Abstract
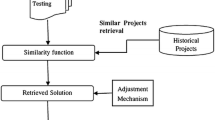
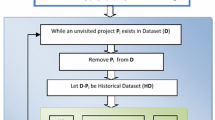
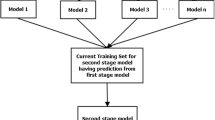
Cost estimation is one of the most important but most difficult tasks in software project management. Many methods have been proposed for software cost estimation. Analogy Based Estimation (ABE), which is essentially a case-based reasoning (CBR) approach, is one popular technique. To improve the accuracy of ABE method, several studies have been focusing on the adjustments to the original solutions. However, most published adjustment mechanisms are based on linear forms and are restricted to numerical type of project features. On the other hand, software project datasets often exhibit non-normal characteristics with large proportions of categorical features. To explore the possibilities for a better adjustment mechanism, this paper proposes Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for Non-linear adjustment to ABE (NABE) with the learning ability to approximate complex relationships and incorporating the categorical features. The proposed NABE is validated on four real world datasets and compared against the linear adjusted ABEs, CART, ANN and SWR. Subsequently, eight artificial datasets are generated for a systematic investigation on the relationship between model accuracies and dataset properties. The comparisons and analysis show that non-linear adjustment could generally extend ABE’s flexibility on complex datasets with large number of categorical features and improve the accuracies of adjustment techniques.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MRE :
-
Magnitude of Relative Error
- MMRE :
-
Mean Magnitude of Relative Error
- PRED(0.25):
-
PREDiction at level 0.25
- MdMRE :
-
Median Magnitude of Relative Error
- ABE :
-
Analogy Based Estimation
- NABE :
-
Non-linear adjusted ABE
- GABE :
-
GA optimized linear adjusted ABE
- LABE :
-
Linear adjusted ABE
- RABE :
-
Regression Toward the Mean adjusted ABE
- ANN :
-
Artificial Neural Network
- CART :
-
Classification and Regression Trees
- OLS :
-
Ordinary Least Square regression
- SWR :
-
Stepwise Regression
References
Albrecht AJ, Gaffney J (1983) Software function, source lines of code, and development effort prediction. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 9:639–648. doi:10.1109/TSE.1983.235271
Angelis L, Stamelos I (2000) A simulation tool for efficient analogy based cost estimation. Empir Softw Eng 5:35–68. doi:10.1023/A:1009897800559
Angelis L, Stamelos I, Morisio M (2000) Building a software cost estimation model based on categorical data. Proceedings of Seventh International Software Metrics Symposium, 4–15
Auer M, Trendowicz A, Graser B, Haunschmid E, Biffl S (2006) Optimal project feature weights in analogy-based cost estimation: Improvement and limitations. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 32:83–92. doi:10.1109/TSE.2006.1599418
Briand LC, El-Emam K, Surmann D, Wieczorek I, Maxwell KD (1999) An assessment and comparison of common cost estimation modeling techniques. Proceeding of the 1999 International Conference on Software Engineering, 313–322
Brieman L, Friedman J, Olshen R, Stone C (1984) Classification and regression trees. Wadsworth, Belmont
Burgess CJ, Lefley M (2001) Can genetic programming improve software effort estimation? A comparative evaluation. Inf Softw Technol 43:863–873. doi:10.1016/S0950-5849(01)00192-6
Cannon AJ (2007) Nonlinear analog predictor analysis: a coupled neural network/analog model for climate downscaling. Neural Netw 20(4):444–453. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2007.04.002
Chang SI, Ho ES (1999) Two-stage neural network approach for process variance change detection and classification. Int J Prod Res 37(7):1581–1599. doi:10.1080/002075499191148
Chiu NH, Huang SJ (2007) The adjusted analogy-based software effort estimation based on similarity distances. J Syst Softw 80:628–640. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2006.06.006
Conte S, Dunsmore H, Shen VY (1986) Software engineering metrics and models. Benjamin Cummings, Menlo Park, CA
Efron B, Gong G (1983) A leisurely look at the bootstrap, the jackknife, and cross-validation. Am Stat 37(1):36–48. doi:10.2307/2685844
De Barcelos Tronto IF, Da Silvaa JDS, Sant Anna N (2007) An investigation of artificial neural networks based prediction systems in software project management. J Syst Softw (in press). Corrected Proof
Desharnais JM (1989) Analyse statistique de la productivitie des projets informatique a partie de la technique des point des foncti on. University of Montreal
Foss T, Stensrud E, Kitchenham B, Myrtveit I (2003) A simulation study of the model evaluation criterion MMRE. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 29:985–995. doi:10.1109/TSE.2003.1245300
Gray AR, Macdonell SG (1997) A comparison of techniques for developing predictive models of software metrics. Inf Softw Technol 39:425–437. doi:10.1016/S0950-5849(96)00006-7
Guh RS (2002) Robustness of the neural network based control chart pattern recognition system to non-normality. Int J Qual Reliab Manage 19(1):97–112. doi:10.1108/02656710210415749
Hagan MT, Demuth HB, Beale MH (1997) Neural network design. PWS, Boston, MA
Hardy RL (1971) Multiquadratic equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J Geophys Res 76:1905–1915. doi:10.1029/JB076i008p01905
Heiat A (2002) Comparison of artificial neural network and regression models for estimating software development effort. Inf Softw Technol 44:911–922. doi:10.1016/S0950-5849(02)00128-3
Huang SJ, Chiu NH (2006) Optimization of analogy weights by genetic algorithm for software effort estimation. Inf Softw Technol 48:1034–1045. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2005.12.020
ISBSG (2007a) International software benchmark and standard group, Data CD Release 10, www.isbsg.org, 2007
ISBSG (2007b) Guidelines for use of ISBSE data, available from web link: http://www.isbsg.org/isbsg.nsf/weben/Repository%20info
Jeffery R, Ruhe M, Wieczorek I (2001) Using public domain metrics to estimate software development effort. Proceedings Seventh International Software Metrics Symposium, 16–27
Jonsson P, Wohlin C (2006) Benchmarking k-nearest neighbour imputation with homogeneous Likert data. Empir Softw Eng 11:463–489. doi:10.1007/s10664-006-9001-9
Jorgensen M (1995) An empirical study of software maintenance tasks. J Softw Mainten 7:27–48. doi:10.1002/smr.4360070104
Jorgensen M (2004) A review of studies on expert estimation of software development effort. J Syst Softw 70:37–60. doi:10.1016/S0164-1212(02)00156-5
Jorgensen M (2005) Evidence-based guidelines for assessment of software development cost uncertainty. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 31:942–954. doi:10.1109/TSE.2005.128
Jorgensen M (2007) Forecasting of software development work effort: evidence on expert judgement and formal models. Int J Forecast 23(3):449–462. doi:10.1016/j.ijforecast.2007.05.008
Jorgensen M, Indahl U, Sjoberg D (2003) Software effort estimation by analogy and “regression toward the mean”. J Syst Softw 68:253–262. doi:10.1016/S0164-1212(03)00066-9
Jun ES, Lee JK (2001) Quasi-optimal case-selective neural network model for software effort estimation. Expert Syst Appl 21:1–14. doi:10.1016/S0957-4174(01)00021-5
Kendall M, Stuart A (1976) The advanced theory of statistics, 4th Edition, Vol. I. Griffin, London
Kirsopp C, Mendes E, Premraj R, Shepperd M (2003) An empirical analysis of linear adaptation techniques for case-based prediction. ICCBR 2003:231–245
Kitchenham BA, Pickard LM, MacDonell SG, Shepperd MJ (2001) What accuracy statistics really measure. IEE Proc Softw 148(3):81–85. doi:10.1049/ip-sen:20010506
Kolodner JL (1993) Case-Based Reasoning. Kaufmann
Lawrence J (1994) Introduction to neural networks: Design, theory, and applications. California Scientific Software, Nevada City, CA
Lee JK, Lee N (2006) Least modification principle for case-based reasoning: a software project planning experience. Expert Syst Appl 30:190–202. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2005.06.021
Li JZ, Ruhe G (2008) Analysis of attribute weighting heuristic for analogy-based software effort estimation method AQUA+. Empir Softw Eng 13(1):63–96. doi:10.1007/s10664-007-9054-4
Li JZ, Ruhe G, Al-Emran A, Richter M (2007) A flexible method for software effort estimation by analogy. Empir Softw Eng 12(1):65–106. doi:10.1007/s10664-006-7552-4
Li YF, Xie M, Goh TN (2008a) A study of project selection and feature weighting for analogy based software cost estimation. J Syst Softw (in press). Accepted Manuscript
Li YF, Xie M, Goh TN (2008b) A study of mutual information based feature selection for case based reasoning in software cost estimation. Expert Syst Appl (in press). Accepted Manuscript
Liu Q, Mintram RC (2005) Preliminary data analysis methods in software estimation. Softw Qual J 13:91–115. doi:10.1007/s11219-004-5262-y
Mair C, Kadoda G, Lefley M, Phalp K, Schofield C, Shepperd M, Webster S (2000) An investigation of machine learning based prediction systems. J Syst Softw 53:23–29. doi:10.1016/S0164-1212(00)00005-4
Maxwell K (2002) Applied statistics for software managers. Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Prentice-Hall
Mendes E, Mosley N, Counsell S (2001) Web metrics—Estimating design and authoring effort. IEEE Multimedia, Special Issue on Web Engineering, 50–57
Mendes E, Watson I, Triggs C, Mosley N, Counsell S (2003) A comparative study of cost estimation models for web hypermedia applications. Empir Softw Eng 8:163–196. doi:10.1023/A:1023062629183
Myrtveit I, Stensrud E (1999) A controlled experiment to assess the benefits of estimating with analogy and regression models. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 25(4):510–525. doi:10.1109/32.799947
Myrtveit I, Stensrud E, Olsson UH (2001) Analyzing data sets with missing data: an empirical evaluation of imputation methods and likelihood-based methods. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 27:999–1013. doi:10.1109/32.965340
Myrtveit I, Stensrud E, Shepperd M (2005) Reliability and validity in comparative studies of software prediction models. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 31(5):380–391. doi:10.1109/TSE.2005.58
Pendharkar PC, Subramanian GH, Rodger JA (2005) A probabilistic model for predicting software development effort. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 31(7):615–624. doi:10.1109/TSE.2005.75
Pickard L, Kitchenham B, Linkman S (2001) Using simulated data sets to compare data analysis techniques used for software cost modeling. IEE Proc Softw 148(6):165–174. doi:10.1049/ip-sen:20010621
Sentas P, Angelis L (2006) Categorical missing data imputation for software cost estimation by multinomial logistic regression. J Syst Softw 79(3):404–414. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2005.02.026
Sentas P, Angelis L, Stamelos I, Bleris G (2005) Software productivity and effort prediction with ordinal regression. Inf Softw Technol 47:17–29. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2004.05.001
Shepperd M, Schofield C (1997) Estimating software project effort using analogies. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 23:736–743. doi:10.1109/32.637387
Shepperd M, Kadoda G (2001) Comparing software prediction techniques using simulation. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 27(11):1014–1022. doi:10.1109/32.965341
Song QB, Shepperd M (2007) A new imputation method for small software project data sets. J Syst Softw 80:51–62. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2006.05.003
Srinivasan R, Fisher D (1995) Machine learning approaches to estimating software development effort. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 21(2):126–137. doi:10.1109/32.345828
Stensrud E (2001) Alternative approaches to effort prediction of ERP projects. Inf Softw Technol 43(7):413–423. doi:10.1016/S0950-5849(01)00147-1
Stensrud E, Foss T, Kitchenham B, Myrtveit I (2003) A further empirical investigation of the relationship between MRE and project size. Empir Softw Eng 8(2):139–161. doi:10.1023/A:1023010612345
Strike K, El-Emam K, Madhavji N (2001) Software cost estimation with incomplete data. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 27(10):890–908. doi:10.1109/32.962560
Van Koten C, Gray AR (2006) Bayesian statistical effort prediction models for data-centred 4GL software development. Inf Softw Technol 48:1056–1067. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2006.01.001
Vapnik V (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Walkerden F, Jeffery DR (1999) An empirical study of analogy-based software effort Estimation. Empir Softw Eng 4(2):135–158. doi:10.1023/A:1009872202035
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful and constructive comments. This research was partially supported by a grant from A*Star (SERC grant number 072 1340050) in Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor:Emilia Mendes, PhD
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y.F., Xie, M. & Goh, T.N. A study of the non-linear adjustment for analogy based software cost estimation. Empir Software Eng 14, 603–643 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-008-9104-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-008-9104-6