Abstract
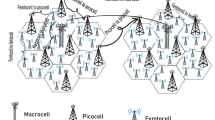
In this paper, we present an efficient data channel assignment (DCA) scheme for a mixed cell (i.e., a 3G cell with embedded WLANs). Our effort is essential to increase the data request (i.e., a call) handling capacity in 3G systems, with a ‘low request dropping probability’. In UMTS-first DCA scheme prefers 3G channel in dual coverage and reduces vertical handoffs from 3G to WLAN. But it deprives some users of high speed service of WLAN even when WLAN facility is available. On the contrary, a WLAN-first DCA scheme overcomes this problem by preferring WLAN system. But the overall call request dropping probability increases with increasing WLAN traffic and at some point, the benefit of WLAN cannot be achieved in a mixed cell. Further, most of the existing models do not consider the reality of non-identical WLAN-hotspots and bidirectional vertical handoffs, restricting the free mobility of the users across 3G and WLAN systems. We propose an improved DCA scheme based on WLAN-first access technique to maximize the usage of WLAN. The proposed model considers the reality of non-identical WLAN-hotspots and allows free mobility between 3G and WLAN. A proposed DCA scheme improves the dropping probability as blocked call request of WLAN are transferred to 3G. Our DCA scheme drops a request only when all the channels of both 3G and WLAN systems are busy. We derive an analytical model for proposed scheme and validate the same with a set of simulation results. We provide an extensive number of numerical results to show that our scheme performs far better than the existing models. The DCA modeling approach can be quite conveniently used for better planning of WLAN hotspots in the mixed cell.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
GPP TS 23.101, “General UMTS Architecture,” Release 7, Jun 2007.
IEEE 802.11, “Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications,” http//standard.ieee.org/getieee802/download/802.11-1999.pdf.
GPP TR 22.934, “Feasibility Study on 3GPP System to Wireles Local Area Network (WLAN) Interworking,” Release. 7, June 2007.
J. Ala-Laurila, J. Mikkonen, and J. Rinnemaa, “Wireless LAN Access Network Architecture for Mobile Operators”, IEEE Communications Magazine, November 2001, pp. 82–89.
I. F. Akyildiz, J. Xie and S. Mohanty “A Survey of Mobility Management in Next-Generation All-IP-Based Wireless Systems”, IEEE Wireless Communications, Aug 2004, pp. 16–28.
A. H. Zahran, B. Liang and A. Faleh, “Modeling and Performance Analysis of 3G integrated Wireless networks,” IEEE International Conrefence on Communications (ICC’06), June 2006, Volume: 4, pp. 1819–1824.
S. Tang and W. Li “Performance Analysis of the 3G Network with Complementary WLANs” Proceeding of IEEE Globecom 2005, pp. 2637–2641.
S. Khara, I. S. Misra and D. Saha, “Performance Analysis of a UMTS Cell with Underlying Tunnel-WLANs,” Proc. of ICDCN 2009, Springer-Verlag, Vol. LNCS 5408, pp. 389–394, 2009.
T. Bejoui and L. Mokdad, “Adaptive Hybrid Call Admission Control Policy for UMTS with Under Lying Tunnel-WLANs Heterogeneous Networks,” Proc. of IEEE ICC 2009, Dresden, 14–18 June 2009.
K. Salkintzis, C. Fors and R. Pazhyannur, “WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks”, IEEE Wireless Commun, Oct 2002, pp. 112–124.
E. Garcia-Palacios, M. Abdelghani, A. Hussian and S.Walsh, “Assessing Capacity in WLAN-UMTS Integrated Networks”, Procededing of AICT/SAPIR/ELETE, 2005, July, pp. 189–194.
E. Steven-Navarro and V. W..S. Wong, “Resource Sharing in an Integrated Wireless Cellular/WLAN System,” Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2007 (CCECE 2007), Vancouver, Canada, April 2007, pp. 631–634.
A. H. Zahran, B. Liang and A. Faleh, “Modeling and Performance Analysis of Behond 3G integrated Wireless networks” in the proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Istanbul, Turkey, June 2006.
S. Song, Y. Cheng, and W. Zhuang, “Improving Voice and Data Services in Cellular/WLAN Integrated Network s by Admission Control”IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 6, no. 11, November 2007, pp. 4025–4036.
G. Lamproppoulos, N. Passas and L. Merakos, “Handover Management Architecture in Integrated WLAN/Cellular networks,” IEEE Commun. Surveys, 4th Quarter 2005, Vol 7, no 4, pp. 30–44.
S. Khara, I. S. Misra and D. Saha, “A One-pass Method of MIP Registration through GPRS Networks”, Proceeding of ICDCN 2006, LNCS 4308, pp. 570–581.
Y. Fang; I. Chlamtac, “A New Mobility Model and its Application in the Channel Holding Time Characterization in PCS Networks,” Proc. INFOCOM’99, Volume 1, Mar 1999, pp. 20–27.
Y. Fang, “Hyper-Erlang Distribution Model and its Application in Wireless Mobile Networks,” Intl. Journal of Wireless Networks: Special issue: Design and Modeling in Mobile and Wireless Systsems, Vol 7, Issue 3, 2001, pp. 211–219.
A. H. Zahran, B. Liang, “Mobility Modeling for Two-Tier Integrated Wireless Multimedia Networks,” 7th IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM’05), 2005, pp. 643–648.
D. Chen, X. Wang and A. K. Elhakeem, “Performance Analysis of UMTS Handover with the Help of WLAN”, Proceeding of Qshine’05, IEEE 2005, Volume, Issue, Aug. 2005.
H. Liu, H. Bhaskaran, D. Raychaudhuri and S Verma, “Capacity Analysis of a Cellular Data System with UMTS/WLAN Interworking” Proceeding of IEEE VTC 2003, vol 3, pp. 1817–1821.
W. Song and W. Zhuang, Multi-Service Load Sharing for Resource Management in the Cellular/WLAN Integrated network, IEEE Transcation on Wireless Communication, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 725–735, 2009.
Lusheng Wang and Geng-Sheng (G.S.) Kuo,“Mathematical Modeling for Network Selection in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks – A Tutorial”, IEEE COMMUNICATIONS SURVEYS & TUTORIALS, VOL. 15, NO. 1, FIRST QUARTER PP 271–292, 2013.
Lim, H.T., Y. Kim, S. Pack and C.H. Kang, “Call admission control with heterogeneous mobile stations in cellular/WLAN interworking systems”. OPEN access EURASIP J. Wireless Commun. Network, 2011.
S. Saha, S. Khara, A. K. Mukhopadhyay and C. K. Ghosh, Call dropping analysis in a UMTS/WLAN Integrated cell, Int. J. Inform. Technol. Knowl. Management., Vol. 2, pp. 411–415, 2010.
Nandakumar, S., Khara, S. “A linear model of call intercepting probability of integrated WLANs in a 3G cell”SPRINGER Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 7135 LNCS 2012, pp. 348–356.
Nanda Kumar, S., Khara, S., Velmurugan, T. “An efficient take-back call admission control scheme for 3G/WLAN integrated cells” SPRINGER, OBCOMM Communications in Computer and Information Science 269 CCIS (PART I) 2012, pp. 342–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
Proof
Say, there are \(H\) hotspots and \(W\) WLAN-hotspots in a mixed cell. The area of any \(ith\) hotspot is \(A_{i}^{H}\) and \(wth\) WLAN-hotspot is \(A^{w}\). Coverage area of a UMTS cell is \({\text{A}}^{\text{u}}\). According to the definition of density ratio we write,
Or,
where \({\text{d}}^{{{\text{w}} - {\text{h}}}}\) is number of users per unit area in hotspots (WLAN or WLAN-less) \({\text{d}}^{{{\text{non}} - {\text{h}}}}\) is number of users per unit area of non-hotspot regions.
From the definition of \({\mathbf{P}}_{\text{c}}\) we write,
Applying Eqs. (41) and (42) in Eq. (43), we get,
where \(A_{total}^{H} = \sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{H} {A_{i}^{H} }\) i.e., total area of all hotspots.
If all hotspots are identical then from Eq. (44) we easily prove that,
where \(A = A^{w} /A^{u} .\)
Appendix 2
Using Eq. (14a) for \(\lambda_{vr}^{w}\)
where \(b = (1/p)\sum\nolimits_{w = 1}^{W} {b^{w} g^{w} }\)
Handoff probability from WLAN to UMTS is assumed to be the same for all WLAN-hotspot and is equal to \(P_{n}^{w}\) and \(P_{vr}^{w}\)
Appendix 3
Proof
We consider the Eqs. (17), (15) and derive the following,
Since \(b = (1/p)\sum\nolimits_{W = 1}^{W} {(g^{w} b^{w} )}\) or \(bp = \sum\nolimits_{W = 1}^{W} {(g^{w} b^{w} )}\), From (10), we have,
where \(q = \frac{1}{bp}\sum\nolimits_{w = 1}^{W} {q^{w} b^{w} p^{w} }\)
Applying Eq. (46) in Eq. (48), we have,
Apply Eq. (47) and \(\lambda_{n}^{W - t} = p\lambda_{n}^{m}\) in Eq. (51)
where \(K_{3} = \frac{{b^{'} p\left[ {P_{n}^{w}\,+\,P_{vr}^{w} \left\{ {b_{1}^{'}\,+\,b_{2}^{'} K_{1} } \right\}\left( {1 - (1 - qb)p} \right)} \right]}}{{1 - b^{'} P_{vr}^{w} b_{2}^{'} p(1 + K_{2} )}}\)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandakumar, S., Khara, S. Modeling and Performance Analysis of an Improved Data Channel Assignment (DCA) Scheme for 3G/WLAN Mixed Cells. Int J Wireless Inf Networks 22, 10–28 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-015-0261-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-015-0261-4