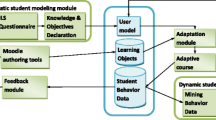
Abstract
Open learning represents a new form of online learning where courses are provided freely online for large numbers of learners. MOOCs are examples of this form of learning. The authors see an opportunity for personalising open learning environments by adapting to learners’ learning styles and providing adaptive support to meet individual learner needs and preferences. Identifying learning styles of learners in open learning environments is crucial to providing adaptive support. Learning styles refer to the manner in which learners receive and perceive information. In the literature, a number of learning style models have been proposed. The Felder and Silverman Learning Styles Model (FSLSM) has been selected as the most appropriate model for open learning. In previous studies two approaches have been used to automatically identify learning styles based on the FSLSM. These approaches are known as the data-driven method and the literature-based method. In the literature, the literature-based method has been shown to be more accurate in identifying learning styles. This method relies on tracking learners’ interactions with the provided learning objects based on a set of pre-determined patterns that help in inferring learning styles. The patterns are monitored based on pre-identified threshold values. This paper aims to apply the literature-based method to open learning environments and introduce the optimal patterns and threshold values for identifying learning styles based on the FSLSM. To achieve this aim, a study was conducted whereby a prototype that simulates the open learning environment was developed and piloted on an undergraduate IT course so that learner behaviour could be tracked and data could be collected. Next, different sets of threshold values from the literature were considered along with some updated threshold values considering the context of open learning environments, and the precision of identifying learning styles was calculated. Eighty-three students participated in the study and used the developed prototype. Precision results from different threshold values presented in the literature along with customised threshold values for this study are reported and analysed in this paper. It is shown that threshold values derived from literature and customised to suit open learning environments provide a high level of accuracy in identifying learning styles. The paper presents the first study of its kind in evaluating threshold values and precision in identifying learning styles based on the FSLSM in open learning environments. The results are promising and indicate that the proposed methodology is efficient in detecting learning styles in open learning environments and useful for developing an adaptive framework.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, N., & Tasir, Z. (2013). Threshold value in automatic learning style detection. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 97, 346–352.
Ahmad, N., Tasir, Z., Kasim, J., & Sahat, H. (2013). Automatic detection of learning styles in learning management systems by using literature-based method. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 103, 181–189.
Atman, N., Inceoğlu, M. M., & Aslan, B. G. (2009). Learning styles diagnosis based on learner behaviors in web based learning Computational Science and its Applications–ICCSA 2009 (pp. 900–909): Springer.
Bajraktarevic, N., Hall, W., & Fullick, P. (2003). Incorporating learning styles in hypermedia environment: Empirical evaluation. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Workshop on Adaptive Hypermedia and Adaptive Web-Based Systems, Nottingham, UK.
Brusilovsky, P. (1996). Methods and techniques of adaptive hypermedia. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction, 6(2–3), 87–129.
Cabada, R. Z., Estrada, M. L. B., Cabada, R. Z., & Garcia, C. A. R. (2009, 9–11 Nov. 2009). A fuzzy-neural network for classifying learning styles in a web 2.0 and mobile learning environment. Paper presented at the Web Congress, 2009. LA-WEB ′09. Latin American.
Carmona, C., Castillo, G., & Millan, E. (2008, 1–5 July 2008). Designing a dynamic Bayesian network for modeling students’ learning styles. Paper presented at the 8th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies ICALT ′08.
Carro, R. M., Pulido, E., & Rodriguez, P. (2001). TANGOW: a model for internet-based learning. International Journal of Continuing Engineering Education and Life Long Learning, 11(1–2), 25–34.
Carver, C. A., Jr., Howard, R. A., & Lane, W. D. (1999). Enhancing student learning through hypermedia courseware and incorporation of student learning styles. IEEE Transactions on Education, 42(1), 33–38. doi:10.1109/13.746332.
Cha, H., Kim, Y., Park, S., Yoon, T., Jung, Y., & Lee, J.-H. (2006). Learning styles diagnosis based on user interface behaviors for the customization of learning interfaces in an intelligent tutoring system. In M. Ikeda, K. Ashley & T.-W. Chan (Eds.), Intelligent Tutoring Systems (Vol. 4053, pp. 513–524): Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Chang, Y.-C., Kao, W.-Y., Chu, C.-P., & Chiu, C.-H. (2009). A learning style classification mechanism for e-learning. Computers & Education, 53(2), 273–285. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2009.02.008.
Claxton, C. S., & Murrell, P. H. (1987). Learning Styles: Implications for Improving Educational Practices: ERIC.
Coffield, F., Moseley, D., Hall, E., & Ecclestone, K. (2004). Should we be using learning styles?: What research has to say to practice. London: Learning & Skills Research Centre.
Coursera. (2012). Coursera. Retrieved 25-7-2012, 2012, from https://www.coursera.org/.
edX. (2012). edX. Retrieved 26-5-2012, 2012, from http://www.edxonline.org/.
Fasihuddin, H., Skinner, G., & Athauda, R. (2013). Boosting the opportunities of open learning (MOOCs) through learning theories. Journal on Computing, 3(3), 112–117.
Fasihuddin, H., Skinner, G., & Athauda, R. (2014). Towards an adaptive model to personalise open learning environments using learning styles. Paper presented at the International Conference on Information, Communication Technology and System (ICTS).
Fasihuddin, H., Skinner, G., & Athauda, R. (2015a). A framework to personalise open learning environments by adapting to learning styles Paper presented at the The 7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, Lisbon, Portugal.
Fasihuddin, H., Skinner, G., & Athauda, R. (2015b). Knowledge maps in open learning environments: an evaluation from learners’ perspectives. Journal of Information Technology and Application in Education, 4, 18–29. doi:10.14355/jitae.2015.04.003.
Felder, R. M., & Silverman, L. K. (1988). Learning and teaching styles in engineering education. Engineering Education, 78(7), 674–681.
Felder, R. M., & Spurlin, J. (2005). Applications, reliability and validity of the index of learning styles. International Journal of Engineering Education, 21(1), 103–112.
García, P., Amandi, A., Schiaffino, S., & Campo, M. (2007). Evaluating Bayesian networks’ precision for detecting students’ learning styles. Computers & Education, 49(3), 794–808.
García, P., Schiaffino, S., & Amandi, A. (2008). An enhanced Bayesian model to detect students’ learning styles in Web-based courses. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 24(4), 305–315. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2729.2007.00262.x.
Graf, S. (2007). Adaptivity in learning management systems focusing on learning styles. (Ph.D. Thesis), Vienna University of Technology, Austria.
Graf, S., & Kinshuk, K. (2007). Providing adaptive courses in learning management systems with respect to learning styles. Paper presented at the World Conference on E-Learning in Corporate, Government, Healthcare, and Higher Education, Quebec City, Canada. http://www.editlib.org/p/26739.
Graf, S., & Tzu-Chien, L. (2009). Supporting teachers in identifying students’ learning styles in learning management systems: An automatic student modelling approach. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 12(4), 3–14.
Graf, S., & Viola, S. (2009). Automatic student modelling for detecting learning style preferences in learning management systems. Paper presented at the Proc. International Conference on Cognition and Exploratory Learning in Digital Age.
Graf, S., Kinshuk, & Tzu-Chien, L. (2008, 1–5 July 2008). Identifying learning styles in learning management systems by using indications from students’ behaviour. Paper presented at the 8th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, 2008. ICALT ′08.
Honey, P., & Mumford, A. (1992). The manual of learning styles (3rd ed.): Peter Honey.
Hong, H., & Kinshuk, D. (2004). Adaptation to student learning styles in web based educational systems. Paper presented at the World Conference on Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia and Telecommunications.
Keefe, J. W. (1988). Profiling and utilizing learning style: ERIC.
Klašnja-Milićević, A., Vesin, B., Ivanović, M., & Budimac, Z. (2011). E-Learning personalization based on hybrid recommendation strategy and learning style identification. Computers & Education, 56(3), 885–899. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2010.11.001.
Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development: Prentice-Hall.
Kuljis, J., & Liu, F. (2005). A comparison of learning style theories on the suitability for e-learning. Web Technologies, Applications, and Services, 2005, 191–197.
Latham, A., Crockett, K., & Mclean, D. (2013). Profiling student learning styles with multilayer perceptron neural networks. Paper presented at the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC).
Moran, A. (1991). What can learning styles research learn from cognitive psychology? Educational Psychology, 11(3–4), 239–245.
Ozpolat, E., & Akar, G. B. (2009). Automatic detection of learning styles for an e-learning system. Computers & Education, 53(2), 355–367. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2009.02.018.
Peña, C.-I., Marzo, J.-L., & Rosa, J.-L. d. l. (2002). Intelligent agents in a teaching and learning environment on the web. Paper presented at the International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies.
Pritchard, A. (2013). Ways of learning: Learning theories and learning styles in the classroom (3rd ed.): Routledge.
Şimşek, Ö., Atman, N., İnceoğlu, M., & Arikan, Y. (2010). Diagnosis of learning styles based on active/reflective dimension of Felder and Silverman’s learning style model in a learning management system. In D. Taniar, O. Gervasi, B. Murgante, E. Pardede & B. Apduhan (Eds.), Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2010 (Vol. 6017, pp. 544–555): Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Soloman, B. A., & Felder, R. M. (n.d.). Index of learning styles questionnaire. Retrieved 7/2/2014, from http://www.engr.ncsu.edu/learningstyles/ilsweb.html.
Udacity (2012). Meet Udacity! , from http://www.udacity.com/.
Udemy (2014). Udemy. Retrieved 22-1-2014, 2014, from https://www.udemy.com/.
Williams, J. J. (2013). Improving learning in MOOCs with cognitive science. Paper presented at the AIED 2013 Workshops Proceedings Volume.
Witkin, H. A., Moore, C. A., Goodenough, D. R., & Cox, P. W. (1977). Field-dependent and field-independent cognitive styles and their educational implications. Review of Educational Research, 47(1), 1–64. doi:10.2307/1169967.
Zywno, M. S. (2003). A contribution to validation of score meaning for Felder-Soloman’s index of learning styles. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2003 American Society for Engineering Education annual conference and exposition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fasihuddin, H., Skinner, G. & Athauda, R. Towards adaptive open learning environments: Evaluating the precision of identifying learning styles by tracking learners’ behaviours. Educ Inf Technol 22, 807–825 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-015-9458-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-015-9458-5