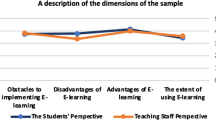
Abstract
The E-learning market is becoming more and more popular in the world. This is evidenced by the increased budget allocations for e-learning programs, the growing prevalence of e-learning in various markets all over the world and new trends in modern technology and tools. The study aims to evaluate the readiness of university management and students for active e-learning. The objective is to identify the prospects and problems of the information and communication technology in educational management when introducing e-learning. To achieve the research objectives, we conducted a survey in the form of a questionnaire among the first-year graduate IT students of three Moscow universities directly involved in e-learning initiatives. The survey involved 135 teachers, 19 information and communication technology (ICT)/e-learning specialists, 6 university managers and 3 heads of university management, one from each of the three universities. The research showed that despite the potential of a learning management system to support both blended learning and e-learning, most e-learning initiatives are not fully realized; they completely or partially fail. Poor marketing strategies, poor service strategies and insufficient technical support are some of the most likely causes of failure. The possibility of students and teachers to interact and the expansion of the geography of education should be noted among the prospects of modern management in the implementation of e-learning. It has been revealed that more than half of the students (54%) independently develop applications and programs for e-learning. The results of our research can become the basis for further research in e-learning and its prevalence in developing countries.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akçayır, M., & Akçayır, G. (2017). Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature. Educational Research Review, 20, 1–11.
Al-Samarraie, H., Teng, B. K., Alzahrani, A. I., & Alalwan, N. (2018). E-learning continuance satisfaction in higher education: A unified perspective from instructors and students. Studies in Higher Education, 43(11), 2003–2019.
Alyushin, M. V., & Kolobashkina, L. V. (2019). Monitoring of the current status of students as a means of increasing the effectiveness of educational process. The Education and science journal, 21(2), 176–197.
Arinto, P. B. (2016). Issues and challenges in open and distance e-learning: Perspectives from the Philippines. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 17(2).
Badwan, J. J., Al Shobaki, M. J., Naser, S. S. A., & Amuna, Y. M. A. (2017). Adopting technology for customer relationship management in higher educational institutions. International Journal of Engineering and Information Systems (IJEAIS), 1(1), 20–28.
Belyakova, E. G., & Zakharova, I. G. (2019). Interaction of university students with educational content in the conditions of information educational environment. The Education and science journal, 21(3), 77–105.
Cruz-Jesus, F., Vicente, M. R., Bacao, F., & Oliveira, T. (2016). The education-related digital divide: An analysis for the EU-28. Computers in Human Behavior, 56, 72–82.
Denchev, S., Pavlova, I., & Pavlova, M. (2016). The reform of higher education through Alternative University teaching models. Creative Education, 7(02), 302.
Ehlers, U. D. (2016). Chapter open educational resources in Germany. OpenEducational Resources: Policy, Costs and, 87.
Gulati, S. (2008). Technology-enhanced learning in developing nations: A review. International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 9(1), 1–16.
Horrigan, J. B. (2016). Lifelong learning and technology. Pew Research Center, 22.
Huynh, M. Q., Umesh, U. N., & Valacich, J. S. (2003). E-learning as an emerging entrepreneurial enterprise in universities and firms. C ommunications of the Association for Information Systems, 12(1), 3.
Kashorda, M., & Waema, T. (2014). E-Readiness survey of Kenyan Universities (2013) report. Nairobi: Kenya Education Network.
Kataoka, H., & Mertala, M. (2017). The role of educators and their challenges in distance learning in new millennium. Palma Journal, 16(3), 423–426.
Krasnova, G. A., Nuhuly, A., & Teslenko, V. A. (2017). E-learning in the world and Russia: State, trends and prospects RUDN. Journal of Informatization in Education/ RUDN Bulletin. Series: Informatization of Education, 14(3), 371–377.
Kuprina, T. V., Beketova, A. P., & Minasyan, S. M. (2019). Self-Organising Systems in the context of academic environment. The Education and science journal, 21(1), 150–169.
Maldonado, U., Feroz Khan, G., Moon, J., & Jeung Rho, J. (2011). E-learning motivation and educational portal acceptance in developing countries. Online Information Review, 35(1), 66–85.
Novikov, D.A. (2009), Theory of educational systems management, M.: National Education, pp. 452.
Pavlova, D. (2015). Government, in the clouds. Proceedings of VIIth International Scientific Seminar, Modern Dimensions in European Education And research Area, Bulgarian-British Cultural Communications, London, pp. 29–34.
Sabi, H. M., Uzoka, F. M. E., Langmia, K., & Njeh, F. N. (2016). Conceptualizing a model for adoption of cloud computing in education. International Journal of Information Management, 36(2), 183–191.
Schmitt, U. (2016). Redefining knowledge management education with the support of personal knowledge management devices, SmartEducation and e-Learning 2016, Springer, Cham, pp. 515–525.
Shakeabubakor, A. A., Sundararajan, E., & Hamdan, A. R. (2015). Cloud computing services and applications to improve productivity of university researchers. International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, 5(2), 153.
Shiau, W. L., & Chau, P. Y. (2016). Understanding behavioral intention to use a cloud computing classroom: A multiple model comparison approach. Information & Management, 53(3), 355–365.
Tamrakar, A., & Mehta, K. K. (2009). Analysis of effectiveness of web based e-learning through information technology. Economics, 6, 7.
Tarus, J. K., Gichoya, D., & Muumbo, A. (2015). Challenges of implementing e-learning in Kenya: A case of Kenyan public universities. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 16(1).
Tena, R. R., Almenara, J. C., & Osuna, J. B. (2016). E-learning of Andalusian University's lecturers. Gender. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 15(2), 25–37.
Touray, A., Salminen, A., & Mursu, A. (2013). ICT barriers and critical success factors in developing countries. The Electronic Journal on Information Systems in Developing Countries, 56(7), 1–17.
Uskov, V. L., Bakken, J. P., Pandey, A., Singh, U., Yalamanchili, M., & Penumatsa, A. (2016). Smart university taxonomy: Features, components, systems. In Smart education and e-learning 2016 (pp. 3–14). Cham: Springer.
Volles, N. (2016). Lifelong learning in the EU: Changing conceptualisations, actors, and policies. Studies in Higher Education, 41(2), 343–363.
Walker, D. S., Lindner, J. R., Murphrey, T. P., & Dooley, K. (2016). Learning management system usage. Quarterly Review of Distance Education, 17(2), 41–50.
Yoon, J., Yang, E., Lee, J. and Hwang, S. J. (2017). Lifelong learning with dynamically expandable networks arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.01547.
Zaharias, P., & Pappas, C. (2016). Quality management of learning management systems: A user experience perspective. Current Issues in Emerging eLearning, 3(1), 5.
Zamani, B. E., & Esfijani, A. (2016). Major barriers for participating in online teaching in developing countries from Iranian faculty members’ perspectives. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 32(3), 38–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vershitskaya, E.R., Mikhaylova, A.V., Gilmanshina, S.I. et al. Present-day management of universities in Russia: Prospects and challenges of e-learning. Educ Inf Technol 25, 611–621 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09978-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09978-0