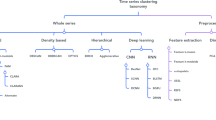
Abstract
Audio signal processing is the most challenging field in the current era for an analysis of an audio signal. Audio signal classification (ASC) comprises of generating appropriate features from a sound and utilizing these features to distinguish the class the sound is most likely to fit. Based on the application’s classification domain, the characteristics extraction and classification/clustering algorithms used may be quite diverse. The paper provides the survey of the state-of art for understanding ASC’s general research scope, including different types of audio; representation of audio like acoustic, spectrogram; audio feature extraction techniques like physical, perceptual, static, dynamic; audio pattern matching approaches like pattern matching, acoustic phonetic, artificial intelligence; classification, and clustering techniques. The aim of this state-of-art paper is to produce a summary and guidelines for using the broadly used methods, to identify the challenges as well as future research directions of acoustic signal processing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulsalam, A. A. (2017). Audio classification based on content features. Journal of College of Education for Women, 28(5), 1415–1423.
Adavanne, S., Drossos, K., Çakir, E., & Virtanen, T. (2017a). Stacked convolutional and recurrent neural networks for bird audio detection. In 2017 25th European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 1729–1733). Kos: IEEE.
Adavanne, S., Parascandolo, G., Pertilä, P., Heittola, T., & Virtanen, T. (2017b). Sound event detection in multichannel audio using spatial and harmonic features. http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02293.
Adavanne, S., & Virtanen, T. (2017). A report on sound event detection with different binaural features. http://arxiv.org/abs/1710.02997.
Ahmad, S., Agrawal, S., Joshi, S., Taran, S., Bajaj, V., Demir, F., et al. (2020). Environmental sound classification using optimum allocation sampling based empirical mode decomposition. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 537, 122613.
Al Maathidi, M. M. (2017). Optimal feature selection and machine learning for high-level audio classification-a random forests approach. Doctoral dissertation, University of Salford.
Alam, M. J., Kenny, P., Bhattacharya, G., & Stafylakis, T. (2015). Development of CRIM system for the automatic speaker verification spoofing and countermeasures challenge 2015. In Sixteenth annual conference of the international speech communication association.
AlHanai, T. W., & Ghassemi, M. M. (2017). Predicting latent narrative mood using audio and physiologic data. In Thirty-first AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
Al-Hussaini, I., Humayun, A. I., Alam, S., Foysal, S. I., Al Masud, A., Mahmud, A., Chowdhury, R. I., Ibtehaz, N., Zaman, S. U., Hyder, R., & Chowdhury, S. S. (2018). Predictive real-time beat tracking from music for embedded application. In 2018 IEEE Conference on multimedia information processing and retrieval (MIPR) (pp. 297–300). Miami: IEEE.
Ali, M., Mosa, A.H., Al Machot, F., & Kyamakya, K. (2018a). Emotion recognition involving physiological and speech signals: A comprehensive review. In Recent advances in nonlinear dynamics and synchronization (pp. 287–302). Cham: Springer.
Ali, H., Tran, S. N., Benetos, E., & Garcez, A. S. D. A. (2018b). Speaker recognition with hybrid features from a deep belief network. Neural Computing and Applications, 29(6), 13–19.
Alías, F., Socoró, J. C., & Sevillano, X. (2016). A review of physical and perceptual feature extraction techniques for speech, music and environmental sounds. Applied Sciences, 6(5), 143–186.
Aljanaki, A., & Soleymani, M. (2018). A data-driven approach to mid-level perceptual musical feature modeling. http://arxiv.org/abs/1806.04903.
Almaadeed, N., Asim, M., Al-Maadeed, S., Bouridane, A., & Beghdadi, A. (2018). Automatic detection and classification of audio events for road surveillance applications. Sensors, 18(6), 1858.
Al-Maathidi, M. M., & Li, F. F. (2015). Audio content feature selection and classification a random forests and decision tree approach. In 2015 IEEE International conference on progress in informatics and computing (PIC) (pp. 108–112). Nanjing: IEEE.
Al-Nasheri, A., Muhammad, G., Alsulaiman, M., Ali, Z., Malki, K. H., Mesallam, T. A., et al. (2017). Voice pathology detection and classification using auto-correlation and entropy features in different frequency regions. IEEE Access, 6, 6961–6974.
Al-Noori, A., Li, F. F., & Duncan, P. J. (2016). Robustness of speaker recognition from noisy speech samples and mismatched languages. In Audio engineering society convention 140. Audio Engineering Society.
Alsaadan, H. (2017). Adaptive audio classification framework for in-vehicle environment with dynamic noise characteristics. Doctoral dissertation, South Dakota State University.
Al-Shoshan, A. I. (2016). A classification of an audio signal using the wold-cramer decomposition. In Advanced computer and communication engineering technology (pp. 473–479). Cham: Springer.
Andersen, K. T., & Moonen, M. (2016). Adaptive time-frequency analysis for noise reduction in an audio filter bank with low delay. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 24(4), 784–795.
Apopei, V. (2015). Detection dangerous events in environmental sounds-a preliminary evaluation. In 2015 International conference on speech technology and human-computer dialogue (SpeD) (pp. 1–5). Bucharest: IEEE.
Arora, V., & Behera, L. (2015). Multiple F0 estimation and source clustering of polyphonic music audio using PLCA and HMRFs. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 23(2), 278–287.
Arumugam, M., & Kaliappan, M. (2018). Feature selection based on MBFOA for audio signal classification under consideration of Gaussian white noise. IET Signal Processing, 12(6), 777–785.
Aryafar, K., & Shokoufandeh, A. (2014). Multimodal music and lyrics fusion classifier for artist identification. In 2014 13th international conference on machine learning and applications (pp. 506–509). Detroit: IEEE.
Ashraf, M., Guohua, G., Wang, X., & Ahmad, F. (2018). Integration of speech/music discrimination and mood classification with audio feature extraction. In 2018 International conference on frontiers of information technology (FIT) (pp. 224–229). Islamabad: IEEE.
Awad, A. (2019). Impulse noise reduction in audio signal through multi-stage technique. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 22(2), 629–636.
Awasthi, D., & Madhe, S. (2015). Analysis of encrypted ECG signal in steganography using wavelet transforms. In 2015 2nd international conference on electronics and communication systems (ICECS) (pp. 718–723). Coimbatore: IEEE.
Aydoğmuş, H. (2018). Multimode microwave sensors for microdroplet and single-cell detection. Doctoral dissertation, Bilkent University.
Bach, J. H., Kollmeier, B., & Anemüller, J. (2017). Matching pursuit analysis of auditory receptive fields’ spectro-temporal properties. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 11, 4.
Bäckström, T. (2017). Speech coding: With code-excited linear prediction. Berlin: Springer.
Badino, L., Canevari, C., Fadiga, L., & Metta, G. (2014). An auto-encoder based approach to unsupervised learning of subword units. In 2014 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 7634–7638). Florence: IEEE.
Bae, S.H., Choi, I., & Kim, N.S. (2016). Acoustic scene classification using parallel combination of LSTM and CNN. In Proceedings of the detection and classification of acoustic scenes and events 2016 workshop (DCASE2016) (pp. 11–15).
Bahuleyan, H. (2018). Music genre classification using machine learning techniques. http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.01149.
Bai, O., Lin, P., Vorbach, S., Floeter, M. K., Hattori, N., & Hallett, M. (2007). A high performance sensorimotor beta rhythm-based brain–computer interface associated with human natural motor behavior. Journal of Neural Engineering, 5(1), 24–35.
Baker, M., Cox, A., Paumgarten, M., & Govil, A. (2017). Directional audio technique.
Banerjee, A., Ghosh, A., Palit, S., & Ballester, M.A.F. (2018). A novel approach to string instrument recognition. In International conference on image and signal processing (pp. 165–175). Cham: Springer.
Barker, T., & Virtanen, T. (2016). Blind separation of audio mixtures through nonnegative tensor factorization of modulation spectrograms. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 24(12), 2377–2389.
Baum, E., Harper, M., Alicea, R., & Ordonez, C. (2018). Sound identification for fire-fighting mobile robots. In 2018 Second IEEE international conference on robotic computing (IRC) (pp. 79–86). Laguna Hills: IEEE.
Beauregard, G.T., Harish, M., & Wyse, L. (2015). Single pass spectrogram inversion. In 2015 IEEE international conference on digital signal processing (DSP) (pp. 427–431). Singapore: IEEE.
Becker, S., Ackermann, M., Lapuschkin, S., Müller, K. R., & Samek, W. (2018). Interpreting and explaining deep neural networks for classification of audio signals. http://arxiv.org/abs/1807.03418.
Bhakre, S. K., & Bang, A. (2016). Emotion recognition on the basis of audio signal using naive bayes classifier. In 2016 International conference on advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI) (pp. 2363–2367). Jaipur: IEEE.
Bhalke, D. G., Rajesh, B., & Bormane, D. S. (2017). Automatic genre classification using fractional fourier transform based mel frequency cepstral coefficient and timbral features. Archives of Acoustics, 42(2), 213–222.
Bhalke, D. G., Rao, C. R., & Bormane, D. S. (2016). Automatic musical instrument classification using fractional fourier transform based-MFCC features and counter propagation neural network. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 46(3), 425–446.
Bhaskar, J., Sruthi, K., & Nedungadi, P. (2015). Hybrid approach for emotion classification of audio conversation based on text and speech mining. Procedia Computer Science, 46, 635–643.
Bhatia, R., Srivastava, S., Bhatia, V., & Singh, M. (2018). Analysis of audio features for music representation. In 2018 7th international conference on reliability, infocom technologies and optimization (trends and future directions)(ICRITO) (pp. 261–266). Noida: IEEE.
Bhattacharjee, M., Prasanna, S. R. M., & Guha, P. (2018). Time-frequency audio features for speech-music classification. http://arxiv.org/abs/1811.01222.
Bi, Y., Reid, T., & Davies, P. (2017). An exploratory study on proposed new sounds for future products. Noise Control Engineering Journal, 65(3), 244–260.
Bietti, A., Bach, F., & Cont, A. (2015). An online EM algorithm in hidden (semi-) Markov models for audio segmentation and clustering. In 2015 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1881–1885). Brisbane: IEEE.
Bisot, V., Serizel, R., Essid, S., & Richard, G. (2016). Acoustic scene classification with matrix factorization for unsupervised feature learning. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6445–6449). Shanghai: IEEE.
Bittner, R. M., Salamon, J., Bosch, J. J., & Bello, J. P. (2017). Pitch contours as a mid-level representation for music informatics. In Audio engineering society conference: 2017 AES international conference on semantic audio. Audio Engineering Society.
Black, M., Katsamanis, A., Lee, C. C., Lammert, A. C., Baucom, B. R., Christensen, A., Georgiou, P. G., & Narayanan, S. S. (2010). Automatic classification of married couples’ behavior using audio features. In Eleventh annual conference of the international speech communication association.
Böck, S., Korzeniowski, F., Schlüter, J., Krebs, F., & Widmer, G. (2016a). Madmom: A new python audio and music signal processing library. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 1174–1178). Amsterdam: ACM.
Böck, S., Krebs, F., & Widmer, G. (2016b). Joint beat and downbeat tracking with recurrent neural networks. In ISMIR (pp. 255–261).
Bohak, C., & Marolt, M. (2016). Probabilistic segmentation of folk music recordings. Mathematical problems in engineering, 2016.
Borde, P., Varpe, A., Manza, R., & Yannawar, P. (2015). Recognition of isolated words using Zernike and MFCC features for audio visual speech recognition. International Journal of Speech Technology, 18(2), 167–175.
Borg, A., & Micallef, P. (2015). A non-parametric based mapping algorithm for use in audio fingerprinting. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, International Journal of Computer, Electrical, Automation, Control and Information Engineering, 9(4), 918–921.
Bugdol, M. D., Bugdol, M. N., Lipowicz, A. M., Mitas, A. W., Bienkowska, M. J., & Wijata, A. M. (2018). Prediction of menarcheal status of girls using voice features. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 100, 296–304.
Burred, J. J., & Lerch, A. (2004). Hierarchical automatic audio signal classification. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 52(7/8), 724–739.
Caesarendra, W., & Tjahjowidodo, T. (2017). A review of feature extraction methods in vibration-based condition monitoring and its application for degradation trend estimation of low-speed slew bearing. Machines, 5(4), 21.
Caetano, M., Saitis, C., & Siedenburg, K. (2019). Audio content descriptors of timbre. In Timbre: Acoustics, perception, and cognition (pp. 297–333). Cham: Springer.
Camarena-Ibarrola, A., Luque, F., & Chavez, E. (2017). Speaker identification through spectral entropy analysis. In 2017 IEEE international autumn meeting on power, electronics and computing (ROPEC) (pp. 1–6). Ixtapa: IEEE.
Cameron, D., Potter, K., Wiggins, G., & Pearce, M. (2017). Perception of rhythmic similarity is asymmetrical, and is influenced by musical training, expressive performance, and musical context. Timing & Time Perception, 5(3–4), 211–227.
Canadas-Quesada, F. J., Vera-Candeas, P., Ruiz-Reyes, N., Munoz-Montoro, A., & Bris-Penalver, F. J. (2016). A method to separate musical percussive sounds using chroma spectral flatness. In SIGNAL 2016 editors, p. 51.
Cao, J., Cao, M., Wang, J., Yin, C., Wang, D., & Vidal, P. P. (2019). Urban noise recognition with convolutional neural network. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 78(20), 29021–29041.
Carlin, M. A., & Elhilali, M. (2015). A framework for speech activity detection using adaptive auditory receptive fields. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 23(12), 2422–2433.
Chandrakala, S., & Jayalakshmi, S. L. (2019a). Environmental audio scene and sound event recognition for autonomous surveillance: A survey and comparative studies. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 52(3), 63.
Chandrakala, S., & Jayalakshmi, S. L. (2019b). Environmental audio scene and sound event recognition for autonomous surveillance: A survey and comparative studies. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR). https://doi.org/10.1145/3322240.
Chatterjee, A., & Yasmin, G. (2019). Human emotion recognition from speech in audio physical features. In Applications of computing, automation and wireless systems in electrical engineering (pp. 817–824). Singapore: Springer.
Cheffena, M. (2015). Fall detection using smartphone audio features. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 20(4), 1073–1080.
Cheng, C. F., Rashidi, A., Davenport, M. A., & Anderson, D. V. (2017). Activity analysis of construction equipment using audio signals and support vector machines. Automation in Construction, 81, 240–253.
Cho, J., Pappagari, R., Kulkarni, P., Villalba, J., Carmiel, Y., & Dehak, N. (2019). Deep neural networks for emotion recognition combining audio and transcripts. http://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00432.
Chourdakis, E., Ward, L., Paradis, M., & Reiss, J.D. (2019). Modelling experts’ decisions on assigning narrative importances of objects in a radio drama mix.
Chouvardas, S., Muma, M., Hamaidi, K., Theodoridis, S., & Zoubir, A. M. (2015). Distributed robust labeling of audio sources in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. In 2015 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 5783–5787). Brisbane: IEEE.
Chrupała, G., Gelderloos, L., & Alishahi, A. (2017). Representations of language in a model of visually grounded speech signal. http://arxiv.org/abs/1702.01991.
Collins, N. (2015). The UbuWeb electronic music corpus: An MIR investigation of a historical database. Organised Sound, 20(1), 122–134.
Colonna, J. G., Gama, J., & Nakamura, E. F. (2016). How to correctly evaluate an automatic bioacoustics classification method. In Conference of the Spanish association for artificial intelligence (pp. 37–47). Cham: Springer.
Corrêa, D. C., & Rodrigues, F. A. (2016). A survey on symbolic data-based music genre classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 60, 190–210.
Correya, A. A., Hennequin, R., & Arcos, M. (2018). Large-scale cover song detection in digital music libraries using metadata, lyrics and audio features. http://arxiv.org/abs/1808.10351.
Cuccovillo, L., & Aichroth, P. (2017). Increasing the temporal resolution of ENF analysis via harmonic distortion. In Audio engineering society conference: 2017 AES international conference on audio forensics. Audio Engineering Society.
Cummins, N., Amiriparian, S., Hagerer, G., Batliner, A., Steidl, S., & Schuller, B. W. (2017). An image-based deep spectrum feature representation for the recognition of emotional speech. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 478–484). Mountain View: ACM.
Czúni, L., & Varga, P. Z. (2017). Time domain audio features for chainsaw noise detection using WSNs. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(9), 2917–2924.
Dalir, A., Beheshti, A. A., & Masoom, M. H. (2018). Classification of vehicles based on audio signals using quadratic discriminant analysis and high energy feature vectors. http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.01212.
Dandashi, A., & AlJaam, J. (2017). A survey on audio content-based classification. In 2017 International conference on computational science and computational intelligence (CSCI) (pp. 408–413). Las Vegas: IEEE.
Dandawate, Y. H., Kumari, P., & Bidkar, A. (2015). Indian instrumental music: Raga analysis and classification. In 2015 1st international conference on next generation computing technologies (NGCT) (pp. 725–729). Dehradun: IEEE.
Daqrouq, K., & Tutunji, T. A. (2015). Speaker identification using vowels features through a combined method of formants, wavelets, and neural network classifiers. Applied Soft Computing, 27, 231–239.
Darji, M. C., Patel, N. M., & Shah, Z. H. (2015). Extraction of video songs from movies using audio features. In 2015 International symposium on advanced computing and communication (ISACC) (pp. 60–64). Silchar: IEEE.
Dave, N. (2013). Feature extraction methods LPC, PLP and MFCC in speech recognition. International Journal for Advance Research in Engineering and Technology, 1(6), 1–4.
Davis, A., & Agrawala, M. (2018). Visual rhythm and beat. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 37(4), 1221–12211.
Demirel, E., Bozkurt, B., & Serra, X. (2018). Automatic Makam recognition using chroma features. In Holzapfel, A., & Pikrakis, A. (eds.) Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on folk music analysis; 2018 Jun 26-29; Thessaloniki, Greece (pp. 19–24). Greece: Aristotle University of Thessaloniki.
Demirel, E., Bozkurt, B., & Serra, X. (2019). Automatic chord-scale recognition using harmonic pitch class profiles. In Barbancho, I., Tardón, L. J., Peinado, A., Barbancho, A. M. (eds.), Proceedings of the 16th sound & music computing conference; 2019 May 28–31; Málaga, Spain.[Málaga]: SMC; 2019. Sound & Music Computing Conference.
Devi, A., & ShivaKumar, K. B. (2016). Novel audio steganography technique for ECG signals in point of care systems (NASTPOCS). In 2016 IEEE international conference on cloud computing in emerging markets (CCEM) (pp. 101–106). Bangalore: IEEE.
Dey, N. (Ed.). (2019). Intelligent speech signal processing. New York: Academic Press.
Dey, N., & Ashour, A. (Eds.). (2016). Classification and clustering in biomedical signal processing. Hershey: IGI global.
Dey, N., & Ashour, A. S. (2018). Direction of arrival estimation and localization of multi-speech sources. Berlin: Springer International Publishing.
Dey, N., Ashour, A. S., & Borra, S. (Eds.). (2017). Classification in BioApps: Automation of decision making (Vol. 26). Berlin: Springer.
Dimaunahan, E. D., Ballado, A. H., Cruz, F. R. G., & Cruz, J. C. D. (2017). MFCC and VQ voice recognition based ATM security for the visually disabled. In 2017IEEE 9th international conference on humanoid, nanotechnology, information technology, communication and control, environment and management (HNICEM) (pp. 1–5). Manila: IEEE.
Diment, A., Cakir, E., Heittola, T., & Virtanen, T. (2015). Automatic recognition of environmental sound events using all-pole group delay features. In 2015 23rd European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 729–733). Nice: IEEE.
Djebbar, F., & Ayad, B. (2017). Energy and entropy based features for WAV audio steganalysis. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing. https://doi.org/10.1177/0020720918787456.
Doherty, J., Curran, K., & McKevitt, P. (2017). Streaming audio using MPEG-7 audio spectrum envelope to enable self-similarity within polyphonic audio. Telkomnika, 15(1), 190.
Dominguez-Morales, J. P., Jimenez-Fernandez, A., Rios-Navarro, A., Cerezuela-Escudero, E., Gutierrez-Galan, D., Dominguez-Morales, M. J., & Jimenez-Moreno, G. (2016). Multilayer spiking neural network for audio samples classification using SpiNNaker. In International conference on artificial neural networks (pp. 45–53). Cham: Springer.
Draa, I. C., Tayeb, J., Niar, S., & Grislin, E. (2015). Application sequence prediction for energy consumption reduction in mobile systems. In 2015 IEEE International conference on computer and information technology; ubiquitous computing and communications; dependable, autonomic and secure computing; pervasive intelligence and computing (pp. 23–30). Liverpool: IEEE.
Dubey, H., Sangwan, A., & Hansen, J.H. (2018a). Robust speaker clustering using mixtures of von mises-fisher distributions for naturalistic audio streams. http://arxiv.org/abs/1808.06045.
Dubey, H., Sangwan, A., & Hansen, J. H. (2018b). Leveraging frequency-dependent kernel and DIP-based clustering for Robust speech activity detection in naturalistic audio streams. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 26(11), 2056–2071.
Durand, S., Bello, J. P., David, B., & Richard, G. (2016). Feature adapted convolutional neural networks for downbeat tracking. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 296–300). Shanghai: IEEE.
Elhilali, M., 2019. Modulation representations for speech and music. In Timbre: Acoustics, perception, and cognition (pp. 335–359). Cham: Springer.
Elzaafarany, K., Aly, M. H., Kumar, G., & Nakhmani, A. (2019). Cerebral artery vasospasm detection using transcranial Doppler signal analysis. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 38(8), 2191–2202.
Emoto, T., Abeyratne, U. R., Shono, T., Nonaka, R., Jinnouchi, O., Kawata, I., et al. (2016). Auditory image model for the characterisation of obstructive sleep apnoea. Screening. https://doi.org/10.2316/P.2016.832-031.
Esparza, T. M., Bello, J. P., & Humphrey, E. J. (2015). From genre classification to rhythm similarity: Computational and musicological insights. Journal of New Music Research, 44(1), 39–57.
Eyben, F. (2015). Real-time speech and music classification by large audio feature space extraction. Berlin: Springer.
Font, R., Espín, J. M., & Cano, M. J. (2017). Experimental analysis of features for replay attack detection-results on the ASVspoof 2017 challenge. In Interspeech (pp. 7–11).
Francombe, J., Mason, R., Dewhirst, M., & Bech, S. (2015). A model of distraction in an audio-on-audio interference situation with music program material. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 63(1/2), 63–77.
Freitag, M., Amiriparian, S., Pugachevskiy, S., Cummins, N., & Schuller, B. (2017). audeep: Unsupervised learning of representations from audio with deep recurrent neural networks. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 18(1), 6340–6344.
Friberg, A., Schoonderwaldt, E., Hedblad, A., Fabiani, M., & Elowsson, A. (2014). Using perceptually defined music features in music information retrieval. http://arxiv.org/abs/1403.7923.
Fujino, T., & Yoshida, T. (2017). A consideration of mechanism of audio signa deterioration caused by propagation noise between audio equipment. In 2017 Asia-Pacific international symposium on electromagnetic compatibility (APEMC) (pp. 155–157). South Korea: IEEE.
García, M.A., & Destéfanis, E.A. (2017). Deep neural networks for shimmer approximation in synthesized audio signal. In Argentine congress of computer science (pp. 3–12). Cham: Springer.
Gebru, I. D., Ba, S., Li, X., & Horaud, R. (2017). Audio-visual speaker diarization based on spatiotemporal bayesian fusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 40(5), 1086–1099.
Gemmeke, J. F., Ellis, D. P., Freedman, D., Jansen, A., Lawrence, W., Moore, R. C., Plakal, M., & Ritter, M. (2017). Audio set: An ontology and human-labeled dataset for audio events. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 776–780). New Orleans: IEEE.
Gencoglu, O., Virtanen, T., & Huttunen, H. (2014). Recognition of acoustic events using deep neural networks. In 2014 22nd European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 506–510). Lisbon: IEEE
George, J., & Jhunjhunwala, A. (2015). Scalable and robust audio fingerprinting method tolerable to time-stretching. In 2015 IEEE International conference on digital signal processing (DSP) (pp. 436–440). Singapore: IEEE.
Gergen, S., & Martin, R. (2016). Estimating source dominated microphone clusters in ad-hoc microphone arrays by fuzzy clustering in the feature space. In Speech communication; 12. ITG symposium (pp. 1–5). VDE.
Gerhard, D. (2000). Audio signal classification: An overview. Canadian Artificial Intelligence, pp.4–6.
Ghaemmaghami, H., Dean, D., Kalantari, S., Sridharan, S., & Fookes, C. (2015). Complete-linkage clustering for voice activity detection in audio and visual speech.
Ghasemzadeh, H., & Arjmandi, M. K. (2014). Reversed-Mel cepstrum based audio steganalysis. In 2014 4th International conference on computer and knowledge engineering (ICCKE) (pp. 679–684). Mashhad: IEEE.
Ghodasara, V., Waldekar, S., Paul, D., & Saha, G. (2016). Acoustic scene classification using block based MFCC features. Detection and classification of acoustic scenes and events.
Ghosal, A., Chakraborty, R., Dhara, B. C., & Saha, S. K. (2015). Perceptual feature-based song genre classification using RANSAC. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Studies, 4(1), 31–49.
Giannakopoulos, T. (2015). Pyaudioanalysis: An open-source python library for audio signal analysis. PLoS ONE, 10(12), e0144610.
Giannakopoulos, T., & Perantonis, S. (2019). Recognizing the quality of urban sound recordings using hand-crafted and deep audio features. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM international conference on pervasive technologies related to assistive environments (pp. 323–324). Rhodes: ACM.
Girisha, G. K., & Pinjare, S. L. (2016). Performance analysis of adaptive filters for noise cancellation in audio signal for hearing aid application. IJSR, 5(5), 6–319.
Gkiokas, A., Katsouros, V., Carayannis, G., Gkiokas, A., Katsouros, V., & Carayannis, G. (2016). Towards multi-purpose spectral rhythm features: An application to dance style, meter and tempo estimation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP), 24(11), 1885–1896.
Godfrey, H. (2016). Basic signal processing with MATLAB.
Goehring, T., Yang, X., Monaghan, J. J., & Bleeck, S. (2016). Speech enhancement for hearing-impaired listeners using deep neural networks with auditory-model based features. In 2016 24th European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 2300–2304). Budapest: IEEE.
Grais, E. M., & Plumbley, M. D. (2017). Single channel audio source separation using convolutional denoising autoencoders. In 2017 IEEE global conference on signal and information processing (GlobalSIP) (pp. 1265–1269). Montreal: IEEE.
Grama, L., Buhuş, E. R., & Rusu, C. (2017). Acoustic classification using linear predictive coding for wildlife detection systems. In 2017 International symposium on signals, circuits and systems (ISSCS) (pp. 1–4). Iasi: IEEE.
Grama, L., & Rusu, C. (2017). Audio signal classification using linear predictive coding and random forests. In 2017 International conference on speech technology and human-computer dialogue (SpeD) (pp. 1–9). Bucharest: IEEE.
Grekow, J. (2015). Audio features dedicated to the detection of four basic emotions. In IFIP international conference on computer information systems and industrial management (pp. 583–591). Cham: Springer.
Grekow, J. (2017). Audio features dedicated to the detection of arousal and valence in music recordings. In 2017 IEEE international conference on innovations in intelligent systems and applications (INISTA) (pp. 40–44). Gdynia: IEEE.
Grzywczak, D., & Gwardys, G. (2014). Audio features in music information retrieval. In International conference on active media technology (pp. 187–199). Cham: Springer.
Guan, H., Liu, Z., Wang, L., Dang, J., & Yu, R. (2017). Speech emotion recognition considering local dynamic features. In International seminar on speech production (pp. 14–23). Cham: Springer.
Gulhane, S. R., Badhe, S. S., & Shirbahadurkar, S. D. (2018). Cepstral (MFCC) feature and spectral (Timbral) features analysis for musical instrument sounds. In 2018 IEEE global conference on wireless computing and networking (GCWCN) (pp. 109–113). Lonavala: IEEE.
Gupta, S., & Dhanda, N. (2015). Audio steganography using discrete wavelet transformation (DWT) & discrete cosine transformation (DCT). IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering, 17(2), 2278–2661.
Guzman-Zavaleta, Z. J., Feregrino-Uribe, C., Menendez-Ortiz, A., & Garcia-Hernandez, J. J. (2014). A robust audio fingerprinting method using spectrograms saliency maps. In The 9th international conference for internet technology and secured transactions (ICITST-2014) (pp. 47–52). London: IEEE.
Gwardys, G., & Grzywczak, D. (2014). Deep image features in music information retrieval. International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications, 60(4), 321–326.
Han, B. J., & Hwang, E. (2009). Environmental sound classification based on feature collaboration. In 2009 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (pp. 542–545). New York: IEEE.
Han, Y., Kim, J., Lee, K., Han, Y., Kim, J., & Lee, K. (2017). Deep convolutional neural networks for predominant instrument recognition in polyphonic music. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP), 25(1), 208–221.
Han, C., Xue, R., Zhang, R., & Wang, X. (2018). A new audio steganalysis method based on linear prediction. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 77(12), 15431–15455.
Hannon, E. E., Schachner, A., & Nave-Blodgett, J. E. (2017). Babies know bad dancing when they see it: Older but not younger infants discriminate between synchronous and asynchronous audiovisual musical displays. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 159, 159–174.
Hassan, N. F., & Alden, S. Q. S. (2018). Gender classification based on audio features. Al-Ma’mon College Journal, 31, 196–213.
Helmrich, C. R., Marković, G., & Edler, B. (2014). Improved low-delay MDCT-based coding of both stationary and transient audio signals. In 2014 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6954–6958). Florence: IEEE.
Heo, J., Baek, H. J., Hong, S., Chang, M. H., Lee, J. S., & Park, K. S. (2017). Music and natural sounds in an auditory steady-state response) based brain–computer interface to increase user acceptance. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 84, 45–52.
Herberger, T., Tost, T., & Engel, T. (2018). Bellevue Investments & Co Kgaa GmbH. System and method for controlled dynamics adaptation for musical content. U.S. Patent 9,991,861.
Herrera-Boyer, P., Peeters, G., & Dubnov, S. (2003). Automatic classification of musical instrument sounds. Journal of New Music Research, 32(1), 3–21.
Hershey, S., Chaudhuri, S., Ellis, D. P., Gemmeke, J. F., Jansen, A., Moore, R. C., Plakal, M., Platt, D., Saurous, R. A., Seybold, B., & Slaney, M. (2017). CNN architectures for large-scale audio classification. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (icassp) (pp. 131–135). New Orleans: IEEE.
Hershey, J. R., Chen, Z., Le Roux, J., & Watanabe, S. (2016). Deep clustering: Discriminative embeddings for segmentation and separation. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 31–35). Shanghai: IEEE.
Heshi, R., Suma, S. M., Koolagudi, S. G., Bhandari, S., & Rao, K. S. (2016). Rhythm and timbre analysis for carnatic music processing. In Proceedings of 3rd international conference on advanced computing, networking and informatics (pp. 603–609). New Delhi: Springer.
Hoefle, S., Engel, A., Basilio, R., Alluri, V., Toiviainen, P., Cagy, M., et al. (2018). Identifying musical pieces from fMRI data using encoding and decoding models. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2266–2278.
Hoffmann, P., & Kostek, B. (2016). Bass enhancement settings in portable devices based on music genre recognition. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 63(12), 980–989.
Hossain, M. S., & Muhammad, G. (2018). Environment classification for urban big data using deep learning. IEEE Communications Magazine, 56(11), 44–50.
Hossain, N., & Naznin, M. (2018). Sensing emotion from voice jitter. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM conference on embedded networked sensor systems (pp. 359–360). Shenzhen: ACM.
Hu, X., Choi, K., & Downie, J. S. (2017). A framework for evaluating multimodal music mood classification. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 68(2), 273–285.
Hu, P., Liu, W., Jiang, W., & Yang, Z. (2014). Latent topic model for audio retrieval. Pattern Recognition, 47(3), 1138–1143.
Huang, J., Child, R., Rao, V., Liu, H., Satheesh, S., & Coates, A. (2016). Active learning for speech recognition: The power of gradients. http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.03226.
Huang, L., & Pun, C. M. (2019). Audio replay spoof attack detection using segment-based hybrid feature and densenet-LSTM network. In ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2567–2571). Brighton: IEEE.
Huang, Z., Weng, C., Li, K., Cheng, Y. C., & Lee, C. H. (2014). Deep learning vector quantization for acoustic information retrieval. In 2014 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1350–1354). Florence: IEEE.
Hyder, R., Ghaffarzadegan, S., Feng, Z., Hansen, J.H., & Hasan, T. (2017). Acoustic scene classification using a CNN-supervector system trained with auditory and spectrogram image features. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 3073–3077).
Isik, Y., Roux, J.L., Chen, Z., Watanabe, S., & Hershey, J.R., 2016. Single-channel multi-speaker separation using deep clustering. http://arxiv.org/abs/1607.02173.
Islam, M. T., Shaan, M. N., Easha, E. J., Minhaz, A. T., Shahnaz, C., & Fattah, S. A. (2017). Enhancement of noisy speech based on decision-directed Wiener approach in perceptual wavelet packet domain. In TENCON 2017-2017 IEEE region 10 conference (pp. 2666–2671). Penang: IEEE.
Jack, R.H., Stockman, T., & McPherson, A. (2016). Effect of latency on performer interaction and subjective quality assessment of a digital musical instrument. In Proceedings of the audio mostly 2016 (pp. 116–123). Norrköping: ACM.
Jalil, M., Butt, F. A., & Malik, A. (2013). Short-time energy, magnitude, zero crossing rate and autocorrelation measurement for discriminating voiced and unvoiced segments of speech signals. In 2013 The international conference on technological advances in electrical, electronics and computer engineering (TAEECE) (pp. 208–212). Konya: IEEE.
Jamil, N., Ramli, M. I., & Seman, N. (2015). Sentence boundary detection without speech recognition: A case of an under-resourced language. Journal of Electrical Systems, 11(3), 308–318.
Jansen, A., Plakal, M., Pandya, R., Ellis, D. P., Hershey, S., Liu, J., Moore, R. C., & Saurous, R. A. (2018). Unsupervised learning of semantic audio representations. In 2018 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 126–130). Calgary: IEEE.
Jarina, R., O’Connor, N., Marlow, S., & Murphy, N. (2002). Rhythm detection for speech-music discrimination in mpeg compressed domain. In 2002 14th international conference on digital signal processing proceedings. DSP 2002 (Cat. No. 02TH8628) (pp. 129–132). Santorini: IEEE.
Javier, R. J., & Kim, Y. (2014). Application of linear predictive coding for human activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 11(10), 1831–1834.
Jayasankar, T., Vinothkumar, K., & Vijayaselvi, A. (2017). Automatic gender identification in speech recognition by genetic algorithm. Applied Mathematics, 11(3), 907–913.
Jleed, H., & Bouchard, M. (2017). Acoustic environment classification using discrete hartley transform features. In 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering (CCECE) (pp. 1–4). Windsor: IEEE.
Jondya, A. G., & Iswanto, B. H. (2017). Indonesian’s traditional music clustering based on audio features. Procedia Computer Science, 116, 174–181.
Jorrín-Prieto, J., Vaquero, C., & García, P. (2016). Analysis of the impact of the audio database characteristics in the accuracy of a speaker clustering system. In Odyssey (pp. 393–399).
Jukić, A., van Waterschoot, T., Gerkmann, T., & Doclo, S. (2015). Multi-channel linear prediction-based speech dereverberation with sparse priors. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP), 23(9), 1509–1520.
Jumelle, M., & Sakmeche, T. (2018). Speaker clustering with neural networks and audio processing. http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.08276.
Kacprzak, S., Chwiećko, B., & Ziółko, B. (2017). Speech/music discrimination for analysis of radio stations. In 2017 International conference on systems, signals and image processing (IWSSIP) (pp. 1–4). Poznan: IEEE.
Kalamani, M., Valarmathy, D. S., & Anith, S. (2015). Hybrid speech segmentation algorithm for continuous speech recognition. International Journal on Applications of Information and Communication Engineering, 1(1), 39–46.
Kapsouras, I., Tefas, A., Nikolaidis, N., Peeters, G., Benaroya, L., & Pitas, I. (2017). Multimodal speaker clustering in full length movies. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 76(2), 2223–2242.
Karaa, W. B. A., Ashour, A. S., Sassi, D. B., Roy, P., Kausar, N., & Dey, N. (2016). Medline text mining: an enhancement genetic algorithm based approach for document clustering. In Applications of intelligent optimization in biology and medicine (pp. 267–287). Cham: Springer.
Karthikeyan, K., & Mala, D. R. (2018). Content based audio classification using artificial neural network techniques. International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology, 9(4), 33–48.
Kartikay, A., Ganesan, H., & Ladwani, V.M. (2016). Classification of music into moods using musical features. In 2016 International conference on inventive computation technologies (ICICT) (Vol. 3, pp. 1–5). Coimbatore: IEEE.
Kaur, K., & Jain, N. (2015). Feature extraction and classification for automatic speaker recognition system—A review. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 5.
Kaur, G., Singh, D., & Kaur, G. (2015). A survey on speech recognition algorithms. International Journal of Emerging Research in Management and Technology, 4(5), 289–298.
Kelkar, T., & Jensenius, A. R. (2017). Exploring melody and motion features in “sound-tracings”. In Proceedings of the SMC conferences (pp. 98–103). Aalto University.
Khalil, M., & Adib, A. (2015). Informed audio watermarking based on adaptive carrier modulation. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 74(15), 5973–5993.
Khonglah, B. K., & Prasanna, S. M. (2016). Speech/music classification using speech-specific features. Digital Signal Processing, 48, 71–83.
Khunarsal, P., Lursinsap, C., & Raicharoen, T. (2013). Very short time environmental sound classification based on spectrogram pattern matching. Information Sciences, 243, 57–74.
Kiktova, E., Lojka, M., Pleva, M., Juhar, J., & Cizmar, A. (2015). Gun type recognition from gunshot audio recordings. In 3rd international workshop on biometrics and forensics (IWBF 2015) (pp. 1–6). Gjovik: IEEE.
Kim, G. H., Bae, I. H., Park, H. J., & Lee, Y. W. (2019). Comparison of cepstral analysis based on voiced-segment extraction and voice tasks for discriminating dysphonic and normophonic Korean speakers. Journal of Voice. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2019.09.009.
Kim, K., Baijal, A., Ko, B.S., Lee, S., Hwang, I., & Kim, Y. (2015). Speech music discrimination using an ensemble of biased classifiers. In Audio engineering society convention, Vol. 139. Audio Engineering Society.
Kim, H. G., Moreau, N., & Sikora, T. (2006). MPEG-7 audio and beyond: Audio content indexing and retrieval. New York: Wiley.
Kim, D., Van Ho, P., & Lim, Y. (2017). A new recognition method for visualizing music emotion. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 7(3), 1246–1254.
Kirch, N., & Zhu, N. (2016). A discourse on the effectiveness of digital filters at removing noise from audio. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 139(4), 2225.
Kiska, T., Galaz, Z., Zvoncak, V., Mucha, J., Mekyska, J., & Smekal, Z. (2018). Music information retrieval techniques for determining the place of origin of a music interpretation. In 2018 10th international congress on ultra modern telecommunications and control systems and workshops (ICUMT) (pp. 1–5). Moscow: IEEE.
Knees, P., & Schedl, M. (2016). Basic methods of audio signal processing. In Music similarity and retrieval (pp. 33–50). Berlin: Springer.
Korvel, G., & Kostek, B. (2017). Examining feature vector for phoneme recognition. In 2017 IEEE international symposium on signal processing and information technology (ISSPIT) (pp. 394–398). Bilbao: IEEE.
Kotti, M., & Stylianou, Y. (2017). Effective emotion recognition in movie audio tracks. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 5120–5124). New Orleans: IEEE.
Koutini, K., Eghbal-zadeh, H., Dorfer, M., & Widmer, G. (2019). The receptive field as a regularizer in deep convolutional neural networks for acoustic scene classification. In 2019 27th European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 1–5). A Coruna: IEEE.
Koutras, P., Zlatintsi, A., Iosif, E., Katsamanis, A., Maragos, P., & Potamianos, A. (2015). Predicting audio-visual salient events based on visual, audio and text modalities for movie summarization. In 2015 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (pp. 4361–4365). Quebec City: IEEE.
Kraljević, L., Russo, M., Mlikota, M., & Šarić, M. (2017). Cochlea-based features for music emotion classification. In 14th international conference on signal processing and multimedia applications.
Kronvall, T., Juhlin, M., Swärd, J., Adalbjörnsson, S. I., & Jakobsson, A. (2017). Sparse modeling of chroma features. Signal Processing, 130, 105–117.
Kulyukin, V. A., & Reka, S. K. (2016). Toward sustainable electronic beehive monitoring: Algorithms for omnidirectional bee counting from images and harmonic analysis of buzzing signals. Engineering Letters, 24(3), 72–82.
Kumar, A., & Florencio, D. (2016). Speech enhancement in multiple-noise conditions using deep neural networks. http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.02427.
Kumar, A., & Raj, B. (2016). Audio event detection using weakly labeled data. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 1038–1047). Amsterdam: ACM.
Kusama, K., & Itoh, T. (2014). Abstract picture generation and zooming user interface for intuitive music browsing. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 73(2), 995–1010.
Kwon, T., Jeong, D., & Nam, J. (2017). Audio-to-score alignment of piano music using RNN-based automatic music transcription. http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.04480.
Lampropoulos, A. S., & Tsihrintzis, G. A. (2012). Evaluation of MPEG-7 descriptors for speech emotional recognition. In 2012 Eighth international conference on intelligent information hiding and multimedia signal processing (pp. 98–101). Piraeus: IEEE.
Lane, N. D., Georgiev, P., & Qendro, L. (2015). DeepEar: Robust smartphone audio sensing in unconstrained acoustic environments using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM international joint conference on pervasive and ubiquitous computing (pp. 283–294). Osaka: ACM.
Lartillot, O., & Grandjean, D. (2019). Tempo and metrical analysis by tracking multiple metrical levels using autocorrelation.
Lavrentyeva, G., Novoselov, S., Malykh, E., Kozlov, A., Kudashev, O., & Shchemelinin, V. (2017). Audio-replay attack detection countermeasures. In International conference on speech and computer (pp. 171–181). Cham: Springer.
Lazaro, A., Sarno, R., Andre, R.J., & Mahardika, M.N. (2017). Music tempo classification using audio spectrum centroid, audio spectrum flatness, and audio spectrum spread based on MPEG-7 audio features. In 2017 3rd international conference on science in information technology (ICSITech) (pp. 41–46). Bandung: IEEE.
Le Cornu, T., & Milner, B. (2017). Generating intelligible audio speech from visual speech. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 25(9), 1751–1761.
Lee, J., Choi, H., Park, D., Chung, Y., Kim, H. Y., & Yoon, S. (2016). Fault detection and diagnosis of railway point machines by sound analysis. Sensors, 16(4), 549–650.
Lee, K., Junokas, M. J., Amanzadeh, M., & Garnett, G. E. (2015a). Exploratory analysis on expressions in two different 4/4 beat patterns. In ICMC.
Lee, J., Kim, T., Park, J., & Nam, J. (2017). Raw waveform-based audio classification using sample-level CNN architectures. http://arxiv.org/abs/1712.00866.
Lee, J., Shin, S., Jang, D., Jang, S.J., & Yoon, K. (2015b). Music recommendation system based on usage history and automatic genre classification. In 2015 IEEE international conference on consumer electronics (ICCE) (pp. 134–135). Las Vegas: IEEE.
Lei, L., & She, K. (2018). Identity vector extraction by perceptual wavelet packet entropy and convolutional neural network for voice authentication. Entropy, 20(8), 1–15.
Levy, M., & Sandler, M. (2008). Structural segmentation of musical audio by constrained clustering. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 16(2), 318–326.
Li, Z., Dey, N., Ashour, A. S., Cao, L., Wang, Y., Wang, D., et al. (2017a). Convolutional neural network based clustering and manifold learning method for diabetic plantar pressure imaging dataset. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics, 7(3), 639–652.
Li, M., Miao, Z., & Ma, C. (2015). Feature extraction with convolutional restricted boltzmann machine for audio classification. In 2015 3rd IAPR Asian conference on pattern recognition (ACPR) (pp. 791–795). Kuala Lumpur: IEEE.
Li, W., Wang, G., & Li, K. (2017b). Clustering algorithm for audio signals based on the sequential Psim matrix and Tabu search. EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, 2017(1), 26–34.
Li, R., Xu, S., & Yang, H. (2016). Spread spectrum audio watermarking based on perceptual characteristic aware extraction. IET Signal Processing, 10(3), 266–273.
Liang, S., & Fan, X. (2014). Audio content classification method research based on two-step strategy. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), 5, 57–62.
Lidy, T. (2015). Spectral convolutional neural network for music classification. In Music information retrieval evaluation eX-change (MIREX), Malaga, Spain.
Lidy, T., & Schindler, A. (2016). CQT-based convolutional neural networks for audio scene classification. In Proceedings of the detection and classification of acoustic scenes and events 2016 workshop (DCASE2016) (Vol. 90, pp. 1032–1048). DCASE2016 challenge.
Lim, W., Jang, D., & Lee, T. (2016). Speech emotion recognition using convolutional and recurrent neural networks. In 2016 Asia-Pacific signal and information processing association annual summit and conference (APSIPA) (pp. 1–4). Jeju: IEEE.
Lim, M., Lee, D., Park, H., Kang, Y., Oh, J., Park, J. S., et al. (2018). Convolutional neural network based audio event classification. KSII Transactions on Internet & Information Systems, 12(6), 2748–2760.
Lin, Y. P., Duann, J. R., Feng, W., Chen, J. H., & Jung, T. P. (2014). Revealing spatio-spectral electroencephalographic dynamics of musical mode and tempo perception by independent component analysis. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation, 11(1), 18.
Lin, X., & Kang, X. (2017). Supervised audio tampering detection using an autoregressive model. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2142–2146). New Orleans: IEEE.
Liu, X., & Bao, C. (2016). Audio bandwidth extension based on ensemble echo state networks with temporal evolution. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 24(3), 594–607.
Liu, Y., Feng, X., & Zhou, Z. (2016). Multimodal video classification with stacked contractive autoencoders. Signal Processing, 120, 761–766.
Liu, Z., & Lu, W. (2017). Fast copy-move detection of digital audio. In 2017 IEEE second international conference on data science in cyberspace (DSC) (pp. 625–629). Shenzhen: IEEE.
Liu, X., Tian, W., Yin, H., & He, L. (2018). Automatic detection of nasal leak in cleft palate speech based on an improved group delay method. In 2018 International symposium on communication engineering & computer science (CECS 2018). Atlantis Press.
López-Serrano, P., Dittmar, C., & Müller, M. (2017). Mid-level audio features based on cascaded harmonic-residual-percussive separation. In Audio engineering society conference: 2017 AES international conference on semantic audio. Audio Engineering Society.
Lostanlen, V., Lafay, G., Andén, J., & Lagrange, M. (2018). Relevance-based quantization of scattering features for unsupervised mining of environmental audio. EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, 2018(1), 15–24.
Loweimi, E., Barker, J., & Hain, T. (2018). Exploring the use of group delay for generalised vts based noise compensation. In 2018 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 4824–4828). Calgary: IEEE.
Lu, L., Zhang, H. J., & Jiang, H. (2002). Content analysis for audio classification and segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 10(7), 504–516.
Ludeña-Choez, J., & Gallardo-Antolín, A. (2015). Feature extraction based on the high-pass filtering of audio signals for acoustic event classification. Computer Speech & Language, 30(1), 32–42.
Lukasik, E., Yang, C., & Kurzawski, L. (2016). Temporal envelope for audio classification. In Audio engineering society convention 140. Audio Engineering Society.
Lukic, Y., Vogt, C., Dürr, O., & Stadelmann, T. (2016). Speaker identification and clustering using convolutional neural networks. In 2016 IEEE 26th international workshop on machine learning for signal processing (MLSP) (pp. 1–6). Vietri sul Mare: IEEE.
Luo, Y., Chen, Z., Hershey, J.R., Le Roux, J., & Mesgarani, N. (2017a). Deep clustering and conventional networks for music separation: Stronger together. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 61–65). New Orleans: IEEE.
Luo, X., Jiang, J., Zhu, J., & Dou, Y. (2017b). Parallel algorithm design for audio feature extraction. In 2017 5th international conference on machinery, materials and computing technology (ICMMCT 2017). Atlantis Press.
Luo, D., Korus, P., & Huang, J. (2018). Band energy difference for source attribution in audio forensics. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 13(9), 2179–2189.
Luo, D., Sun, M., & Huang, J. (2016). Audio postprocessing detection based on amplitude cooccurrence vector feature. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 23(5), 688–692.
Luo, D., Yang, R., & Huang, J. (2015). Identification of AMR decompressed audio. Digital Signal Processing, 37, 85–91.
Luque, J., Larios, D., Personal, E., Barbancho, J., & León, C. (2016). Evaluation of MPEG-7-based audio descriptors for animal voice recognition over wireless acoustic sensor networks. Sensors, 16(5), 1–22.
Luque, A., Romero-Lemos, J., Carrasco, A., & Barbancho, J. (2018). Non-sequential automatic classification of anuran sounds for the estimation of climate-change indicators. Expert Systems with Applications, 95, 248–260.
Lykartsis, A., & Lerch, A. (2015). Beat histogram features for rhythm-based musical genre classification using multiple novelty functions. In Proceedings of the 16th ISMIR Conference (pp. 434-440).
Lykartsis, A., & Weinzierl, S. (2016). Rhythm description for music and speech using the beat histogram with multiple novelty functions: First results.
Lykartsis, A., Wu, C.W., & Lerch, A. (2015). Beat histogram features from NMF-based novelty functions for music classification. In ISMIR (pp. 434–440).
Ma, M., Ramabhadran, B., Emond, J., Rosenberg, A., & Biadsy, F. (2019). Comparison of data augmentation and adaptation strategies for code-switched automatic speech recognition. In ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6081–6085). Brighton: IEEE.
Ma, X., Yang, H., Chen, Q., Huang, D., & Wang, Y. (2016a). Depaudionet: An efficient deep model for audio based depression classification. In Proceedings of the 6th international workshop on audio/visual emotion challenge (pp. 35–42). Amsterdam: ACM.
Ma, Z., Yu, H., Tan, Z. H., & Guo, J. (2016b). Text-independent speaker identification using the histogram transform model. IEEE Access, 4, 9733–9739.
Madikeri, S. R., Talambedu, A., & Murthy, H. A. (2015). Modified group delay feature based total variability space modelling for speaker recognition. International Journal of Speech Technology, 18(1), 17–23.
Magare, M., & Dahake, R. (2016). Audio based music classification based on genre and emotion using Gaussian process. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering.
Mahana, P., & Singh, G. (2015). Comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms for audio signals classification. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security (IJCSNS), 15(6), 49.
Mahardhika, F., Warnars, H. L. H. S., & Heryadi, Y. (2018). Indonesian’s dangdut music classification based on audio features. In 2018 Indonesian association for pattern recognition international conference (INAPR) (pp. 99–103). Jakarta: IEEE.
Marshall, O. (2019). Jitter: Clocking as audible media. International Journal of Communication, 13, 17.
Mayvan, A. D., Beheshti, S. A., & Masoom, M. H. (2015). Classification of vehicles based on audio signals using quadratic discriminant analysis and high energy feature vectors. International Journal on Soft Computing, 6(1), 53.
McAdams, S., & Siedenburg, K. (2019). Perception and cognition of musical timbre. In Foundations in music psychology: Theory and research.
McFee, B., Raffel, C., Liang, D., Ellis, D. P., McVicar, M., Battenberg, E., & Nieto, O. (2015). librosa: Audio and music signal analysis in python. In Proceedings of the 14th python in science conference (Vol. 8).
McPherson, A.P., & Morreale, F. (2017). Technology and community in toolkits for musical interface design. CHI.
Medhat, F., Chesmore, D., & Robinson, J. (2017). Masked conditional neural networks for audio classification. In International conference on artificial neural networks (pp. 349–358). Cham: Springer.
Meng, X., Li, C., & Tian, L. (2018). Detecting audio splicing forgery algorithm based on local noise level estimation. In 2018 5th international conference on systems and informatics (ICSAI) (pp. 861–865). China: IEEE.
Mesaros, A., Heittola, T., Dikmen, O., & Virtanen, T. (2015). Sound event detection in real life recordings using coupled matrix factorization of spectral representations and class activity annotations. In 2015 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 151–155). Brisbane: IEEE.
Meudt, S., & Schwenker, F. (2014). Enhanced autocorrelation in real world emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 16th international conference on multimodal interaction (pp. 502–507). Istanbul: ACM.
Miano, T. (2018). Hear and see: End-to-end sound classification and visualization of classified sounds (No. e27280v1). PeerJ Preprints.
Min, D., Park, B., & Park, J. (2018). Artificial engine sound synthesis method for modification of the acoustic characteristics of electric vehicles. Shock and Vibration. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5209207.
Mingming, L., Hui, Z., & Qinghong, S. H. E. N. (2016). Realization of audio fingerprint based on power spectrum feature. Electronic Measurement Technology, 39(9), 69–72.
Mishra, S. R., Somani, S. B., Deshmukh, P., & Soni, D. (2012). EEG signal processing and classification of sensorimoter rhythm-based BCI. International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, 1(4), 1–4.
Mitrovic, D., Zeppelzauer, M., & Breiteneder, C. (2006). Discrimination and retrieval of animal sounds. In 2006 12th international multi-media modelling conference (p. 5). Beijing: IEEE.
Mo, S., & Niu, J. (2017). A novel method based on OMPGW method for feature extraction in automatic music mood classification. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2724515.
Mocanu, D. C., Mocanu, E., Nguyen, P. H., Gibescu, M., & Liotta, A. (2016). A topological insight into restricted boltzmann machines. Machine Learning, 104(2–3), 243–270.
Moffat, D., Ronan, D., & Reiss, J. D. (2015). An evaluation of audio feature extraction toolboxes.
Molina, R., Gazzano, J. D., Rincon, F., Gil-Costa, V., Barba, J., Petrino, R., et al. (2018). Heterogeneous SoC-based acceleration of MPEG-7 compliance image retrieval process. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 15(1), 161–172.
Monge-Alvarez, J., Hoyos-Barceló, C., Lesso, P., & Casaseca-de-la-Higuera, P. (2018). Robust detection of audio-cough events using local Hu moments. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 23(1), 184–196.
Muhammad, G., Alotaibi, Y. A., Alsulaiman, M. & Huda, M. N. (2010). Environment recognition using selected MPEG-7 audio features and mel-frequency cepstral coefficients. In 2010 Fifth international conference on digital telecommunications (pp. 11–16). Athens: IEEE.
Muhammad, G., & Melhem, M. (2014). Pathological voice detection and binary classification using MPEG-7 audio features. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 11, 1–9.
Mukherjee, H., Obaidullah, S. M., Phadikar, S., & Roy, K. (2018a). MISNA-A musical instrument segregation system from noisy audio with LPCC-S features and extreme learning. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 77(21), 27997–28022.
Mukherjee, H., Obaidullah, S. M., Santosh, K. C., Phadikar, S., & Roy, K. (2018b). Line spectral frequency-based features and extreme learning machine for voice activity detection from audio signal. International Journal of Speech Technology, 21(4), 753–760.
Mun, S., Shon, S., Kim, W., Han, D. K., & Ko, H. (2017). Deep neural network based learning and transferring mid-level audio features for acoustic scene classification. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 796–800). New Orleans: IEEE.
Murthy, Y. S., & Koolagudi, S. G. (2018). Classification of vocal and non-vocal segments in audio clips using genetic algorithm based feature selection (GAFS). Expert Systems with Applications, 106, 77–91.
Nagathil, A., Schlattmann, J.W., Neumann, K., & Martin, R. (2017). A feature-based linear regression model for predicting perceptual ratings of music by cochlear implant listeners. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 346–350). New Orleans: IEEE.
Nagavi, T. C., & Bhajantri, N. U. (2017). A new approach to query by humming based on modulated frequency features. In 2017 International conference on wireless communications, signal processing and networking (WiSPNET) (pp. 1675–1679). Chennai: IEEE.
Nalini, N. J., & Palanivel, S. (2016). Music emotion recognition: The combined evidence of MFCC and residual phase. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 17(1), 1–10.
Nandi, D., Ashour, A. S., Samanta, S., Chakraborty, S., Salem, M. A., & Dey, N. (2015). Principal component analysis in medical image processing: a study. International Journal of Image Mining, 1(1), 65–86.
Nanni, L., Costa, Y. M., Lucio, D. R., Silla, C. N., Jr., & Brahnam, S. (2017). Combining visual and acoustic features for audio classification tasks. Pattern Recognition Letters, 88, 49–56.
Nasr, M. A., Abd-Elnaby, M., El-Fishawy, A. S., El-Rabaie, S., & El-Samie, F. E. A. (2018). Speaker identification based on normalized pitch frequency and mel frequency cepstral coefficients. International Journal of Speech Technology, 21(4), 941–951.
Nath, S. S., Mishra, G., Kar, J., Chakraborty, S., & Dey, N. (2014). A survey of image classification methods and techniques. In 2014 International conference on control, instrumentation, communication and computational technologies (ICCICCT) (pp. 554–557). Kanyakumari: IEEE.
Nawasalkar, R. K., Thakare, V. M., Jambhekar, N. D., & Butey, P. K. (2015). Performance analysis of different audio with raga Yaman. In 2015 1st international conference on next generation computing technologies (NGCT) (pp. 929–931). Dehradun: IEEE.
Nemer, J. S., Kohlberg, G. D., Mancuso, D. M., Griffin, B. M., Certo, M. V., Chen, S. Y., et al. (2017). Reduction of the harmonic series influences musical enjoyment with cochlear implants. Otology & Neurotology, 38(1), 31–37.
Niu, L., Saiki, S., & Nakamura, M. (2017). Integrating environmental sensing and BLE-based location for improving daily activity recognition in OPH. In Proceedings of the 19th international conference on information integration and web-based applications & services (pp. 330–337). Salzburg: ACM.
Noda, J., Travieso, C., & Sánchez-Rodríguez, D. (2016). Automatic taxonomic classification of fish based on their acoustic signals. Applied Sciences, 6(12), 443.
Noda, K., Yamaguchi, Y., Nakadai, K., Okuno, H. G., & Ogata, T. (2015). Audio-visual speech recognition using deep learning. Applied Intelligence, 42(4), 722–737.
Nonaka, R., Emoto, T., Abeyratne, U. R., Jinnouchi, O., Kawata, I., Ohnishi, H., et al. (2016). Automatic snore sound extraction from sleep sound recordings via auditory image modeling. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 27, 7–14.
Nousias, S., Lakoumentas, J., Lalos, A., Kikidis, D., Moustakas, K., Votis, K., & Tzovaras, D. (2016). Monitoring asthma medication adherence through content based audio classification. In 2016 IEEE symposium series on computational intelligence (SSCI) (pp. 1–5). Athens: IEEE.
Ntalampiras, S. (2015). Audio pattern recognition of baby crying sound events. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 63(5), 358–369.
Ntalampiras, S. (2018). On acoustic monitoring of farm environments. In International symposium on signal processing and intelligent recognition systems (pp. 53–63). Singapore: Springer.
Nuanáin, C. Ó., Herrera, P., & Jordá, S. (2017). Rhythmic concatenative synthesis for electronic music: Techniques, implementation, and evaluation. Computer Music Journal, 41(2), 21–37.
Obermayer, A. (2016). Glossary of literary terms-S. Otago German Studies, 2.
Oletic, D., Bilas, V., Magno, M., Felber, N., & Benini, L. (2016). Low-power multichannel spectro-temporal feature extraction circuit for audio pattern wake-up. In 2016 Design, automation & test in Europe conference & exhibition (DATE) (pp. 355–360). Dresden: IEEE.
Olteanu, E., Miu, D. O., Drosu, A., Segarceanu, S., Suciu, G., & Gavat, I. (2019). Fusion of speech techniques for automatic environmental sound recognition. In 2019 International conference on speech technology and human-computer dialogue (SpeD) (pp. 1–8). Timisoara: IEEE.
Oo, M. M., & Oo, L. L. (2019). Acoustic scene classification by using combination of MODWPT and spectral features.
Ooi, C. S., Seng, K. P., Ang, L. M., & Chew, L. W. (2014). A new approach of audio emotion recognition. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(13), 5858–5869.
Oord, A. V. D., Dieleman, S., Zen, H., Simonyan, K., Vinyals, O., Graves, A., Kalchbrenner, N., Senior, A., & Kavukcuoglu, K. (2016). Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio. http://arxiv.org/abs/1609.03499.
Oramas, S., Nieto, O., Barbieri, F., & Serra, X. (2017). Multi-label music genre classification from audio, text, and images using deep features. http://arxiv.org/abs/1707.04916.
Ortolani, F. (2019). A comparative study on using phased or timed arrays in audio surveillance applications. In 2019 IEEE 39th international conference on electronics and nanotechnology (ELNANO) (pp. 808–812). Kyiv: IEEE.
Owens, A., & Efros, A. A. (2018). Audio-visual scene analysis with self-supervised multisensory features. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 631–648).
Ozer, I., Ozer, Z., & Findik, O. (2017). Lanczos kernel based spectrogram image features for sound classification. Procedia Computer Science, 111, 137–144.
Özseven, T., & Düğenci, M. (2018). SPeech ACoustic (SPAC): A novel tool for speech feature extraction and classification. Applied Acoustics, 136, 1–8.
Padilla, P., Knights, F., Ruiz, A.T., & Tidhar, D. (2017). Identification and evolution of musical style I: Hierarchical transition networks and their modular structure. In International conference on mathematics and computation in music (pp. 259–278). Cham: Springer.
Palo, H. K., & Mohanty, M. N. (2015). Classification of emotional speech of children using probabilistic neural network. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 5(2), 311–317.
Palo, H. K., & Mohanty, M. N. (2017). Wavelet based feature combination for recognition of emotions. Ain Shams Engineering Journal.
Palo, H. K., & Sagar, S. (2018). Comparison of neural network models for speech emotion recognition. In 2018 2nd international conference on data science and business analytics (ICDSBA) (pp. 127–131). Changsha: IEEE.
Panda, R., Malheiro, R. M., & Paiva, R. P. (2018). Novel audio features for music emotion recognition. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing.
Parascandolo, G., Huttunen, H., & Virtanen, T. (2016). Recurrent neural networks for polyphonic sound event detection in real life recordings. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6440–6444). Shanghai: IEEE.
Parekh, S., Font, F., & Serra, X. (2016). Improving audio retrieval through loudness profile categorization. In 2016 IEEE international symposium on multimedia (ISM) (pp. 565–568). San Jose: IEEE.
Paszkowski, W., & Loska, A. (2017). The use of data mining methods for the psychoacoustic assessment of noise in urban environment. International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: SGEM: Surveying Geology & mining Ecology Management, 17, 1059–1066.
Patil, S. R., & Machale, S. J. (2020). Indian musical instrument recognition using Gaussian mixture model. In Techno-societal 2018 (pp. 51–57). Cham: Springer.
Patil, N. M., & Nemade, M. U. (2019a). Content-based audio classification and retrieval using segmentation, feature extraction and neural network approach. In Advances in computer communication and computational sciences (pp. 263–281). Singapore: Springer.
Patil, N. M., & Nemade, M. U. (2019b). Content-based audio classification and retrieval using segmentation, feature extraction and neural network. Advances in computer communication and computational sciences: Proceedings of IC4S 2018, p. 263.
Patterson, R. D., Allerhand, M. H., & Giguere, C. (1995). Time-domain modeling of peripheral auditory processing: A modular architecture and a software platform. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 98(4), 1890–1894.
Peeters, G. (2006). Template-based estimation of time-varying tempo. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2007(1), 067215.
Peeters, G., McAdams, S., & Herrera, P. (2000). Instrument sound description in the context of MPEG-7.
Phan, H., Hertel, L., Maass, M., Koch, P., Mazur, R., & Mertins, A. (2017a). Improved audio scene classification based on label-tree embeddings and convolutional neural networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 25(6), 1278–1290.
Phan, H., Hertel, L., Maass, M., & Mertins, A. (2016). Robust audio event recognition with 1-max pooling convolutional neural networks. http://arxiv.org/abs/1604.06338.
Phan, H., Koch, P., Katzberg, F., Maass, M., Mazur, R., McLoughlin, I., & Mertins, A. (2017b). What makes audio event detection harder than classification?. In 2017 25th European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 2739–2743). Kos: IEEE.
Phillips, Y. F., Towsey, M., & Roe, P. (2018). Revealing the ecological content of long-duration audio-recordings of the environment through clustering and visualisation. PLoS ONE, 13(3), e0193345.
Picart, B., Brognaux, S., & Dupont, S. (2015). Analysis and automatic recognition of human beatbox sounds: A comparative study. In 2015 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 4255–4259). Brisbane: IEEE.
Piczak, K. J. (2015a). Environmental sound classification with convolutional neural networks. In 2015 IEEE 25th international workshop on machine learning for signal processing (MLSP) (pp. 1–6). Boston: IEEE.
Piczak, K. J. (2015b). ESC: Dataset for environmental sound classification. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 1015–1018). Australia: ACM.
Pires, I. M., Santos, R., Pombo, N., Garcia, N. M., Flórez-Revuelta, F., Spinsante, S., et al. (2018). Recognition of activities of daily living based on environmental analyses using audio fingerprinting techniques: A systematic review. Sensors, 18(1), 160–182.
Pishdadian, F., Pardo, B., & Liutkus, A. (2017). A multi-resolution approach to common fate-based audio separation. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 566–570). New Orleans: IEEE.
Pokorny, F. B., Schuller, B. W., Marschik, P. B., Brueckner, R., Nyström, P., Cummins, N., Bölte, S., Einspieler, C., & Falck-Ytter, T. (2017). Earlier identification of children with autism spectrum disorder: An automatic vocalisation-based approach. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 309–313).
Pons, J., & Serra, X. (2019). Randomly weighted CNNs for (music) audio classification. In ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 336–340). Brighton: IEEE.
Pop, G.P. (2017). Discriminate animal sounds using TESPAR analysis. In International conference on advancements of medicine and health care through technology (pp. 185–188). Cluj-Napoca, Cham: Springer.
Poria, S., Cambria, E., Howard, N., Huang, G. B., & Hussain, A. (2016). Fusing audio, visual and textual clues for sentiment analysis from multimodal content. Neurocomputing, 174, 50–59.
Poria, S., Hussain, A., & Cambria, E. (2018). combining textual clues with audio-visual information for multimodal sentiment analysis. In Multimodal sentiment analysis (pp. 153–178). Cham: Springer.
Prego, T. D. M., de Lima, A. A., Zambrano-López, R., & Netto, S. L. (2015). Blind estimators for reverberation time and direct-to-reverberant energy ratio using subband speech decomposition. In 2015 IEEE workshop on applications of signal processing to audio and acoustics (WASPAA) (pp. 1–5). New Paltz: IEEE.
Pressnitzer, D., de Cheveigne, A., McAdams, S., & Collet, L. (Eds.). (2006). Auditory signal processing: Physiology, psychoacoustics, and models. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.
Qiu-Yu, Z., Yang-Wei, L., Yi-Bo, H., Peng-Fei, X., & Zhong-Ping, Y. (2014). Perceptual hashing algorithm for speech content identification based on spectrum entropy in compressed domain. International Journal on Smart Sensing & Intelligent Systems, 7(1).
Rachman, F. H., Sarno, R., & Fatichah, C. (2018). Music emotion classification based on lyrics-audio using corpus based emotion. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 8(3), 1720.
Radmard, M., Hadavi, M., & Nayebi, M. M. (2011). A new method of voiced/unvoiced classification based on clustering. Journal of Signal and Information Processing, 2(4), 336–347.
Rajan, R., Misra, M., & Murthy, H. A. (2017). Melody extraction from music using modified group delay functions. International Journal of Speech Technology, 20(1), 185–204.
Rajanna, A. R., Aryafar, K., Shokoufandeh, A., & Ptucha, R. (2015). Deep neural networks: A case study for music genre classification. In 2015 IEEE 14th international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA) (pp. 655–660). Miami: IEEE.
Rajesh, B., & Bhalke, D. G. (2016). Automatic genre classification of Indian Tamil and western music using fractional MFCC. International Journal of Speech Technology, 19(3), 551–563.
Rakotomamonjy, A., & Gasso, G. (2014). Histogram of gradients of time–frequency representations for audio scene classification. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 23(1), 142–153.
Ramirez, M. A. M., Benetos, E., & Reiss, J. D. (2019). A general-purpose deep learning approach to model time-varying audio effects. http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.06148.
Rasjid, Z. E., & Setiawan, R. (2017). Performance comparison and optimization of text document classification using k-nn and naïve bayes classification techniques. Procedia Computer Science, 116, 107–112.
Rawlinson, H., Segal, N., & Fiala, J. (2015). Meyda: An audio feature extraction library for the web audio api. In The 1st web audio conference (WAC). Paris, Fr.
Ren, J., Mao, D., Wang, Z., & Gao, C. (2009). The effect of packet delay on VOIP speech quality: failure of Hurst method. In 2009 WRI world congress on computer science and information engineering (pp. 230–234). Los Angeles: IEEE.
Ren, Y., & Wu, Y. (2014). Convolutional deep belief networks for feature extraction of EEG signal. In 2014 International joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN) (pp. 2850–2853). Beijing: IEEE.
Ren, J. M., Wu, M. J., & Jang, J. S. R. (2015). Automatic music mood classification based on timbre and modulation features. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 6(3), 236–246.
Renjith, S., & Manju, K. G. (2017). Speech based emotion recognition in Tamil and Telugu using LPCC and hurst parameters—A comparitive study using KNN and ANN classifiers. In 2017 International conference on circuit, power and computing technologies (ICCPCT) (pp. 1–6). Kollam: IEEE.
Rida, I. (2018). Feature extraction for temporal signal recognition: An overview. http://arxiv.org/abs/1812.01780.
Ridoean, J. A., Sarno, R., Sunaryo, D., & Wijaya, D. R. (2017). Music mood classification using audio power and audio harmonicity based on MPEG-7 audio features and support vector machine. In 2017 3rd International conference on science in information technology (ICSITech) (pp. 72–76). Bandung: IEEE.
Rinaldi, A. M. (2014). A multimedia ontology model based on linguistic properties and audio-visual features. Information Sciences, 277, 234–246.
Robertson, S., Penn, G., & Wang, Y. (2019). Exploring spectro-temporal features in end-to-end convolutional neural networks. http://arxiv.org/abs/1901.00072.
Rocha, B. M., Mendes, L., Chouvarda, I., Carvalho, P., & Paiva, R. P. (2018). Detection of cough and adventitious respiratory sounds in audio recordings by internal sound analysis. In Precision Medicine Powered by pHealth and Connected Health (pp. 51–55). Singapore: Springer.
Rocha, B. M., Mendes, L., Couceiro, R., Henriques, J., Carvalho, P., & Paiva, R. P. (2017). Detection of explosive cough events in audio recordings by internal sound analysis. In 2017 39th Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC) (pp. 2761–2764). Seogwipo: IEEE.
Roma, G., Xambó, A., Green, O., & Tremblay, P.A. (2018). A javascript library for flexible visualization of audio descriptors. In Proceedings of the 4th web audio conference.
Ronan, D., Gunes, H., Moffat, D., & Reiss, J.D. (2015). Automatic subgrouping of multitrack audio.
Rong, F. (2016). Audio classification method based on machine learning. In 2016 International conference on intelligent transportation, big data & smart city (ICITBS) (pp. 81–84). Changsha: IEEE.
Roy, T., Marwala, T., & Chakraverty, S. (2019). Precise detection of speech endpoints dynamically: A wavelet convolution based approach. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 67, 162–175.
Rubin, J., Abreu, R., Ganguli, A., Nelaturi, S., Matei, I., & Sricharan, K. (2016). Classifying heart sound recordings using deep convolutional neural networks and mel-frequency cepstral coefficients. In 2016 Computing in cardiology conference (CinC) (pp. 813–816). Vancouver: IEEE.
Saggese, A., Strisciuglio, N., Vento, M., & Petkov, N. (2016). Time-frequency analysis for audio event detection in real scenarios. In 2016 13th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS) (pp. 438–443). Colorado Springs: IEEE.
Sailor, H. B., & Patil, H. A. (2016). Filterbank learning using convolutional restricted Boltzmann machine for speech recognition. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 5895–5899). Shanghai: IEEE.
Saki, F., & Kehtarnavaz, N. (2014). Background noise classification using random forest tree classifier for cochlear implant applications. In 2014 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 3591–3595). Florence: IEEE.
Saki, F., Sehgal, A., Panahi, I., & Kehtarnavaz, N. (2016). Smartphone-based real-time classification of noise signals using subband features and random forest classifier. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2204–2208). Shanghai: IEEE.
Salamon, J., & Bello, J. P. (2017). Deep convolutional neural networks and data augmentation for environmental sound classification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 24(3), 279–283.
Salishev, S., Klotchkov, I., & Barabanov, A. (2017). Microphone array post-filter in frequency domain for speech recognition using short-time log-spectral amplitude estimator and spectral harmonic/noise classifier. In International conference on speech and computer (pp. 525–534). Cham: Springer.
Santosh, K. C., Borra, S., Joshi, A., & Dey, N. (2019). Preface: Special section: Advances in speech, music and audio signal processing (Articles 1–13). International Journal of Speech Technology, 22(2), 293–294.
Sarafianos, N., Giannakopoulos, T., & Petridis, S. (2016). Audio-visual speaker diarization using fisher linear semi-discriminant analysis. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 75(1), 115–130.
Sardar, V. M., & Shirbahadurkar, S. D. (2018). Speaker identification of whispering sound using selected audio descriptors. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 13(9), 6660–6666.
Sarikaya, R., Hinton, G. E., & Deoras, A. (2014). Application of deep belief networks for natural language understanding. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP), 22(4), 778–784.
Sarkar, R., Biswas, N., & Chakraborty, S. (2018). Music genre classification using frequency domain features. In 2018 Fifth international conference on emerging applications of information technology (EAIT) (pp. 1–4). Kolkata: IEEE.
Sarno, R., Ridoean, J. A., Sunaryono, D., & Wijaya, D. R. (2018). Classification of music mood using MPEG-7 audio features and SVM with confidence interval. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools, 27(05), 1850016.
Sarode, M., & Bhalke, D. G. (2017). Automatic music mood recognition using support vector regression. International Journal of Computers and Applications, 163(5), 32–35.
Sarroff, A. M., & Casey, M. A. (2014). Musical audio synthesis using autoencoding neural nets. In ICMC.
Sauder, C., Bretl, M., & Eadie, T. (2017). Predicting voice disorder status from smoothed measures of cepstral peak prominence using praat and analysis of dysphonia in speech and voice (ADSV). Journal of Voice, 31(5), 557–566.
Scardapane, S., & Uncini, A. (2017). Semi-supervised echo state networks for audio classification. Cognitive Computation, 9(1), 125–135.
Scaringella, N., & Zoia, G. (2004). A real-time beat tracker for unrestricted audio signals. In Proc. of SMC, 4.
Scarpiniti, M., Scardapane, S., Comminiello, D., & Uncini, A. (2020). Music genre classification using stacked auto-encoders. In Neural approaches to dynamics of signal exchanges (pp. 11–19). Singapore: Springer.
Scherer, K. R., Schuller, B. W., & Elkins, A. (2017). Computational analysis of vocal expression of affect: Trends and challenges. Social Signal Processing. DOI, 10(1017/9781316676202), 006.
Schindler, A., & Rauber, A. (2015). An audio-visual approach to music genre classification through affective color features. In European conference on information retrieval (pp. 61–67). Cham: Springer.
Schmitt, M., Ringeval, F., & Schuller, B. W. (2016). At the border of acoustics and linguistics: Bag-of-audio-words for the recognition of emotions in speech. In Interspeech (pp. 495–499). San Francisco.
Schröder, J., Goetze, S., & Anemüller, J. (2015). Spectro-temporal Gabor filterbank features for acoustic event detection. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 23(12), 2198–2208.
Sebastian, J., Kumar, M., & Murthy, H. A. (2016). An analysis of the high resolution property of group delay function with applications to audio signal processing. Speech Communication, 81, 42–53.
Sell, G., & Clark, P. (2014). Music tonality features for speech/music discrimination. In 2014 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2489–2493). Florence: IEEE.
Sen, S., Dutta, A., & Dey, N. (2019a). Audio indexing. In Audio processing and speech recognition (pp. 1–11). Singapore: Springer.
Sen, S., Dutta, A., & Dey, N. (2019b). Speech processing and recognition system. In Audio processing and speech recognition (pp. 13–43). Singapore: Springer.
Sen, S., Dutta, A., & Dey, N. (2019c). Audio Processing and Speech Recognition: Concepts, Techniques and Research Overviews. Berlin: Springer.
Senevirathna, E. N. W., & Jayaratne, L. (2015). Audio music monitoring: Analyzing current techniques for song recognition and identification. GSTF Journal on Computing (JoC), 4(3), 23–34.
Seo, J. S., Kim, J., & Park, J. (2017). An investigation of chroma n-gram selection for cover song search. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of Korea, 36(6), 436–441.
Sephus, N. H., Lanterman, A. D., & Anderson, D. V. (2015). Modulation spectral features: In pursuit of invariant representations of music with application to unsupervised source identification. Journal of New Music Research, 44(1), 58–70.
Serizel, R., Bisot, V., Essid, S., & Richard, G. (2018). Acoustic features for environmental sound analysis. In Computational analysis of sound scenes and events (pp. 71–101). Cham: Springer.
Shafee, S., & Anuradha, B. (2015). Isolated Telugu speech recognition using MFCC and gamma tone features by radial basis networks in noisy environment. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering (IJIRCCE), 3(3), 1481–1488.
Shakya, A., Gurung, B., Thapa, M.S., Rai, M., & Joshi, B. (2017). Music classification based on genre and mood. In International conference on computational intelligence, communications, and business analytics (pp. 168–183). Singapore: Springer.
Shamma, S., & Fritz, J. (2014). Adaptive auditory computations. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 25, 164–168.
Sharan, R. V., & Moir, T. J. (2016). An overview of applications and advancements in automatic sound recognition. Neurocomputing, 200, 22–34.
Sharma, S., Fulzele, P., & Sreedevi, I. (2018). Novel hybrid model for music genre classification based on support vector machine. In 2018 IEEE symposium on computer applications & industrial electronics (ISCAIE) (pp. 395–400). Penang: IEEE.
Sharma, U., Maheshkar, S., & Mishra, A.N. (2015). Study of robust feature extraction techniques for speech recognition system. In 2015 International conference on futuristic trends on computational analysis and knowledge management (ABLAZE) (pp. 654–658). Noida: IEEE.
Sharma, R., Murthy, Y. S., & Koolagudi, S. G. (2016). Audio songs classification based on music patterns. In Proceedings of the second international conference on computer and communication technologies (pp. 157–166). New Delhi: Springer.
Shirahama, K., & Grzegorzek, M. (2016). Towards large-scale multimedia retrieval enriched by knowledge about human interpretation. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 75(1), 297–331.
Siegler, M. A., Jain, U., Raj, B., & Stern, R. M. (1997). Automatic segmentation, classification and clustering of broadcast news audio. In Proc. DARPA speech recognition workshop (Vol. 1997).
Singh, I., & Koolagudi, S. G. (2017). Classification of Punjabi folk musical instruments based on acoustic features. In Proceedings of the international conference on data engineering and communication technology (pp. 445–454). Singapore: Springer.
Smith, D., Cheng, E., & Burnett, I. S. (2010). Musical onset detection using MPEG-7 audio descriptors. In Proceedings of the 20th international congress on acoustics (ICA), Sydney, Australia, Vol. 2327, pp. 1014–1020.
Sonnleitner, R., Arzt, A., & Widmer, G. (2016). Landmark-based audio fingerprinting for DJ mix monitoring. In ISMIR (pp. 185–191).
Spanias, A. (2015). Advances in speech and audio processing and coding. In 2015 6th international conference on information, intelligence, systems and applications (IISA) (pp. 1–2). Corfu: IEEE.
Stenzel, H., & Jackson, P. J. (2018). Perceptual thresholds of audio-visual spatial coherence for a variety of audio-visual objects. In Audio engineering society conference: 2018 AES international conference on audio for virtual and augmented reality. Audio Engineering Society.
Stowell, D., Giannoulis, D., Benetos, E., Lagrange, M., & Plumbley, M. D. (2015). Detection and classification of acoustic scenes and events. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 17(10), 1733–1746.
Strisciuglio, N., Vento, M., & Petkov, N. (2015). Bio-inspired filters for audio analysis. In International workshop on brain-inspired computing (pp. 101–115). Cham: Springer.
Stupacher, J., Hove, M. J., & Janata, P. (2016). Audio features underlying perceived groove and sensorimotor synchronization in music. Music Perception: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 33(5), 571–589.
Subramaniam, A., Patel, V., Mishra, A., Balasubramanian, P., & Mittal, A. (2016). Bi-modal first impressions recognition using temporally ordered deep audio and stochastic visual features. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 337–348). Cham: Springer.
Sudarma, M., & Harsemadi, I. G. (2017). Design and analysis system of KNN and ID3 algorithm for music classification based on mood feature extraction. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 7(1), 486.
Suh, Y., & Kim, H. (2014). Discriminative likelihood score weighting based on acoustic-phonetic classification for speaker identification. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2014(1), 126.
Sumarno, L., & Adi, K. (2019). The influence of sampling frequency on tone recognition of musical instruments. TELKOMNIKA, 17(1), 253–260.
Surís, D., Duarte, A., Salvador, A., Torres, J., & Giró-i-Nieto, X. (2018). Cross-modal embeddings for video and audio retrieval. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV).
Ta, K. (2016). Speaker recognition system usi stress Co.
Távora, R. G., & Nascimento, F. A. (2015). Detecting replicas within audio evidence using an adaptive audio fingerprinting scheme. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 63(6), 451–462.
Teixeira, J. P., Fernandes, P. O., & Alves, N. (2017). Vocal acoustic analysis-classification of dysphonic voices with artificial neural networks. Procedia Computer Science, 121, 19–26.
Thaler, T., Potočnik, P., Bric, I., & Govekar, E. (2014). Chatter detection in band sawing based on discriminant analysis of sound features. Applied Acoustics, 77, 114–121.
Tharwat, A., Gaber, T., Awad, Y. M., Dey, N., & Hassanien, A. E. (2016). Plants identification using feature fusion technique and bagging classifier. In The 1st international conference on advanced intelligent system and informatics (AISI2015), November 28–30, 2015, Beni Suef, Egypt (pp. 461–471). Cham: Springer.
Theodorou, T., Mporas, I., & Fakotakis, N. (2014). An overview of automatic audio segmentation. International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science (IJITCS), 6(11), 1.
Therese, S. S., & Lingam, C. (2017). A linear visual assessment tendency based clustering with power normalized cepstral coefficients for audio signal recognition system. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-017-0653-7.
Thirumuru, R., & Vuppala, A. K. (2018). Automatic detection of retroflex approximants in a continuous Tamil speech. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 37(7), 2837–2851.
Thiruvengatanadhan, R., Dhanalakshmi, P., & Palanivel, S. (2015). GMM based indexing and retrieval of music using MFCC and MPEG-7 features. In Emerging ICT for bridging the future-proceedings of the 49th annual convention of the Computer Society of India (CSI) Vol. 1 (pp. 363–370). Cham: Springer.
Thomas, M., Murthy, Y. S., & Koolagudi, S. G. (2016). Detection of largest possible repeated patterns in indian audio songs using spectral features. In 2016 IEEE Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering (CCECE) (pp. 1–5). Vancouver: IEEE.
Tian, M., & SANDLER, M. (2016). Music structural segmentation across genres with Gammatone features.
Torcoli, M., Freke-Morin, A., Paulus, J., Simon, C., & Shirley, B. (2019). Background ducking to produce esthetically pleasing audio for TV with clear speech. In Audio Engineering Society convention 146. Audio Engineering Society.
Tralie, C. J., & Harer, J. (2017). Mobius beats: The twisted spaces of sliding window audio novelty functions with rhythmic subdivisions. In 18th International Society for music information retrieval (ismir), late breaking session.
Trochidis, K., & Lui, S. (2015). Modeling affective responses to music using audio signal analysis and physiology. In International symposium on computer music multidisciplinary research (pp. 346–357). Cham: Springer.
Tu, W., Yang, Y., Du, B., Yang, W., Zhang, X., & Zheng, J. (2019). RNN-based signal classification for hybrid audio data compression. Computing, pp.1–15.
Twomey, R., & McCrea, M. (2017). Transforming the commonplace through machine perception: light field synthesis and audio feature extraction in the rover project. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2017 art gallery (pp. 400–408). Los Angeles: ACM.
Upadhya, S. S., Cheeran, A. N., & Nirmal, J. H. (2017). Statistical comparison of jitter and shimmer voice features for healthy and Parkinson affected persons. In 2017 second international conference on electrical, computer and communication technologies (ICECCT) (pp. 1–6). Coimbatore: IEEE.
Upadhyay, A., & Pachori, R. B. (2015). Instantaneous voiced/non-voiced detection in speech signals based on variational mode decomposition. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 352(7), 2679–2707.
Urbano, J., Bogdanov, D., Boyer, H., Gómez Gutiérrez, E., & Serra, X. (2014). What is the effect of audio quality on the robustness of MFCCs and chroma features?. In Proceedings of the 15th conference of the international society for music information retrieval (ISMIR 2014); 2014 Oct 27-31; Taipei (pp. 573–578). Taiwan: International Society for Music Information Retrieval.
Uzkent, B., Barkana, B. D., & Cevikalp, H. (2012). Non-speech environmental sound classification using SVMs with a new set of features. International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control, 8(5), 3511–3524.
Valada, A., Spinello, L., & Burgard, W. (2018). Deep feature learning for acoustics-based terrain classification. In Robotics research (pp. 21–37). Cham: Springer.
Valero, X., & Alías, F. (2012). Classification of audio scenes using narrow-band autocorrelation features. In 2012 Proceedings of the 20th European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO). Bucharest: IEEE.
Välimäki, V. (2017). Analysis of audio signals.
van de Water, L. F. (2017). Assessing stress at the workplace: An explorative study on measuring emotion using unobtrusive sensor techniques. Master’s thesis.
Vásquez-Correa, J. C., Orozco-Arroyave, J. R., Arias-Londoño, J. D., Vargas-Bonilla, J. F., & Nöth, E. (2016). Non-linear dynamics characterization from wavelet packet transform for automatic recognition of emotional speech. In Recent advances in nonlinear speech processing (pp. 199–207). Cham: Springer.
Velarde, G., Cancino Chacón, C., Meredith, D., Weyde, T., & Grachten, M. (2018). Convolution-based classification of audio and symbolic representations of music. Journal of New Music Research, 47(3), 191–205.
Velayatipour, M., & Mosleh, M. (2014). A review on speech-music discrimination methods. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Solution, 2(2), 67–78.
Verma, P., & Smith, J.O. (2018). Neural style transfer for audio spectograms. http://arxiv.org/abs/1801.01589.
Vrysis, L., Tsipas, N., Dimoulas, C., & Papanikolaou, G. (2015). Mobile audio intelligence: From real time segmentation to crowd sourced semantics. In Proceedings of the audio mostly 2015 on interaction with sound (p. 37). Thessaloniki: ACM.
Vrysis, L., Tsipas, N., Dimoulas, C., & Papanikolaou, G. (2016). Crowdsourcing audio semantics by means of hybrid bimodal segmentation with hierarchical classification. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 64(12), 1042–1054.
Vrysis, L., Tsipas, N., Dimoulas, C., & Papanikolaou, G. (2017). Extending Temporal Feature Integration for Semantic Audio Analysis. In Audio Engineering Society convention 142. Audio Engineering Society.
Waldekar, S., & Saha, G. (2018a). Classification of audio scenes with novel features in a fused system framework. Digital Signal Processing, 75, 71–82.
Waldekar, S., & Saha, G. (2018b). Wavelet-based audio features for acoustic scene classification. Tech. Rep., DCASE2018 challenge.
Wang, Y., & Hu, W. (2018). Speech emotion recognition based on improved MFCC. In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on computer science and application engineering (p. 88). Hohhot: ACM.
Wang, C., Li, Z., Dey, N., Li, Z., Ashour, A. S., Fong, S. J., et al. (2018). Histogram of oriented gradient based plantar pressure image feature extraction and classification employing fuzzy support vector machine. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics, 8(4), 842–854.
Wang, J. C., Lin, C. H., Chen, B. W., & Tsai, M. K. (2013). Gabor-based nonuniform scale-frequency map for environmental sound classification in home automation. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 11(2), 607–613.
Wang, H., Liu, Z., & Song, Y. (2015). Analysis on wavelength components in pantograph-catenary contact force of electric railway based on multiple EEMD. Journal of the China Railway Society, 37(5), 34–41.
Wang, Y., Neves, L., & Metze, F. (2016). Audio-based multimedia event detection using deep recurrent neural networks. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2742–2746). Shanghai: IEEE.
Wang, Y., Rawat, S., & Metze, F. (2014). Exploring audio semantic concepts for event-based video retrieval. In 2014 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1360–1364). Florence: IEEE.
Wang, Y., Shi, F., Cao, L., Dey, N., Wu, Q., Ashour, A. S., et al. (2019). Morphological segmentation analysis and texture-based support vector machines classification on mice liver fibrosis microscopic images. Current Bioinformatics, 14(4), 282–294.
Wang, J. C., Wang, J. F., He, K. W., & Hsu, C. S. (2006). Environmental sound classification using hybrid SVM/KNN classifier and MPEG-7 audio low-level descriptor. In The 2006 IEEE international joint conference on neural network proceedings (pp. 1731–1735). Canada: IEEE.
Wang, K. C., Yang, Y. M., & Yang, Y. R. (2017). Speech/music discrimination using hybrid-based feature extraction for audio data indexing. In 2017 international conference on system science and engineering (ICSSE) (pp. 515–519). Ho Chi Minh City: IEEE.
Weiß, C. (2017). Computational methods for tonality-based style analysis of classical music audio recordings. Doctoral dissertation, Technische Universität Ilmenau.
Weiß, C., & Schaab, M. (2015). On the Impact of key detection performance for identifying classical music styles. Work, 32, 33.
Wieczorkowska, A., Kubera, E., Słowik, T., & Skrzypiec, K. (2018). Spectral features for audio based vehicle and engine classification. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 50(2), 265–290.
Wilson, A., & Fazenda, B. (2016). Variation in multitrack mixes: analysis of low-level audio signal features. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 64(7/8), 466–473.
Witkowski, M., Kacprzak, S., Zelasko, P., Kowalczyk, K., & Galka, J. (2017). Audio replay attack detection using high-frequency features. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 27–31).
Won, M., Alsaadan, H., & Eun, Y. (2017). Adaptive audio classification for smartphone in noisy car environment. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia (pp. 1672–1679). Mountain View: ACM.
Wu, Y., & Lee, T. (2018). Reducing model complexity for DNN based large-scale audio classification. In 2018 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 331–335). Calgary: IEEE.
Wu, C. W., & Vinton, M. (2017). Blind bandwidth extension using k-means and support vector regression. In 2017 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 721–725). New Orleans: IEEE.
Wyse, L. (2017). Audio spectrogram representations for processing with convolutional neural networks. http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.09559.
Xiao, X., Zhao, S., Zhong, X., Jones, D. L., Chng, E. S., & Li, H. (2015). A learning-based approach to direction of arrival estimation in noisy and reverberant environments. In 2015 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2814–2818). Brisbane: IEEE.
Xie, J., Towsey, M., Truskinger, A., Eichinski, P., Zhang, J., & Roe, P. (2015). Acoustic classification of australian anurans using syllable features. In 2015 IEEE tenth international conference on intelligent sensors, sensor networks and information processing (ISSNIP) (pp. 1–6). Singapore: IEEE.
Xie, J., & Zhu, M. (2019). Investigation of acoustic and visual features for acoustic scene classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 126, 20–29.
Xu, Y., Kong, Q., Wang, W., & Plumbley, M. D. (2018). Large-scale weakly supervised audio classification using gated convolutional neural network. In 2018 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 121–125). Calgary: IEEE.
Xu, H., & Ou, Z. (2016). Scalable discovery of audio fingerprint motifs in broadcast streams with determinantal point process based motif clustering. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 24(5), 978–989.
Xu, X., Zhao, M., Lin, J., & Lei, Y. (2016). Envelope harmonic-to-noise ratio for periodic impulses detection and its application to bearing diagnosis. Measurement, 91, 385–397.
Yadati, K., Liem, C., Larson, M., & Hanjalic, A. (2017). On the automatic identification of music for common activities. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on international conference on multimedia retrieval (pp. 192–200). Bucharest: ACM.
Yamada, M., Doeda, O., Matsuo, A., Hara, Y., & Mine, K. (2017). A rhythm practice support system with annotation-free real-time onset detection. In 2017 International conference on advanced informatics, concepts, theory, and applications (ICAICTA) (pp. 1–6). Denpasar: IEEE.
Yang, L., & Chen, K. (2017). Performance comparison of two types of auditory perceptual features in robust underwater target classification. Acta Acustica United with Acustica, 103(1), 56–66.
Yang, J., Deng, J., Li, S., & Hao, Y. (2017a). Improved traffic detection with support vector machine based on restricted Boltzmann machine. Soft Computing, 21(11), 3101–3112.
Yang, X. K., He, L., Qu, D., Zhang, W. Q., & Johnson, M. T. (2016a). Semi-supervised feature selection for audio classification based on constraint compensated Laplacian score. EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, 2016(1), 9–18.
Yang, L., Jiang, D., He, L., Pei, E., Oveneke, M. C., & Sahli, H. (2016b). Decision tree based depression classification from audio video and language information. In Proceedings of the 6th international workshop on audio/visual emotion challenge (pp. 89–96). Amsterdam: ACM.
Yang, W., Krishnan, S., Yang, W., & Krishnan, S. (2017b). Combining temporal features by local binary pattern for acoustic scene classification. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 25(6), 1315–1321.
You, S. D., & Chen, W. H. (2015). Comparative study of methods for reducing dimensionality of MPEG-7 audio signature descriptors. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 74(10), 3579–3598.
You, M., Liu, Z., Chen, C., Liu, J., Xu, X. H., & Qiu, Z. M. (2017). Cough detection by ensembling multiple frequency subband features. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 33, 132–140.
Yuan, X. C., Pun, C. M., & Chen, C. P. (2015). Robust Mel-Frequency Cepstral coefficients feature detection and dual-tree complex wavelet transform for digital audio watermarking. Information Sciences, 298, 159–179.
Zahid, S., Hussain, F., Rashid, M., Yousaf, M. H., & Habib, H. A. (2015). Optimized audio classification and segmentation algorithm by using ensemble methods. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015.
Zao, L., Coelho, R., & Flandrin, P. (2014). Speech enhancement with emd and hurst-based mode selection. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 22(5), 899–911.
Zeiler, S., Nicheli, R., Ma, N., Brown, G. J., & Kolossa, D. (2016). Robust audiovisual speech recognition using noise-adaptive linear discriminant analysis. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2797–2801). Shanghai: IEEE.
Zemmal, N., Azizi, N., Dey, N., & Sellami, M. (2016). Adaptive semi supervised support vector machine semi supervised learning with features cooperation for breast cancer classification. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics, 6(1), 53–62.
Zeng, Y., Mao, H., Peng, D., & Yi, Z. (2019). Spectrogram based multi-task audio classification. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 78(3), 3705–3722.
Zhang, Y., Lv, D. J., & Wang, H. S. (2014). The application of multiple classifier system for environmental audio classification. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 462, 225–229.
Zhang, S., Qin, Y., Sun, K., & Lin, Y. (2019). Few-shot audio classification with attentional graph neural networks. Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, 2019, 3649–3653.
Zhang, L., Towsey, M., Xie, J., Zhang, J., & Roe, P. (2016). Using multi-label classification for acoustic pattern detection and assisting bird species surveys. Applied Acoustics, 110, 91–98.
Zhang, Q. Y., Xing, P. F., Huang, Y. B., Dong, R. H., & Yang, Z. P. (2015a). An efficient speech perceptual hashing authentication algorithm based on wavelet packet decomposition. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 6(2), 311–322.
Zhang, X., Zhu, B., Li, L., Li, W., Li, X., Wang, W., et al. (2015b). SIFT-based local spectrogram image descriptor: A novel feature for robust music identification. EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, 2015(1), 6.
Zhao, S., Zhang, Y., Xu, H., & Han, T. (2019). Ensemble classification based on feature selection for environmental sound recognition. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019.
Zieliński, S. K. (2018). Feature extraction of surround sound recordings for acoustic scene classification. In International conference on artificial intelligence and soft computing (pp. 475–486). Cham: Springer.
Zirmite, M. P. P., Patil, M. M. K., & Salgar, M. S. P. (2016). Separating voiced segments from music file using MFCC, ZCR and GMM.
Zong, Y. X., Zhang, L., Li, T. J., & Ding, Y. H. (2016a). System design for fault diagnosis based on EMD-ICA audio feature extraction. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 9, 25.
Zong, Y., Zheng, W., Huang, X., Yan, K., Yan, J., & Zhang, T. (2016b). Emotion recognition in the wild via sparse transductive transfer linear discriminant analysis. Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces, 10(2), 163–172.
Zuhaib, S., Manton, R., Griffin, C., Hajdukiewicz, M., Keane, M. M., & Goggins, J. (2018). An indoor environmental quality (IEQ) assessment of a partially-retrofitted university building. Building and Environment, 139, 69–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaki, J. Pattern analysis based acoustic signal processing: a survey of the state-of-art. Int J Speech Technol 24, 913–955 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-020-09681-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-020-09681-3