Abstract
Variants of adaptation techniques have been proposed in previous studies to improve the performance of analogy-based effort estimation. The results of these studies are often contradictory and cannot simply be generalized because there are many uncontrollable source of variations between adaptation studies. The study presented in this paper has been carried out in order to replicate the assessment and comparison of different adaptation techniques utilised in analogy-based software effort prediction. Empirical evaluation of variants of adaptation techniques with Jack-knifing procedure have been carried out. Seven datasets come from PROMISE data repository were used for benchmarking. The results are also investigated within the presence/absence of feature subset selection algorithm. The current study permitted us to discover that linear adjustment approaches are more accurate than nonlinear adjustment because of the nature of the employed datasets that have, in most cases, normality characteristics.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
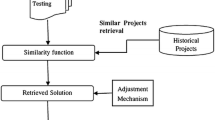
All datasets used in this study are available on PROMISE website(http://www.promisedata.org)
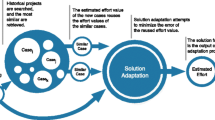
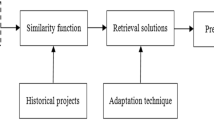
Local similarity degree can be measured based on single feature, while global can be measured by aggregating all local similarity degrees.
\( {\text{PRED = }}100 \times (\lambda /n) \) is used to count the percentage of estimates that have magnitude relative error less than 25%., where \( \lambda \) is the number of projects where magnitude relative error less than or equal 25%., and n is the number of all
References
Albrecht AJ, Gaffney J (1983) Software function, source lines of code, and development effort prediction. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 9:639–648
Angelis L, Stamelos I (2000) A simulation tool for efficient analogy based cost estimation. Empir Softw Eng 5:35–68
Auer M, Trendowicz A, Graser B, Haunschmid E, Biffl S (2006) Optimal project feature weights in analogy-based cost estimation: Improvement and limitations. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 32:83–92
Azzeh M, Neagu D, Cowling P (2008) Fuzzy feature subset selection for software effort estimation, in proceedings of international workshop on software predictors PROMISE’08. Leipzig, Germany, pp 71–78
Azzeh M, Neagu D, Cowling P (2010) Fuzzy grey relational analysis for software effort estimation. Empir Softw Eng 15:60–90
Boehm B (1981) Software engineering economics. Prentice-Hall, NY
Boetticher G, Menzies T, Ostrand T (2010) PROMISE Repository of empirical software engineering data http://promisedata.org/ repository, West Virginia University, Department of Computer Science
Briand LC, El-Emam K, Surmann D, Wieczorek I, Maxwell KD (1999) An assessment and comparison of common cost estimation modeling techniques. Proceeding of the 1999 International Conference on Software Engineering, pp 313–322
Chen Z, Menzies T, Port D, Boehm B (2005) Feature subset selection can improve software effort estimation accuracy, in proceedings of workshop predictor models in software engineering PROMISE’05. ACM, St. Louis, pp 1–6
Chiu NH, Huang SJ (2007) The adjusted analogy-based software effort estimation based on similarity distances. J Syst Softw 80:628–640. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2006.06.006
Desharnais JM (1989) Analyse statistique de la productivitie des projets informatique a partie de la technique des point des foncti on. University of Montreal
Foss T, Stensrud E, Kitchenham B, Myrtveit I (2003) A simulation study of the model evaluation criterion MMRE. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 29:985–995
Idri A, Abran A, Khoshgoftaar T (2001) Fuzzy Analogy: a New Approach for Software Effort Estimation, In: 11th International Workshop in Software Measurements, pp 93–101
ISBSG (2007) International software benchmark and standard group, Data CDRelease 10, www.isbsg.org, 2007
Jeffery R, Ruhe M, Wieczorek I (2001) Using public domain metrics to estimate software development effort. Proceedings Seventh International Software Metrics Symposium, pp 16–27
Jorgensen M, Indahl U, Sjoberg D (2003) Software effort estimation by analogy and “regression toward the mean”. J Syst Softw 68:253–262
Kemerer CF (1987) An empirical validation of software cost estimation models, Comm. ACM 30:416–429
Keung J, Kitchenham B, Jeffery DR (2008) Analogy-X: providing statistical inference to analogy-based software cost estimation. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 34(4):471–484
Kirsopp C, Mendes E, Premraj R, Shepperd M (2003) An empirical analysis of linear adaptation techniques for case-based prediction. International Conference on CBR. pp 231–245
Kocaguneli E, Menzies T, Bener A, Keung J (2011) Exploiting the Essential Assumptions of Analogy-based Effort Estimation, IEEE transaction on Software Engineering. ISSN: 0098-5589
Li JZ, Ruhe G, Al-Emran A, Richter M (2007) A flexible method for software effort estimation by analogy. Empir Softw Eng 12(1):65–106
Li YF, Xie M, Goh TN (2009) A study of the non-linear adjustment for analogy based software cost estimation. Empir Softw Eng 14:603–643
Maxwell K (2002) Applied statistics for software managers. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Mendes E, Mosley N, Counsell S (2003a) A replicated assessment of the use of adaptation rules to improve Web cost estimation, International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering, pp 100–109
Mendes E, Watson I, Triggs C, Mosley N, Counsell S (2003b) A comparative study of cost estimation models for web hypermedia applications. Empir Softw Eng 8:163–196
Menzies T, Chen Z, Hihn J, Lum K (2006) Selecting best practices for effort estimation. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 32:883–895
Miller J (2005) Replicating software engineering experiments: a poisoned chalice or the Holy Grail? Inf Softw Technol 47:233–244
Myrtveit I, Stensrud E, Shepperd M (2005) Reliability and validity in comparative studies of software prediction models. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 31(5):380–391
Shepperd M, Cartwright M (2005) A Replication of the Use of Regression towards the Mean (R2M) as an Adjustment to Effort Estimation Models, 11th IEEE International Software Metrics Symposium (METRICS’05), p 38
Shepperd M, Kadoda G (2001) Comparing software prediction techniques using simulation. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 27(11):1014–1022
Shepperd M, Schofield C (1997) Estimating software project effort using analogies. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 23:736–743
Walkerden F, Jeffery DR (1999) An empirical study of analogy-based software effort Estimation. Empir Softw Eng 4(2):135–158
Acknowledgement
The author is grateful to the Applied Science Private University, Amman, Jordan, for the financial support granted to this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editors: Martin Shepperd and Tim Menzies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azzeh, M. A replicated assessment and comparison of adaptation techniques for analogy-based effort estimation. Empir Software Eng 17, 90–127 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-011-9176-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-011-9176-6