Abstract
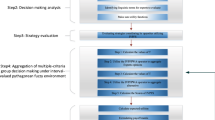
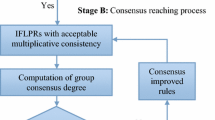
The aim of the paper is to solve the group decision making problems which contain inconsistent probabilistic linguistic preference relations (PLPRs) and unknown expert weights. When the PLPRs are inconsistent, there are contradictories in the preference relations expressed by the experts. The evaluation value with contradictory information will bring out an incorrect consequence in decision making. Hence, this paper develops a novel consistency measure method to gauge the consistency level of PLPRs. Moreover, a nonlinear optimization model is newly constructed to optimize the inconsistent PLPRs. The proposed methods overcome the limitations in the existing methods and ameliorate the interpretation and complexities of inconsistency PLPRs revise strategies. Additionally, a weighting method using fuzzy cooperative games with PLPRs is put forward to derive the weight vector of experts. It helps to balance the deviations between the individual PLPRs and the group PLRP. At last, a numerical example illustration for physician selection is put forward to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model and its practical applicability. The comparative analysis gives deep insights into the rationality of the proposed model.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong, Y. C., Xu, Y. F., & Li, H. Y. (2008). On consistency measures of linguistic preference relations. European Journal of Operational Research, 189(2), 430–444.
Gao, J., Xu, Z. S., Liang, Z. L., & Liao, H. C. (2019). Expected consistency-based emergency decision making with incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Knowledge-Based Systems, 176, 15–28.
Gao, J. W., Yang, X. F., & Liu, D. (2017). Uncertain Shapley value of coalitional game with application to supply chain alliance. Applied Soft Computing, 56, 551–556.
Herrera, F., & Martinez, L. (2000). A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 8(6), 746–752.
Li, B., Zhang, Y. X., & Xu, Z. S. (2019). The aviation technology two-sided matching with the expected time based on the probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Journal of the Operations Research Society of China. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40305-019-00274-9.
Liao, H. C., Jiang, L. S., Xu, Z. S., Xu, J. P., & Herrera, F. (2017). A linear programming method for multiple criteria decision making with probabilistic linguistic information. Information Sciences, 415–416, 341–355.
Liao, H. C., Mi, X. M., & Xu, Z. S. (2019). A survey of decision-making methods with probabilistic linguistic information: bibliometrics, preliminaries, methodologies, applications and future directions. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-019-09309-5.
Liao, H. C., Xu, Z. S., Zeng, X. J., & Merigó, J. M. (2015). Qualitative decision making with correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Knowledge-Based Systems, 76, 127–138.
Luo, S. Z., Zhang, H. Y., Wang, J. Q., & Li, L. (2019). Group decision-making approach for evaluating the sustainability of constructed wetlands with probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 70(12), 2039–2055.
Neumann, J. V., & Morgenstern, O. (1944). The theory of games and economic behaviour, No. 1 (Vol. 26, pp. 131–141). Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Nie, R. X., & Wang, J. Q. (2019). Prospect theory-based consistency recovery strategies with multiplicative probabilistic linguistic preference relations in managing group decision making. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04053-9.
Pang, Q., Wang, H., & Xu, Z. S. (2016). Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Information Sciences, 369, 128–143.
Peng, H. G., Zhang, H. Y., & Wang, J. Q. (2018). Cloud decision support model for selecting hotels on TripAdvisor.com with probabilistic linguistic information. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 68, 124–138.
Rodriguez, R. M., Martinez, L., & Herrera, F. (2012). Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 20(1), 109–119.
Shapley, L. S. (1953). A value for n-person games. Contributions to the Theory of Games, 2(28), 307–317.
Sun, R. X., Hu, J. H., Zhou, J. D., & Chen, X. H. (2018). A hesitant fuzzy linguistic projection-based MABAC method for patients’ prioritization. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 20(7), 2144–2160.
Tao, Z. F., Liu, X., Chen, H. Y., & Chen, Z. Q. (2015). Group decision making with fuzzy linguistic preference relations via cooperative games method. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 83, 184–192.
Xiao, F., & Wang, J. Q. (2019). Multistage decision support framework for sites selection of solar power plants with probabilistic linguistic information. Journal of Cleaner Production, 230, 1396–1409.
Xie, W. Y., Xu, Z. S., & Ren, Z. L. (2019). An analysis on the influence of Chinese “new four inventions” under the incomplete hybrid probabilistic linguistic environment. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 21(5), 1349–1366.
Xu, Z. S., He, Y., & Wang, X. Z. (2019). An overview of probabilistic-based expressions for qualitative decision-making: Techniques, comparisons and developments. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 10(6), 1513–1528.
Yang, Y., Hu, J. H., An, Q. X., & Chen, X. H. (2017). Group decision making with multiplicative triangular hesitant fuzzy preference relations and cooperative games method. International Journal for Uncertainty Quantification, 7(3), 271–284.
Zadeh, L. A. (1974). The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. In K. S. Fu & J. T. Tou (Eds.), Learning systems and intelligent robots (pp. 1–10). Boston, MA: Springer, us.
Zhang, Y. X., Xu, Z. S., Wang, H., & Liao, H. C. (2016). Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Applied Soft Computing, 49, 817–833.
Zhou, H., Ma, X. Y., Zhou, L. G., Chen, H. Y., & Ding, W. R. (2018). A novel approach to group decision-making with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations via shapley value. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 20(4), 1172–1187.
Zhu, B., & Xu, Z. S. (2014). Consistency measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 22(1), 35–45.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported partially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71871229, 71771219 and 91846301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not required as no human or animals were involved.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, P., Hu, J., Li, B. et al. A group decision making with probability linguistic preference relations based on nonlinear optimization model and fuzzy cooperative games. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 19, 499–528 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-020-09329-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-020-09329-6