Abstract
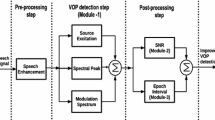
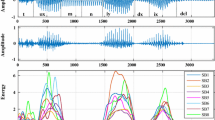
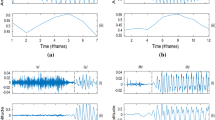
Vowel onset point (VOP) and vowel end point (VEP) are the instants of starting and ending of a vowel, respectively. VOPs and VEPs are equally important for accurate detection of vowels and development of different speech based applications. In a single algorithm, simultaneously detecting VOPs and VEPs is very challenging. In this paper, an efficient approach is proposed for robustly extracting the magnitude dynamics at each time instant of the speech signal. The mean and variance of the magnitude dynamics over an analysis frame happen to be significantly higher for the vowels when compared to other nonvowel, silence and noise regions. In this study, the average magnitude dynamics (AMD) over an analysis frame is used as the front-end feature. The AMD values at each time instant are then nonlinearly mapped (NL-AMD) by using sigmoidal function to sharpen the transitions at the VEPs and suppress the variations in the higher magnitude regions. The NL-AMD is equally discriminative at the VOPs and the VEPs. Consequently, most of the VOPs and the VEPs are detected within a smaller deviation. The experimental evaluations presented in this study show that, for the clean as well as noisy test conditions, the proposed feature outperforms the earlier reported front-end features for the task of detecting the VOPs and the VEPs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaadeed, N., Aggoun, A., & Amira, A. (2015). Text-independent speaker identification using vowel formants. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 82(3), 345–356.
Daqrouq, K., & Tutunji, T. A. (2015). Speaker identification using vowels features through a combined method of formants, wavelets, and neural network classifiers. Applied Soft Computing, 27, 231–239.
Deb, S., & Dandapat, S. (2017). Emotion classification using segmentation of vowel-like and non-vowel-like regions. The IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 99, 1–15.
Fakotakis, N., Tsopanoglou, A., & Kokkinakis, G. (1993). A text-independent speaker recognition system based on vowel spotting. Speech Communication, 12(1), 57–68.
Garofolo, J., Lamel, L., Fisher, W., Fiscus, J., Pallett, D., Dahlgren, N., et al. (1993). TIMIT acoustic-phonetic pontinuous ppeech porpus LDC93S1 (Vol. 33). Philadelphia: Linguistic Data Consortium.
Hermes, D. J. (1990). Vowel onset detection. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 87(2), 866–873.
Krishna, V. H., Reddy, K. S., & Kumar, V. A. (2016). Vowel-based non-uniform prosody modification for emotion conversion. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 35(5), 1643–1663.
Kumar, A., Shahnawazuddin, S., & Pradhan, G. (2016). Exploring different acoustic modeling techniques for the detection of vowels in speech signal. In: Proceedings of National Conference on Communication (NCC), pp. 1–5.
Kumar, A., Shahnawazuddin, S., & Pradhan, G. (2016). Improvements in the detection of vowel onset and offset points in a speech sequence. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 36, 1–26.
Kumar, A., Shahnawazuddin, S., & Pradhan, G. (2017). Non-local estimation of speech signal for vowel onset point detection in varied environments. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, pp. 429–433.
Panda, S. P., & Nayak, A. K. (2016). Automatic speech segmentation in syllable centric speech recognition system. International Journal of Speech Technology, 19(1), 9–18.
Pradhan, G., & Prasanna, S. M. (2013). Speaker verification by vowel and nonvowel like segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 21(4), 854–867.
Prasanna, S. M., & Pradhan, G. (2011). Significance of vowel-like regions for speaker verification under degraded conditions. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19(8), 2552–2565.
Prasanna, S. R. M., Reddy, B. V. S., & Krishnamoorthy, P. (2009). Vowel onset point detection using source, spectral peaks, and modulation spectrum energies. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 17(4), 556–565.
Prasanna, S.R.M., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2005). Detection of vowel onset point events using excitation source information. In: Proceedings of Interspeech, pp. 1133–1136.
Rao, J., Sekhar, C.C., & Yegnanarayana, B. (1999). Neural network based approach for detection of vowel onset points. In: Proceedings of International Conference Advanced Pattern Recognition Digital Technology, vol. 1, pp. 316–320.
Rao, K. S., & Vuppala, A. K. (2013). Non-uniform time scale modification using instants of significant excitation and vowel onset points. Speech Communication, 55(6), 745–756.
Rao, K. S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2009). Duration modification using glottal closure instants and vowel onset points. Speech Communication, 51(12), 1263–1269.
Reddy, B.S., Rao, K.V., & Prasanna, S.M. (2008). Keyword spotting using vowel onset point, vector quantization and hidden Markov modeling based techniques. In: Proceedings of TENCON, pp. 1–4.
Sabine, S., Wenke, V., & Uwe, S. (2011). Vowel articulation in parkinson’s disease. Journal of Voice, 25(4), 467–472.
Stefan, S., Lucas, G. M., Gratch, J., Rizzo, A. S., & Louis-Philippe, M. (2016). Self-reported symptoms of depression and ptsd are associated with reduced vowel space in screening interviews. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 7(1), 59–73.
Stevens, K. N. (2000). Acoustic Phonetics. London: The MIT Press Cambridge.
Themistocleous, C. (2017). Dialect classification using vowel acoustic parameters. Speech Communication, 92, 13–22.
Varga, A., & Steeneken, H. J. M. (1993). Assessment for automatic speech recognition: II. NOISEX-92: A database and an experiment to study the effect of additive noise on speech recognition systems. Speech Communication, 12(3), 247–251.
Vuppala, A., Yadav, J., Chakrabarti, S., & Rao, K. S. (2012). Vowel onset point detection for low bit rate coded speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 20(6), 1894–1903.
Vuppala, A. K., Rao, K. S., & Chakrabarti, S. (2011). Improved consonant-vowel recognition for low bit-rate coded speech. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 26(4), 333–349.
Vuppala, A. K., Rao, K. S., & Chakrabarti, S. (2012). Improved vowel onset point detection using epoch intervals. AEU—International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 66(8), 697–700.
Vuppala, A. K., Rao, K. S., & Chakrabarti, S. (2012). Spotting and recognition of consonant-vowel units from continuous speech using accurate detection of vowel onset points. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 31(4), 1459–1474.
Väyrynen, E., Toivanen, J., & Seppänen, T. (2011). Classification of emotion in spoken finnish using vowel-length segments: Increasing reliability with a fusion technique. Speech Communication, 53(3), 269–282.
Wang, J., Hu, C., Hung, S., & Lee, J. (1991). A hierarchical neural network based C/V segmentation algorithm for Mandarin speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 39(9), 2141–2146.
Wang, J.H., & Chen, S.H. (1999). A C/V segmentation algorithm for Mandarin speech using wavelet transforms. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, vol. 1, pp. 417–420.
Wolfe, V., Cornell, R., & Fitch, J. (1995). Sentence/vowel correlation in the evaluation of dysphonia. Journal of Voice, 9(3), 297–303.
Yadav, J., & Rao, K. S. (2013). Detection of vowel offset point from speech signal. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 20(4), 299–302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garnaik, S., Kumar, A., Pradhan, G. et al. An efficient approach for detecting vowel onset and offset points in speech signal. Int J Speech Technol 23, 643–651 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-020-09714-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-020-09714-x