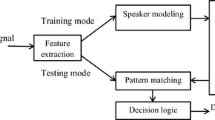
Abstract
This paper presents two pre-processing methods that can be implemented for noise reduction in speaker recognition systems. These methods are adaptive noise canceller (ANC) and Savitzky-Golay (SG) filter. Also, discrete cosine transform (DCT), discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and discrete sine transform (DST) are considered for consistent feature extraction from noisy speech signals. A neural network with only one hidden layer is used as a classifier. The performances of the proposed noise reduction methods are compared with those of a hybrid method that comprises empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and spectral subtraction and also with spectral subtraction method only. Recognition rate is taken as a performance metric to evaluate the behavior of the system with these enhancement strategies. Simulation results prove that the DCT is the optimum transform with the suggested methods, while the DWT is the best one with the hybrid method and the spectral subtraction method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Samie, F.E. (2011). El-Samie ‘information security for automatic speaker identification. Springer Briefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering.
Alotaiby, T., Alshebeili, S.A., Alshawi, T., Ahmad, I., Abd El-Samie, F.E. (2014). EEG seizure detection and prediction algorithms: A survey. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing.
Anand, V., Shah, S., Kumar, S. (2013). Intelligent adaptive filtering for noise cancellation. International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering 2.
Awal, Md A, Mostafa, S. S., & Ahmad, M. (2011). Performance analysis of savitzky-golay smoothing filter using ECG signal. IJCIT,01, 90–95.
Campbell, J.P. (1997). Speaker recognition: A tutorial, Senior Member, IEEE. In Proceedings of IEEE, Vol. 85.
Das, A., Jena, M. R., & Barik, K. K. (2014). Mel-frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC)—A novel method for speaker recognition. Digital Technologies,1(1), 1–3.
Dhubkarya, D. C., Katara, A., & Thenua, R. K. (2012). Simulation of adaptive noise canceller for an ECG signal analysis. International Journal on Signal & Image Processing,03(01), 1–12.
Dreyfus, G. (2005). Neural networks: Methodology and applications (pp. 1–83). Berlin: Springer.
El-Moneim, S. A., Dessouky, M. I., Nassar, M. A., El-Naby, M. A., & Abd El-Samie, F. E. (2015). Hybrid speech enhancement with empirical mode decomposition and spectral subtraction for efficient speaker identification. International Journal of Speech Technology,2015(18), 555–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-015-9293-5.
Evans, N.W.D., Mason, J.S., Liu, W.M. and Fauve, B. (2006). An assessment on the fundamental limitations of spectral subtraction. In IEEE (pp. 145–148).
Fisusi, A.A., Yesufu, T.K. (2007). Speaker recognition systems: A tutorial. African Journal of Information and Communication Technology, 3(2).
Furui, S. (1981). Cepstral analysis technique for automatic speaker verification. IEEE Transactions of Acoustics, and Signal Processing,29(2), 254–272.
Galushkin, A. I. (2007). Neural network theory. Berlin: Springer.
Guiñón, J. L. et al. (2007). Moving average and savitzki-golay smoothing filters using mathcad. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Education—ICEE.
Hossain, M.M., Ahmed, B. and Asrafi, M. (2007). A real time speaker identification using artificial neural network, conference: Computer and information technology, IEEE.
Jafari, M.G., and Chambers, J.A. (2003). Adaptive noise cancellation and blind source separation. In 4th International symposium on independent component analysis and blind signal separation (pp. 627–632).
Kaladharan, N. (2014). Speech enhancement by spectral subtraction method. International Journal of Computer Applications,96(13), 45–48.
Karam, M., Khazaal, H. F., Aglan, H., & Cole, C. (2014). Noise removal in speech processing using spectral subtraction. Journal of Signal and Information Processing,5, 32–41.
Kim, D., & Oh, H.-S. (2009). EMD: A package for empirical mode decomposition and hilbert spectrum. The R Journal,1(1), 40–46.
Love, B.J., Vining, J., Sun, X. (2004). Automatic speaker recognition using neural network, intro (pp. 1–25). Neural Networks Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, The University of Texas at Austin, Spring.
Muda, L., Begam, M., & Elamvazuthi, I. (2010). Voice recognition algorithms using mel frequency cepstral coefficient (MFCC) and dynamic time warping (DTW) techniques. Journal of Computing,2, 138–143.
Nasr, Marwa A., et al. (2018). Speaker identification based on normalized pitch frequency and Mel frequency cepstral coefficients. International Journal of Speech Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9524-7.
Pawar, A.P., Choudhari, K.B. (2013). Enhancement of speech in noisy conditions. The International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, 2(7).
Reynolds, D.A. (2002). An overview of automatic speaker recognition technology. IEEE, pp. 4072–4075.
Rilling, G., Flandrin, P. and Goncalves, P. (2003). On empirical mode decomposition and its algorithms. In IEEE-EURASIP workshop on nonlinear signal and image processing.
Schafer, R.W. (2011). What is a Savitzky-Golay filter. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine.
Shajeesh, K. U., Sachin Kumar, S., & Soman, K. P. (2012). A two stage algorithm for denoising of speech signal. IOSR. Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSRJCE),8, 48–53.
Shanmugam, A., et al. (2013a). Adaptive noise cancellation for speech processing in real time environment. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA),3(2), 1102–1106.
Shanmugam, et al. (2013b). Adaptive noise cancellation for speech processing in real time environment. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA),3, 1102–1106.
Sharma, A., Singh, S. P., & Kumar, V. (2005). Text-independent speaker identification using backpropagation MLP network classifier for a closed set of speakers (pp. 665–669). IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology: INDIA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Moneim, S.A., EL-Rabaie, ES.M., Nassar, M.A. et al. Speaker recognition based on pre-processing approaches. Int J Speech Technol 23, 435–442 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-019-09659-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-019-09659-w