Abstract
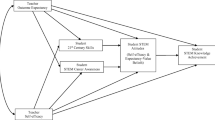
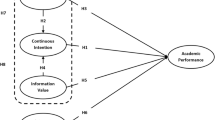
The purpose of this paper is to analyze e-learning system quality through the analysis of student satisfaction and the usage of learning materials. This analysis takes into consideration both online and traditional students who are using the same e-learning system. The goal of the analysis is to identify factors which influence student satisfaction and to address heterogeneous styles and needs of both groups of students, so that future pedagogical and motivational methods in teaching and learning can be appropriately selected, developed and implemented. It was of particular interest to explore student satisfaction with quality of an e-learning system and online study approach. Reasons that may influence opinions of online and traditional students are examined and presented. The results are used to give recommendations for e-learning improvements and to propose the model with 4 groups of dimensions for performance measurement each of which best represents satisfaction of both groups of students.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LMS:
-
Learning Management System
- PMS:
-
Performance Management System
- TQM:
-
Total Quality Management
- JSP:
-
JavaServer Pages
References
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215.
Barolli, L., Koyama, A., Durresi, A., & Marco, G. (2006). A web-based e-learning system for increasing study efficiency by stimulating learner’s motivation. Information Systems Frontiers, 8(4), 297–306.
Beer, M., Slack, F., & Armitt, G. (2005). Collaboration and teamwork: Immersion and presence in an online learning environment. Information Systems Frontiers, 7(1), 27–37.
Bhuasiri, W., Haymoungkhoun, O., Zo, H., & Rho, J. J. (2012). Critical success factors for e-learning in developing countries: A comparative analysis between ICT experts and faculty. Computers & Education, 58, 843–855.
Carchiolo, V., Longheu, A., Malgeri, M., & Mangioni, G. (2007). A model for a web-based learning system. Information Systems Frontiers, 9(2–3), 267–282.
Cook-Sather, A. (2002). Authorizing students’ perspectives: Toward trust, dialogue, and change in education. Educational Researcher, 31(4), 3–14.
Costa, G. J. M. & Silva, N. S. A. (2010). Knowledge versus content in e-learning: A philosophical discussion. Information Systems Frontiers, 12(4), 399–413.
Davis Jr, F. (1986). A technology acceptance model for empirically testing new end-user information systems: Theory and results. Dissertation. Massachusetts Institute of Technology
DeLone, W. H. & McLean, E. R. (1992). Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Information Systems Research, 3(1), 60–95.
DeLone, W. H. & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: a ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9–30.
Gibson, A. (2010). Measuring business student satisfaction: A review and summary of the major predictors. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 32(3), 251–259.
Higher education statistics agency, UK, https://www.hesa.ac.uk/
Holsapple, C. & Lee-Post, A. (2006). Defining, Assessing, and Promoting E-Learning Success: An Information Systems Perspective. Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative Education, 4(1), 67–85.
IEEE Learning Technology Standards Committee. (2001). IEEE Computer Society, Draft standard for learning technology – learning technology systems architecture (LTSA). IEEE P1484.1/D9, 2001-11–30.
Jankulovic, A., & Raspopovic, M. (2013). Performance measures analysis for online and traditional studies. 7th International Quality Conference, Kragujevac, Serbia, 423–428.
Jung, I. (2012). Asian learners’ perception of quality in distance education and gender differences. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 13(2), 1–25.
Kaplan, R., & Norton D. (1996). The balanced scorecard: translating strategy into action. Harvard Business Press.
Kim, S. W. & Lee, M. G. (2008). Validation of an evaluation model for learning management systems. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 24(4), 284–294.
Kim, Y., Song, S., Sambamurthy, V., & Lee, Y. (2012). Entrepreneurship, knowledge integration capability, and firm performance: An empirical study. Information Systems Frontiers, 14(5), 1047–1060.
Levy, Y. (2008). An empirical development of critical value factors (CVF) of online learning activities: An application of activity theory and cognitive value theory. Computers & Education, 51(4), 1664–1675.
Mai, L. (2005). A comparative study between UK and US: The student satisfaction in higher education and its influential factors. Journal of Marketing Management, 21(7–8), 859–878.
Marsh, H. W., & Cheng, J. (2008). National student survey of teaching in UK universities: Dimensionality, multilevel structure, and differentiation at the level of university and discipline: Preliminary results. Retrieved June, 23(2010), 603–641.
Mun, Y. Y. & Hwang, Y. (2003). Predicting the use of web-based information systems: self-efficacy, enjoyment, learning goal orientation, and the technology acceptance model. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 59(4), 431–449.
Neely, A., Gregory, M., & Platts, M. (1995). Performance measurement system design: a literature review and research agenda. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 15(4), 80–116.
Neely, A., Filippini, R., Forza, C., Vinelli, A., & Hii, J. (2001). A framework for analysing business performance, firm innovation and related contextual factors: perceptions of managers and policy makers in two European regions. Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 12(2), 114–124.
Ozkan, S. & Koseler, R. (2009). Multi-dimensional students’ evaluation of e-learning systems in the higher education context: An empirical investigation. Computers & Education, 53(4), 1285–1296.
Peinl, R. & Maier, R. (2011). SimKnowledge—Analyzing impact of knowledge management measures on team organizations with multi agent-based simulation. Information Systems Frontiers, 13(5), 621–636.
Pituch, K. A. & Lee, Y. K. (2006). The influence of system characteristics on e-learning use. Computers & Education, 47(2), 222–244.
Ramayah, T. & Chow Lee, J. W. (2012). System Characteristics, Satisfaction and E-Learning Usage: A Structural Equation Model (SEM). Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 11(2), 196–206.
Raspopovic, M., Jankulovic, A., Runic, J., & Lucic, V. (2014). Success factors for e-learning in a developing country: A case study of Serbia. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 15(3), 1–23.
Selim, H. M. (2003). An empirical investigation of student acceptance of course websites. Computers & Education, 40(4), 343–360.
Selim, H. M. (2007). Critical success factors for e-learning acceptance: Confirmatory factor models. Computers & Education, 49(2), 396–413.
Shee, D. Y. & Wang, Y.-S. (2008). Multi-criteria evaluation of the web-based e-learning system: A methodology based on learner satisfaction and its applications. Computers & Education, 50(3), 894–905.
van Dinther, M., Dochy, F., & Segers, M. (2011). Factors affecting students’ self-efficacy in higher education. Educational Research Review, 6(2), 95–108.
Wu, H.-Y. & Lin, H.-Y. (2012). A hybrid approach to develop an analytical model for enhancing the service quality of e-learning. Computers & Education, 58(4), 1318–1338.
Acknowledgments
The work presented here was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (project III44006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raspopovic, M., Jankulovic, A. Performance measurement of e-learning using student satisfaction analysis. Inf Syst Front 19, 869–880 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9636-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9636-z