constraint. Technical report – T2002-14: Swedish Institute of Computer Science.
Benchimol, P., Van Hoeve, W.J., Régin, J.-C., Rousseau, L.-M., & Rueher, M. (2012). Improved filtering for weighted circuit constraints. Constraints, 17(3), 205–233.
Bessiere, C., Hebrard, E., Hnich, B., Kiziltan, Z., & Walsh, T. (2006). Filtering algorithms for the nvalue constraint. Constraints, 11(4), 271–293.
Bessiere, C., Katsirelos, G., Narodytska, N., Quimper, C.-G., & Walsh, T. (2010). Decomposition of the nvalue constraint In Cohen, D. (Ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming – CP 2010, volume 6308 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 114–128). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Cambazard, H. Np-hard contraints involving costs: examples of applications and filtering. In Dixièmes Journées Francophones de Programmation par Contraintes – JFPC. 2014. Exposé invité.
Cambazard, H., O’Mahony, E., & O’Sullivan, B. (2012). A shortest path-based approach to the multileaf collimator sequencing problem. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 160(1–2), 81–99.
Cambazard, H., & Penz, B. (2012). A constraint programming approach for the traveling purchaser problem. In Milano, M. (Ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming - 18th International Conference, CP 2012, Quėbec City, QC, Canada, October 8-12, 2012. Proceedings, volume 7514 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 735–749): Springer.
Cooper, M.C., de Givry, S., Sanchez, M., Schiex, T., Zytnicki, M., & Werner, T. (2010). Soft arc consistency revisited. Artificial Intelligence, 174(7–8), 449–478.
Van den Bergh, J., Belieën, J., De Bruecker, P., Demeulemeester, E., & De Boeck, L. (2013). Personnel scheduling: a literature review. European Journal of Operational Research, 226(3), 367–385.
Erlenkotter, D. (1978). A dual-based procedure for uncapacitated facility location. Operations Research, 26(6), 992–1009.
Fages, J.-G., & Lapègue, T. (2014). Filtering atmostnvalue with difference constraints: application to the shift minimisation personnel task scheduling problem. Artificial Intelligence, 212(0), 116–133.
Fages, J.-G., Lorca, X., & Rousseau, L.-M. (2014). The salesman and the tree: the importance of search in CP. Constraints, 1–18.
Focacci, F., Lodi, A., & Milano, M. (1999). Cost-based domain filtering In Jaffar, J. (Ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming – CP’99, volume 1713 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 189–203). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Fontaine, D., Michel, L.D., & Van Hentenryck, P. Constraint-based lagrangian relaxation. In O’Sullivan, B. (Ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming - 20th International Conference, CP 2014, Lyon, France, September 8-12, 2014. Proceedings, volume 8656 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 324–339) (p. 2014). Berlin: Springer.
Gaspers, S., & Szeider, S. (2011). Kernels for global constraints, CoRR. arXiv: 1104.2541.
Geoffrion, A.M. (1974). Lagrangean relaxation for integer programming. In Balinski, M.L. (Ed.) Approaches to integer programming, volume 2 of mathematical programming studies, (pp. 82–114). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Held, M., & Karp, R.M. (1971). The traveling-salesman problem and minimum spanning trees: part II. Mathematical Programming, 1(1), 6–25.
Kadioglu, S., Malitsky, Y., Sellmann, M., & Tierney, K. (2010). ISAC - instance-specific algorithm configuration. In ECAI, volume 215 of Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, (pp. 751–756): IOS Press.
Lee, J.H.M., & Leung, K.L. (2012). Consistency techniques for flow-based projection-safe global cost functions in weighted constraint satisfaction. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 43(1), 257–292.
Menana, J., & Demassey, S. (2009). Sequencing and counting with the multicost-regular constraint. In Van Hoeve, W.J., & Hooker, J.N. (Eds.) Integration of AI and OR Techniques in Constraint Programming for Combinatorial Optimization Problems, 6th International Conference, CPAIOR 2009, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, May 27-31, 2009, Proceedings, volume 5547 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 178–192): Springer.
Narula, S.C., Ogbu, U.I., & Samuelsson, H.M. (1977). An algorithm for the p-median problem. Operations Research, 25(4), 709–713.
Prud’homme, C., Fages, J.-G., & Lorca, X. (2014). Choco3 Documentation. TASC, INRIA Rennes, LINA CNRS UMR 6241, COSLING S.A.S.
Sellmann, M. (2004). Theoretical foundations of cp-based lagrangian relaxation. In Wallace, M. (Ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming – CP 2004, volume 3258 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 634–647). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Sellmann, M., & Fahle, T. (2003). Constraint programming based lagrangian relaxation for the automatic recording problem. Annals OR, 118(1–4), 17–33.
Slusky, M.R., & Van Hoeve, W.J. (2013). A lagrangian relaxation for golomb rulers. In Gomes, C.P., & Sellmann, M. (Eds.) Integration of AI and OR Techniques in Constraint Programming for Combinatorial Optimization Problems, 10th International Conference, CPAIOR 2013, Yorktown Heights, NY, USA, May 18-22, 2013. Proceedings, volume 7874 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 251–267): Springer.
Wah, B.W., & Wu, Z. (1999). The theory of discrete lagrange multipliers for nonlinear discrete optimization. In Jaffar, J. (Ed.) Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming - CP’99, 5th International Conference, Alexandria, Virginia, USA, October 11-14, 1999, Proceedings, volume 1713 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, (pp. 28–42): Springer.
Wolsey, L.A. (1998). Integer programming. Wiley-Interscience series in discrete mathmatics and optimization. New York: Wiley.
Zhao, X., & Luh, P.B. (2002). New bundle methods for solving lagrangian relaxation dual problems. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 113(2), 373–397.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cambazard, H., Fages, JG. New filtering for AtMostNValue and its weighted variant: A Lagrangian approach. Constraints 20, 362–380 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10601-015-9191-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10601-015-9191-0